Ägypten |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Ägypten |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
National-,
Staats- und Handelsflagge |
 |
Kriegsflagge und Flagge des Heeres
|
 |
Marineflagge
– naval flag, |
 |
Flagge der Luftwaffe
– flag of the air force, |
 |
Flagge des Präsidenten
– flag of the president, |
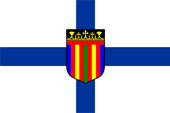 |
Flagge
der Koptischen Christen |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
ca. 1793–1844, Flagge des Osmanischen Reiches – flag of the Ottoman Empire, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1844–1914, Flagge des Osmanischen Reiches – flag of the Ottoman Empire, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1914–1922, Flagge des Sultanats Ägypten – flag of the Sultanate of Egypt, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1922–1958, Flagge des Königreichs Ägypten – flag of the kingdom of Egypt, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1922–1958, Marineflagge des Königreichs Ägypten – naval flag of the kingdom, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1922–1958, Flagge des ägyptischen Heeres – flag of the Egypt Army, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1922–1958, Flagge der ägyptischen Luftwaffe – flag of the Egypt Air Force, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1922–1952, Standarte des Königs von Ägypten zur See – standard of the King of Egypt at sea, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1922–1952, Standarte des Königs von Ägypten an Land – standard of the King of Egypt ashore, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
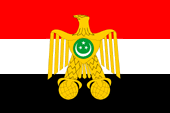 |
1952–1958, Arabische Befreiungsflagge – Arab freedom flag, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1958–1972, Flagge Ägyptens als Teil der Vereinigten Arabische Republik* – Egypt as a part of the United Arab Republic, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World * Vereinigte Arabische Republik – Abkürzung VAR (UAR), der politische Zusammenschluss Ägyptens und Syriens 1958–1961 |
 |
1958–1972, Präsidentenflagge zur See – Flag of the President at sea, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:7, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1972–1984, National- und Handelsflagge – national and merchant flag, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen |
 |
1972–1984, Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die heutige Flagge Ägyptens zeigt drei waagerechte, gleichbreite Streifen in Rot, Weiß und Schwarz mit dem goldenen (gelben) Adler Saladins, und wurde in ihrer heutigen Form am 04.10.1984 gehisst. In ihrer Gestaltung geht sie auf die nach Abschaffung der Monarchie im Jahre 1952 eingeführte Arabische Befreiungsflagge zurück. Der Adler in der heutigen Flagge ist, wie auch in der Arabischen Befreiungsflagge, das Symbol des Sultans Saladin und seiner Nachfahren, der Aijubiden-Kalifen, und eine Idolfigur der Arabischen Einheit. Er trägt heute ein Brustschild, welches in den Farben der Flagge gehalten ist, und hält in den Fängen ein Schriftband mit dem Namen des Staates. Speziell für Ägypten haben die Farben folgende Bedeutung: Rot erinnert an die Kämpfe der Revolution und das dabei vergossene Blut, Weiß steht für eine strahlende Zukunft und Schwarz für die dunkle Vergangenheit. | The today's flag of
Egypt shows three horizontal, same wide stripes in red, white and black with the golden
(yellow) Eagle of Saladin, and was hoisted up in her today's form on 4th of October in
1984. The styling of the flag goes back to the after the abolition of the monarchy in the
year 1952 introduced Arabic liberation flag. The eagle in the today's flag is, how in the Arabic liberation flag, too, the of the sultan Saladin and his descendants, the Aijubide-Kalifs, and is an idol-figure of the Arabian unity, too. He sustains today a breast shield, which is colored in the colors of the flag, and holds a font-ribbon with the name of the state in it's claws. Specially for Egypt the colors have the following meaning, too: red remembers the fights in the revolution abd the thereby given blood, white stands for a shining future and black for the dark past. |
| Der Farbendreiklang von Rot, Weiß und Schwarz wird manchmal als Panarabische Farben bezeichnet. Das ist so nicht ganz richtig. Die drei Farben gehen zurück auf Gamal Abd el-Nasser, ägyptischer Offizier, Politiker sowie späterer Staats- und Ministerpräsident (1918–1970), wichtigster Vertreter des arabischen Nationalismus und Panarabismus. Nach der nationalen Revolution des Jahre 1952 wurde in Ägypten die Arabische Befreiungsflagge eingeführt, welche eben diese Ideale repräsentierte. Sie wurde, zumindest in der Auswahl und Anordnung Vorbild für viele andere arabische Staaten und Staatenbündnisse. Die Farben stehen immer für die Revolution (Rot), die Zukunft (Weiß) und die Vergangenheit (Schwarz). Die Farben Rot, Weiß und Schwarz gehen auf die Flagge des Arabischen Aufstandes im Ersten Weltkrieg zurück. Zu den Farben des Arabischen Aufstandes (Arabische Bewegung) gehört allerdings noch Grün. | The colour triad of
red, white and black is referred as Panarabian colours. This is not entirely
correct. The three colours go back to the late Gamal Abd el-Nasser (1918–1970),
Egyptian military officer, politician as well as later the state's president and prime
minister, and most important representative of the Arabian nationalism and panarabism. After the national revolution of 1952 the Arabian Liberation Flag was introduced in Egypt, which represented those ideals. It was, at least in choice and arrangement a model for many other Arabian
states and state alliances. The colours stand always for the revolution (red), the future
(white) and the past (black). The colours have their roots in the flag of the Arabian
Revolt during the First World War. Yet the colours of the Arabian Revolt (Arabian
Movement) include even green. |
| Der Farbenvierklang von Grün, Weiß, Schwarz und Rot ist ein speziell arabisches Farbsymbol, die Panarabischen Farben. Die (pan)arabischen Farben wurden während des 1. Weltkriegs, bei der Loslösung des Königreichs Hedschas vom Osmanischen Reich, durch den Scherifen Hussein von Mekka – aus dem Geschlecht der Haschemiden – als Farben der Arabischen Bewegung offiziell eingeführt. Als Vorlage diente die Flagge des Hedschas. Die Farben haben folgende Bedeutung: Rot ist die Farbe von Omar, dem zweiten Kalifen; Weiß steht für die Omajiaden, eine Kalifendynastie, die auf den fünften Kalifen Moawija I. zurückgeht; Grün steht für die Fatimiden, eine ismailitisch-schiitische Kalifendynastie, die auf den vierten Kalifen Ali zurückgeht; und Schwarz steht für die Abbasiden, eine Kalifendynastie, die auf den Kalifen Abbas I. zurückgeht. Rot ist außerdem die Farbe der Haschemiden, eine arabische Herrscherdynastie, die wahrscheinlich auf Haschim ibn Abd al-Manaf, den Großvater Mohammeds, zurückgeht. Grün ist außerdem die Farbe des Islam im Allgemeinen, und bezieht sich somit nicht nur auf die arabischen Länder. | The colour quartet of
four, green, white, black and red is a special Arabian colours symbol, the Panarabian
colours. The (Pan)Arabian colours were officially introduced by the Sheriff Hussein of
Mekka – of the lineage of the Hashemides – as colours of the Arabian Movement
during the First World War at the secession of the Kingdom of Hedjas from the Ottoman
Empire. The flag of Hedjas served as pattern. The colours have the following meaning: Red is the colour of Omar, the
second calif; white stands for the Omajiades, a calif-dynasty, which goes back to
the fifth calif Moawija I.; green stands for the Fatimides, a ismailitic-shiit
calif-dynasty, which goes back to the fourth calif Ali; and black stands for the
Abbasides, a calif-dynasty, which goes back to the calif Abbas I. Red is also the colour
of the Hashemides, an Arabian sovereign-dynasty, which probably goes back to Hashim ibn
Abd al-Manaf, the grandfather of Mohammed. Green is in addition generally the colour of
Islam, and does not refer only to the Arabian countries. |
| Zur Flaggengeschichte Ägyptens: Die Flagge des türkischen Vizekönigreiches Ägypten (1867-1882) ist eindeutig türkischen Ursprungs, wie an der Farbgebung und an den Symbolen feststellbar ist. Die Flagge des Königreichs Ägypten geht auf das islamische Grün zurück, wobei die islamische Symbolik noch ein wenig an die türkische Zeit erinnert. Das Grün soll auch an das fruchtbare Nildelta erinnern. Diese Flagge wurde, auch nach dem Ende des Königreiches (1952), bis 1958 weiter benutzt. Die Flagge der VAR (1958-1961) zeigt drei Streifen in Rot, Weiß und Schwarz, die in Ägypten mit der Arabischen Befreiungsflagge bereits 1952 offiziell eingeführt worden waren, ergänzt um zwei Sterne, von denen der eine für Ägypten steht und der andere für Syrien. Auch nach dem Ende der VAR (1961) behielt Ägypten diese Flagge bis 1972 bei. Zum Zuge der Bildung der "Föderation Arabischer Republiken" zwischen Libyen, Ägypten und Syrien im Jahre 1972, wurde vereinbart, dass diese drei Staaten rot-schwarz-weiße Flaggen verwenden sollten, die in der Mitte einen goldenen Falken zeigen. Der einzige Unterschied sollte der Name des jeweiligen Landes in dem Schriftband sein, das des Falke in seinen Fängen hält. Ägypten führte eine solche Flagge 1972 ein, und behielt sie bis 1984 bei (Libyen bis 1977, Syrien bis 1980). | The flag history of
Egypt: The flag of the Turkish vice kingdom of Egypt (1867-1882) is clearly from Turkish
origin, how it is to see in the coloration and the symbols. The flag of the Kingdom of
Egypt goes back to the islamic green, but the islamic symbolism remembers even slightly
the Turkish times. The green should remind the fruitful Nile delta, too. This flag was in
use till 1958, so as well after the end of the kingdom (1952). The flag of the UAR
(1958-1961) shows three stripes in red, white and black, which were already officially
introduced in Egypt in 1952, with the introduction of the Arabic liberation flag,
completed by two stars, from them the one stands for Egypt and the other for Syria. Even
after the end of the UAR (1961) Egypt maintaines this flag till 1972. In context with the formation of the "Federation of Arabic republics" between Libya, Egypt and Syria in the year 1972, was arranged, that these three states have to use red-black-white flags, which show in the center a golden hawk. The only difference should be the name of the respective state in the font ribbon, which holds the hawk in his claws. Egypt introduced such a flag in 1972, and maintained her until 1984 (Libya until 1977, Syria until 1980). |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (D), Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
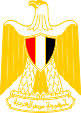 |
Wappen von Ägypten – coat of arms of Egypt, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D), Corel Draw 4 |
 |
Wappen von Ägypten auf der Flagge – coat of arms of Egypt on the flag, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D), Corel Draw 4 |
historische Wappen – historical coats of Arms: |
|
 |
1922–1958, Wappen Königreich Ägypten – coat of arms of the Kingdom Egypt, Quelle/Source nach/by: Der neue Brockhaus |
 |
1958–1972, Wappen von Ägypten – coat of arms of Egypt, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D), Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1972–1984, Wappen von Ägypten – coat of arms of Egypt, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (D), Corel Draw 4 |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das heutige Wappen Ägyptens ist das Symbol des Sultans Saladin und seiner Nachfahren, der Aijubiden-Kalifen, und eine Idolfigur der Arabischen Einheit. Er trägt heute ein Brustschild, welches in den Farben der Flagge gehalten ist, und hält in den Fängen ein Schriftband mit dem Namen des Staates. | The today's coat of arms of egypt is the symbol of the sultan Saladin and his descendants, the Aijubide's Kalifs, and is an idol-figure of the Arabian unity, too. He sustains today a breast shield, which is colored in the colors of the flag, and holds a font-ribbon with the name of the state in it's claws. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
1945–1958, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1958–1972, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
seit/since 1972, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Die
Lage Ägyptens – position of Egypt: |
Ägypten – Egypt: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 3000 bis 800
v.Chr. · antikes Ägypten 525 v.Chr. · persische Eroberung 332 v.Chr. · griechische Eroberung 30 v.Chr. · römische Eroberung 640 · arabische Eroberung 1517 · türkische Eroberung 1805 · türkisches Vizekönigreich 1882 · britische Eroberung 1914 · Ende des Vizekönigreichs 1922 · Unabhängigkeit als Königreich 1952 · Ende der Monarchie |
History: |
| 3000 to 800
B.C. · ancient Egypt 525 B.C. · Persian conquest 332 B.C. · Greek conquest 30 B.C. · Roman conquest 640 · Arabic conquest 1517 · Turkish conquest 1805 · Turkish vice kingdom 1882 · British conquest 1914 · end of the vice kingdom 1922 · independence as kingdom 1952 · end of monarchy |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), World Statesmen |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Ägypten" ist vom antiken Zweitnamen der Stadt Memphis angeleitet. Dieser war "Hutkaptah", "Heiligtum des Gottes Ptah". Manchmal wird auch das griechische Wort "aigyptos", "dunkel" bemüht, dessen Übereinstimmung ist jedoch Zufall. Die alten Ägypter nannten ihr Land "Kemet", "Das schwarze Land". Die heutigen, arabischstämmigen Ägypter nennen es "Misr". |
The name "Egypt" comes
from the ancient second name of the city of Memphis. This was
"Hutkaptah","Shrine of the god Ptah". Sometimes is also the Greek word
"aigyptos", "dark" tryed to be compliant, but it is a coincidence. The
ancient Egyptians called their land "Kemet," "The Black Land". The today's
Arab-Egyptians call it "Misr". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |