mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Belarus
- presidial republic
- own name: Respublika Belarus
- other name: Byelorussia (to translate as "White Russia")
- former name: White Ruthenia
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Regional Flag
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)



Flag of the border patrol,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




Flag of the president,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)





1917–1919,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




1919,
Flag of the Socialist Soviet Republic of Belaus,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1920–1927,
Flag of the Socialist Soviet Republic of Belaus,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1927–1937,
Flag of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1937–1951,
Flag of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1951–1991,
Flag of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1991–1995,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




1991–1995,
National flag - unofficial variant with coat of arms




1995–2012,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)







Flag of the muslim Tatars in Belarus,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




The white-red-white flag appeared immediately after the abdication of the Russian Tsar in 1917 and has its roots in the heraldic figure of the White Knight of Lithuania (Pahonia). According to another theory, the colours represent the name of the country, White = "Bela", Red = "Rus". From the word "Rus" is derived the name of "Russia" because it refers to the reddish-blond hair of the Normans, the forefathers of the Russian state.
After a successful communist coup d’etat in 1919 a single coloured red flag with the golden initials "SSRB" in the upper canton was introduced, to which, perhaps in 1937, were added a golden hammer and sickle. On the 25th of December 1951 a new flag was introduced. It showed two stripes of red and green in the ratio 2:1, and at the leech on a red vertical bar a folk art ornament and in the upper canton of the red stripe star, hammer and sickle. Red stands for communism, green for the forests and agriculture. The red and white ornament symbolizes the history of the country. On the 19th of September 1991 it was decided in the Supreme Soviet of the Independent Republic of White Russia, to reintroduce the civil state symbols of the years 1917 until 1919.
After A. G. Lukaschenko had become president in 1994, he, as a part of his pro-soviet policies, forced the reintroduction of the old symbols. This way a referendum about the state symbols was initiated by veterans organizations, of course under the leadership of President Lukaschenko, on the 14th of May in 1995. Ahead of this, however, a few changes were recommended. The hammer, the sickle and the star were removed, and the ornament appeared in red on white. The new pro-communist flag was officially introduced on the 7th of June 1995, with a few minor changes at a later date (a vertical white stripe). This referendum also decided over the new old coat of arms of the state. It was officially introduced on the 7th of June 1995. The colors of the national flag are regulated in the "Order STB 911-2008 National flag of the Republic of Belarus". They are indicated as follows: Red = Pantone 186, Green = Pantone 356. On 20th of February in 2012 some small changes for the flag were adopted. The narrow red stripes on the left and right of the folk art ornament became removed, it reaches now directly to the edge, and the width of the ornament is set to one-ninth of the width of the flag.
Source: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Flags of the World,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Wappen, Wikipedia (EN)


1917–1919, 1991–1995,
Coat of arms of Belarus,
Source: Wikipedia (D)

1981–1991,
Coat of arms of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic,
Source: Jam123, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

1995–2020,
Coat of arms of Belarus,
Source: Wikipedia (D)

seit/since 2020,
Coat of arms of Belarus,
Source: Wikipedia (D)

The new pro-communist emblem was, as the flag, officially introduced on 7th of June in 1995 through a referendum. It is similar to the arms of the Soviet Republic. This shows, instead of hammer and sickle, a green outline of the map of the Belorussian Republic (White Russia) in golden sunbeams above the globe. Above the map is situated a red five-pointed star. The whole coat of arms is surrounded by a wreath of golden ears, with inwoven clover blossoms from the right and inwoven flax blossoms from the left. The ears are enveloped by a green-red ribbon instead of a red one, which carries the golden inscription "Respublika Belarus" in the lower part. In the year 2020 the coat of arms was changed a little: the contour of the map was changed from green to gold and the red star was enlarged a little bit.
The civil coat of arms of White Russia is named "Pahonia", and is the national emblem of Belarus and the historical coat of arms of many cities in Belarus. It originated in ancient Navahradak (Novgorodok), the first capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. "Pahonia" means "Pursuit" and symbolizes the pursuit of an enemy in defense of the homeland. It was the coat of arms of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, of which Belarus was an integral part for over five centuries. In 1918 the Belarussian Democratic Republic adopted it as its coat of arms and so did the parliament of the independent Republic of Belarus in 1991.
Source:
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Wikipedia (D),
Volker Preuss


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
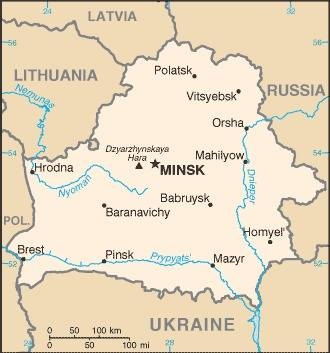
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 80.152 square miles
Inhabitants: 9.504.700 (2017), thereof 84% White Russians (Belorussians), 8% Russians, 3% Poles, 2% Ukrainians, and even 3.500 Germans
Religions: 48% Russian Orthodox, 7% Catholics, 41% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 118 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Mensk (Minsk), 2.020.600 inh. (2020)
official Languages: Belorussian, Russian
Currency: 1 Belarusian Ruble (Br, BYN) = 100 Copecks
Time Zone: GMT + 3 h
Source: Wikipedia (D)

882–1240 · to the Kiev Rus
1240 · Mongolian conquest
1322 · to Lithuania
1569 · to Poland
1654 · ceding of territories to Russia
1772–1795 · step by step annexation by Russia
1917 · German occupation
25th of March in 1918 · proclamation of the White Russian Republic
1919 · communist coup d’etat, establishment of a Soviet Republic
1919 · occupation by Poland
1920 · conquest by the USSR
1921 · ceding of territories to Poland
1922 · joining to the Soviet Union (USSR)
1941–1944 · German occupation
1945 · annexation of Polish territories
August 1991 · independence
1994 · onset of soviet restoration
Source: Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (D)

The name "White Russia" is a literal translation of the word "Belarus", the Belarusian proper name of the country. The origin lies in the past of the Slavs, or even of the Mongols, and means the traditional designation of the compass with colours. Slavic: North = White, East = Red, Black = South, West = Blue; Mongolian: North = Black, East = Blue, Red = South, West = White. The old Latin name of Russia is Ruthenia, the Ruthenians were the common ancestors of the Ukrainians, Russians and Belarusians. Ruthenia was from the 13th to the 15th century occupied or dependent by the Mongols – the period in which emerged the nation of the Belarussians – and it is not possible to determine whether he meant with "white" now the north or the west. "Belarus" means in this way "Northern Russia" or "Western Russia". A similar name, which is no longer in use today, is "Red Russia", the eastern Galicia of the later period, the region around Lviv (Lwow, Lemberg) in today's Ukraine. Red Russia is placed in the east of the former Kievan Rus, an indication that with Red is meant East here.
The name "Russia" has its roots in the medieval name of the Russian states – the "Rus". About the meaning of the word "Rus" are known two theories: 1st) "Rus" goes back to the teutonic word for "red" and refers to the strawberry blond hair of the Normans – the ancestors of the Russian state. 2nd) "Rus" goes back to the teutonic word for "oarsmen, the Finnen nennen die Schweden bis heute "Ruotsi". Sometimes is used this very poetic but improbable derivation of the origin of the name: The color white in the country's name comes from the many birch forests of the country, which characterize – with their white trunks – the appearance of the country.
Today there are attempts to implant a difference between White Russia as Belarus and Russia itself by use of politically controlled language acrobatics, because spelling with just an "s" would not allow identification with Russia. But, all Ruthenian countries have their roots in a single state, the Kievan Rus, also in ethnically common ancestors, the Ruthenians. It doesn't matter whether these countries are called Russia, Ukraine or Belarus today. It is clearly a matter of so-called "framing", which politically agitates and manipulates by use of special logical-sounding formulations. Strangely enough, this political language regulation – with the reference to the Rus with an "s" – shows the commonality of the Ruthenian states.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Volker Preuss


![]()
















































