mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag
![]()










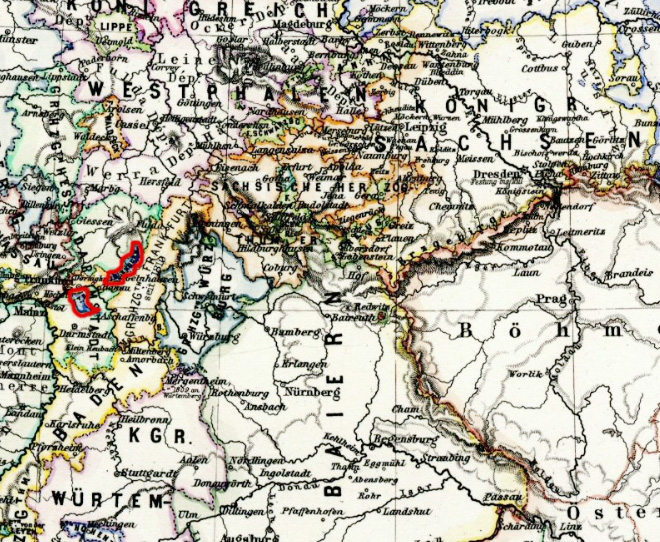
11th century · the ancestors of the Isenburgs live in Rommersdorf near Heimbach-Weis
ca. 1100 · build of the Isenburg Castle, the owners now call themselves "Lords of Isenburg", by marriages and inheritancesthe property will increase
1137 · split of the Hose of Isenburg into the lines of Braunsberg, Kempenich and Limburg
1210 · Isenburg-Braunsberg splits in a younger line (Lower Isenburg) and an older line (Upper Isenburg, Isenburg-Wied)
1371 · the line Isenburg-Arenfels (out of the line Isenburg-Limburg) becomes the Counts of Wied
1424· Isenburg-Kempenich is extincts
1511 · the line Isenburg-Buedingen (out of the line of Isenburg-Limburg) splits into the lines of Isenburg-Birstein and Isenburg-Ronneburg
1601 · Isenburg-Ronneburg extincts
1628 · Isenburg-Birstein splits into the lines of Isenburg-Offenbach and Isenburg-Buedingen
1664 · the last line of Lower Isenburg extincts
1685 · from Isenburg-Buedingen separate the lines of Isenburg-Waechtersbach, Isenburg-Meerholz (to 1929) and Isenburg-Marienborn (to 1725)
1685 · Isenburg-Offenbach splits into the lines of Isenburg-Birstein and Isenburg-Philippseich
1744 · Count Wolfgang Ernst I. of Isenburg-Birstein is levied by Emperor Charles VII to the rank of a Prince
1792, 1796, 1800 and 1805 · invasions of French revolutionary troops under Napoleon in the German Empire, the German Empire subjectes and becomes territorially transformed
1801 · all left-bank territories of the River Rhine ceded to France, and incorporated by this (in this way the in the Eifel Mountains placed Duchy of Arenberg)
1803 · German Mediatisation (Reichsdeputationshauptschluss), transformation of the territorial partition of the German Empire, ecclesiastical possessions become confiscated, old princely territories and free cities become confiscated or dissolved or annexed to old or new principalities, the number of sovereign authorities and territorial entities of the empire is thus reduced from 300 to 60
12th of July in 1806 · Napoleon forces the creation of the Rhine Confederation, an alliance of sixteen southern and southwestern German states under French protectorate, the Principality of Isenburg-Birstein is one of the founding members
1st of August 1806 · the states of the Rhine Confederation declare themselves sovereign and resign from the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation, the Principality of Isenburg-Birstein beomes in this way fully sovereign as a state, but even over the possessions of the Counts of Isenburg (Isenburg-Buedingen, Isenburg-Waechtersbach, Isenburg-Meerholz and Isenburg-Philippseich), and furthermore over the possessions of the Counts of Schoenborn-Heusenstamm and Lerchenfeld
6th of August in 1806 · Emperor Franz II. lays down the crown of the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation, the empire ends
October 1813 · Napoleon's defeat at Leipzig, the Rhine Confederation begins to fall apart, Napoleon and his troops withdraw behind the Rhine River
2nd of April in 1814 · Napoleón is deposed as emperor of France and exiled to Elba
1814–1815 · Vienna Congress, reorganization of Europe after the Napoleonic era
1815 · the Principality of Isenburg-Birstein comes to the Empire of Austria
1816 · the Principality of Isenburg-Birstein comes mostly to the Grand Duchy of Hesse, and a smaller part to the Electorate of Hesse, the title "Prince of Isenburg" goes over to the Hessian ruler
1840 · Count Ernst Casimir III. of Isenburg-Buedingen is levied to the rank of a Prince, but now the line calls itself "Princes of Ysenburg and Buedingen"
1865 · Ferdinand of Isenburg-Waechtersbach is levied to the rank of a prince
1918 · the line Isenburg-Birstein calls itself only "Isenburg"
Source:
Wikipedia (D)
![]()