mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Plurinational State of Bolivia
- presidial republic
- own name: Estado Plurinacional de Bolívia
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Historical Coats of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National and merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (ES)



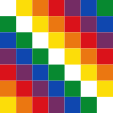
since 2009,
Wiphala flag, = national symbol
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (ES)




State flag
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (ES)






War flag
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (ES)



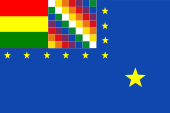
since 2013,
Naval flag
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (ES)



Naval jack
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)




1548–1776,
The region belongs to the Spanish Viceroyalty of Peru,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)



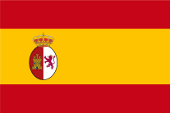
1776–1825,
The region belongs to the Spanish Viceroyalty of Río de la Plata,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1825–1826,
State flag,
Source, by:
World Statesmen,
FOTW




1825–1826,
National and merchant flag,
Source, by:
World Statesmen,
FOTW




1831–1851,
State flag,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (ES)




1831–1851,
National and merchant flag,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (ES)




1851–1888,
State flag,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (ES)




1966-2013,
Naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)




The today's design of the flag of Bolivia descents from 1851. The today's variant was introduced on the 14th of July, 1888. It consists of three horizontal stripes, red, yellow and green. Red represents the fauna, yellow the minerals resources, and green the vegetation and agriculture. Red also symbolizes the bravery and valor of the Bolivian soldiers. The colors of the flag go back to the first president of the land, Antonio José de Sucre (1795–1830). He introduced in 1826 a flag with the colors yellow, red and green, which was modeled after the design of the flag of Greater Colombia. In 1851 the new sequence of colors was laid down. It has been maintained until now.
Source: Wikipedia (ES), Translator of the English text: Joachim Nuthack


Coat of arms of Bolivia,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4,
Wikipedia (ES)


1825–1826,
Coat of arms of Bolivia,
Source, by: Wikipedia (ES)

1826–1851,
Coat of arms of Bolivia,
Source, by: Wikipedia (ES)

1851–1888,
Coat of arms of Bolivia,
Source, by: Wikipedia (ES)

Today's coat of arms of Bolivia was introduced in 1888, and in substance goes back to the coat of arms of 1825. The number of stars in the coat of arms always varied with the number of departments/provinces. It last showed nine stars. In 1963 the tenth star was added in memory of the department Cobija, which Bolivia lost in the Pacific War (1879–1884) to Chile. The oval blazon shows the mountain of Potosí, it represents the riches of minerals and ores, and a scenery with a alpaca, a sheaf and a palm tree, which represent the abundance of nature. The sun is an Inca symbol, and the condor above the shield symbolizes freedom. The first coat of arms of Bolivia was introduced in 1825 and showed already the elements of the today's coat of arms: the mountain of Potosi, an alpaca, and a palm tree, surrounded by a palm-twig and an oil-twig. Above the shield appeared a Phrygian Cap hold (a symbol of freedom), and two allegorical figures with a banner with the name of the country. The second coat of arms of Bolivia was introduced in 1826 and resembled already the todays coat of arms. The Phrygian Cap was replaced by a Condor in 1851.
Source:
Wikipedia (ES)

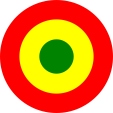
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
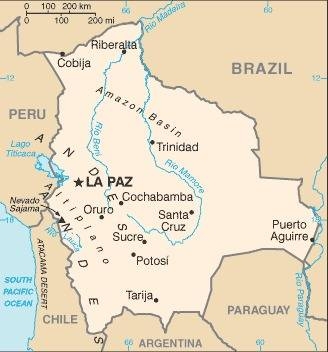
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 422.531 square miles
Inhabitants: 11.080.649 (2018), thereof 68% Mestizos, 20% Indians (Quechua, Aymara), 5% Europeans (thereof ca. 30.000 Germans)
Religions: 78% Roman Catholic, 19% Protestant, 3% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 26 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Sucre, 237.480 inh. (2012)
Seat of Government: La Paz, 757.184 inh. (2012)
official Languages: Spanish, Quechua, Aymara, Guarani
other Languages: 33 different indigenous languages
Currency: 1 Boliviano (BOB, Bs) = 100 Centavos
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

1471–1538 · the West of the today's country is a part of the Inca-Empire
1538–1545 · conquest by Spain, the region gets the name Upper Peru (Alto Perú)
1548 · part of the Vice-Kingdom Peru
1776 · part of the Vice-Kingdom Río de la Plata
1809 · onset of the liberation fight
1816 · Upper Peru becomes re-incorporated to Peru
1825 · Upper Peru becomes subordinated under Peruan military gouvernment
6th of August 1825 · Upper Peru proclaims independence
11th of August 1825 · proclamation of the República Bolívar
18th of May 1826 · Peru recognizes Bolivian independence
1836–1839 · Confederation Peru-Bolivia
1879–1884 · Pacific War, Bolivia looses its coastal
province, the Departement of Cobija, to Chile
1899–1903 · war against the renegading Province of Acre
1903 · Peru has to cede large parts of Acre to Brazil and Peru
1932–1935 · war against Paraguay
18th of March 2009 · the Republic of Bolivia becomes renamed in "Plurinational State of Bolivia"
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

The region of the present-day Bolivia was called Upper Peru, Charcas or even Chuquisaca in the Spanish time. In honor of the freedom fighter Simón Bolívar, the in 1825 independent Republic was called "Bolivia" . In the Indian population (Quechua and Aymara), the country is often called "Qullasuyu".
Source:
World Statesmen,
Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()



















































