mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Possession of the United Kingdom
- Chagos Archipelago
- usual abbreviations: BIOT, B.I.O.T.
• Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History

since 1990,
National flag,
ratio – ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D),
Flags of all Nations






to 1990,
Flag of the United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen





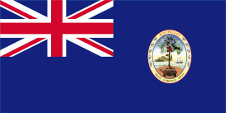
1965–1976,
The territory belongs to the Seychelles,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: World Statesmen




The Union Jack points to the connexion to Great Britain. Remarkable is that the British Indian Ocean Territory (B.I.O.T.) uses a flag which is not following the British ensign system, because the base consists of white and blue wave lines, symbolizing the Indian Ocean. In the flying end of the flag is the badge. It shows a palm tree, an indication of the vegetation, and an image of the British crown. It stands for the islands, especially the island of Diego Garcia, which is the only inhabited. The flag and badge were introduced in 1990.
Source: Flaggen Enzyklopädie

Source:
CIA World Factbook
Map of the Country:
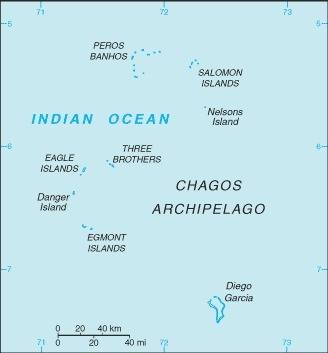
Source:
CIA World Factbook

Area: 24 square miles
Inhabitants: ca. 3.500 (military only)
Density of Population: 144 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Diego Garcia
official Language: English
Currency: 1 Pound Sterling (£) = 100 Pence, 1 US-Dollar ($) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: MEZ + 6 h
Source: Wikipedia (EN)

1814 · United Kingdomtook possession
1965 · separation from Mauritius, affiliation with the Seychelles
1966 · Anglo-US-American treaty of usage
1969–1971 · evacuation of the population
1976 · ceding of territories to the Seychelles
The colonial British Indian Ocean Territory (B.I.O.T.) was formed in 1965 and includes the Chagos Archipelago of which the coral island group of Diego Garcia is the largest, and which encompasses an ocean area of 21.042 square miles. For many years now, the B.I.O.T. has no original population. It produced copra and was evacuated to Mauritius between 1969 and 1971. Today’s residents are personnel of the Anglo-US-American military base on the island of Diego Garcia. In 1965 the Chagos Archipelago was retained by Great Britain Mauritius. During independence negotiations with Mauritius in 1968, Great Britain made her continuing stay in the archipelago, under British rule, a precondition. The original B.I.O.T island groups of Aldabra, Farquahr and Desroche had to be returned to the Seychelles in 1976. The presently uninhabited islands have by way of their proximity to the Gulf Region only strategic value. The treaty of 1966 between Great Britain and the USA envisioned combined usage of the territory for at least 50 years. In spite of protests by neighbouring states, Diego Garcia is being developed by the USA as a naval and air force base since 1974. Demands by Mauritius, and supported amongst others by the Organization of African Unity (OAU) and India, were rejected by the Government of Great Britain, however, as soon as no more military needs are evident, Great Britain will return the islands to Mauritius.
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen,
Länder der Erde


![]()














