




In the flag history of the "Third Reich" are to differ two timespans. The first phase, between 1933 and 1935 is characterized by the ousting or redesign of the unpopular black-red-golden flags and the re-introduction of their respective black-white-red counterparts. A complete re-introduction of the imperial flags occured not because of political reasons. The national socialists saw themself as renewers, and contemplate the empire as reactionary. Their affection to the colors black, white and red was not affected from there, because they were the colors of Germany on the battlefields in the world war. The second phase of the flag history of the "Third Reich" began actually at the end of the year 1934, as the empire's president Hindenburg died. Hitler, hitherto empire's chancellor, took over this function too, and named hisself not empire's president anymore, but "leader". All the control was now concentrated in one hand and the national socialists ruled unrestricted. Not only the state hisself, but even his heraldic symbolism goes in this way through a policization in the year 1935. The party flag of the NSDAP (swastika flag) became now the exclusive national and merchant flag of the empire, and all other flags were now redesigned in the design of the NSDAP. The swastika-symbolism became in this way omnipresent.
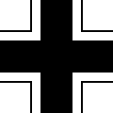
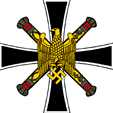
The new created war flag of the "Third Reich" is in principle a combination of the imperial war flag and the swastika flag. It is possible to distinguish in it also the flag of the Order of the Teutonic Knights, or the cross flag of the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation.
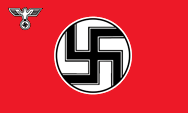
The swastika flag is a design by Adolf Hitler, and was showed in the public for the first time in the year 1920. It was a complete break with the hitherto habit's of designing and caused a lot sensation. As a sign for a absolute restart after the failed policy of the "Weimar Republic" and the results of the Versaille Dictate it became from there very popular. The swastika is in the used shape a in the Indo-european region far spreaded sign with always the same meaning: sun, luck, health and prosperity. Important was thereby the point of rotation of the cross. If the flag was printed in print-through, appeared the swastika on the other side in reversed point of rotation, and with this contorts the symbolism in its contrary. For flags to use offshore was that's why later ordered the doublesited production.
Source: Volker Preuß
"In the color red Adolf Hitler saw the social thoughts, in the white circle the national socialistic (race-) thoughts, in the black swastika the will to fight and will to victory of the "Aryan" human (of European descent) and the thought of the "producing" (productive) work."
Source: F.R.


1922–1936,
The seal and lesser coat of arms of the German Empire
The seal was created by the artist Sigmund von Weech in 1921, and officially introduced for the German Empire in 1922, with the "Decree on the Seals". It was used until 1936, then abolished. According to § 5 of the "Decree on the imperial seal from 7th of March in 1936" it was, however, allowed to continue the use of "existing seals with the former imperial eagle or coats of arms of the countries until 30th of September in 1938". After the Second World War it was adopted again in 1950 for the Federal Republic of Germany.
Source:
Jürgen Kaltschmitt, Wikipedia (D)


1936–1945,
The National Emblem of the German Empire
The emblem of the German Empire under the National Socialists goes also back to the NSDAP Nazi-Party. However, as the party-eagle, the eagle looks the other way.
Source: Uniform-Fibel, rechtlicher Hinweis


1936–1945,
on coins to 1,2 and 10 Reichspfennige, 2 und 5 Reichsmark

1936–1945,
on coins to 1 Reichsmark

1936–1945,
on coins to 5 and 50 Reichspfennige
The shape of the lowermost eagle was retained on the coins issued by the Allies between 1945 and 1949, of course without swastika. However, the inscriptions "Deutsches Reich" and "Reichspfennig" have been retained.

1917–1945
Aircraft Roundel,
Source: Wikipedia (EN)

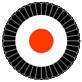
to 1945, Cockade of the German Empire

The German Empire with the Gau-Districts of the NSDAP

Source: Von Bennet Schulte - Eigenes Werk, CC BY-SA 3.0 de, Link

Area: 180.998 square miles (1933)
Inhabitants: 65.161.400 (1933)
Density of Population: 360 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Berlin
official Language: German
Currency: 1 Reichsmark (RM) = 100 Reichspfennig (Rpf.)
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

30th of January in 1933 · Hitler's appointment to the Reichskanzler by the President of the Reich
24th of March in 1933 · The democratic parties in the Reichstag cede under the influence of extreme leftist actions and attacks the sovereignty of the parliament as the legislator to the government under the leadership of the National Socialists, the Weimar Constitution is suspended, the National Socialist rule becomes now dictatorial and installs a totalitarian national socialist one-party regime
1934 · the territorial structure of the countries in the German Empire becomes replaced by the districts of the Nazi Party, the countries become meaningless
1935 · plebiscite in the Saar Area, re-incorporation to the German Empire
1938 · annexation of Austria
1938 · annexation of the by an German majority populated Sudetenland
March 1939 · invasion of Czechia and the establishment of the "Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia", re-incorporation of the Memel Area
1st of September 1939 to 9th of May 1945 · Second World War, end with the total defeat of the German Empire
23rd of May in 1945 · the government of the German Empire is arrested
1945 · the German Empire becomes occupied and split in occupation zones by the four Allies, large areas in the east will be subjected to Polish and Russian administration, the German population there becomes murdered or expelled
1945–1949 · between the Allies, United States, Great Britain and France on the one hand, and the Soviet Union on the other hand, arise tensions, because the communist Soviet Union and the West also, want Germany to integrate into their respective political and economic systems, a peace treaty with the German Empire does not come into existence, because there are exist no more German authorities
1945–1947 · the countries of the German Empire become restructured by the Allies, partially abolished (eg. Prussia on 25th of February in 1947), there were sometimes created entirely new countries (eg. North Rhine-Westphalia)
23rd of May in 1949 · the countries under the control of the Western Allies set up the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG)
7th of October 1949 · the countries under the control of the Soviet Union set up the German Democratic Republic (GDR)
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97,
Volker Preuß

Germany is the land of the Germans. The Germans themselves are not a growed nation in the usual sense, but originally an alliance of Germanic tribes. The Gemans call themselves "Deutsche". The word "Deutsche" comes from the ancient word "teudisk", what translated means "belonging to the tribe." It was used by the tribes which have spoken the "Theodisk" language, which goes back to the tribe of the Teutons. In 843 the Teutons were first called as "Teutisci". Over the yearhundreds "teudisk" became to "tiutsch" and later "deutsch". Neighboring nations or tribes, who were not "teudisk" took over the word for the Germans. In this way the Italians say: "Tedeschi", the Germanic Scandinavians: "Tysk" the Dutchman: "Duitse". Others simply called the "teudisk" as Germans, even if they were Germanic themselves, so the English: "Germans", but other nations acted in the same way, e.g. the Greeks: "Germanoi", or the Romanians: "Germani". Other neighbors took over the name of the tribe, with whom they had to do on their border, over all the tribes of the land, so the Frenchman: "Allemand," which goes back to the tribe of the Alemanni. This is internationally widespread. The Finns, call the Germans "Saksa," which goes back to the tribe of the Saxons. The Russians call Germany "Germania", but the inhabitants and their language they call "Nemjetski", which can be translated with "the dumb" because the Germans in Russia was once forbidden to speak their own language. Even this "Nemjetski" became widespread, so in all Slavic languages and as well as in the Hungarian language as "Nemat".
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Volker Preuß

The documents of capitulation of the German War Might of the 7th of May in 1945 and of the 9th of May in 1945 finished indeed the struggles, but not the existence of the German Empire. The government of the empire became arrested on the 23rd of May in 1945. A peace treaty was not signed, neither with the FRG nor with the former GDR, and is lacking until today.
The Federal Constitution Court in Karlsruhe (President Prof. Dr. Jutta Limbach) decided on 31st of July in 1973 [BVerfGE Bd. 36, 1-37 (LT1-9) BGBl I 1973, 1058] and on the 21st of October in 1987 [Bd.77, S.137,150,154,160,167] unanimous and how intended, that the German Empire in 1945 not perished but continued. Page 15 to 16: ... "The Grundgesetz (Basic Law) – not only a thesis of the International Law and of the State Law sees that the German Empire outlasted the breakdown of 1945 and neither perished by the capitulation nor by the exertion of foreign state power in Germany by the allied occupation mights nor perished later; this is to recognize from the preamble, from article 16, article 23, article 116 and article 146 of the Basic Law. This corresponds to the jurisdiction of the Federal Constitution Court in which the senat persists. ...
The German Empire (see e.g. BVerfG, 1956-08-17, 1 BvB 2/51, BVerfGE 2, 266 (277); 3,288 (319f); 5,85 (126); 6,309, 336, 363) owns still competence in law, but is as whole state not able to act by itself because of lacking organization, especially because of lacking institutionalized organs ... the responsibility for „Germany as whole thing" (= German Empire) have – even – the four mights. The Federal Republic of Germany is in this way not "successor in law" of the German Empire, but identical as state with the state of the "German Empire", – under reference to its territorial expanse only "partially identical", so that insofar the identity demands no exclusivity. The Federal Republic of Germany includes in this way, concerning its state people and its state territory, not the whole Germany regardless of that it recognizes a consistent state people of the subject of the International Law "Germany" (German Empire) ... and a consistent state territory „Germany" (German Empire) ... It (= Federal Republic of Germany) limits its sovereignty in legal terms of state to the field of application of the Basic Law.
"The Federal Republic of Germany agrees the statement of the four mights and emphasizes that the in this statement mentioned incidents and circumstances will not occure, what means, that a peace treaty or a peace regulation is not intended". Protocol of the Bureau of the Federal Chancellor in negotiations of the 17th of July on 1990 in Paris, appendix No. 354 B. (furthermore dissertation of Dr. Michael Rensmann, occupation law in the re-united Germany)
Due to a so-called "small request" out of the Bundestag on 20th of February in 2015, question 27, answered the government of the Federal Republic of Germany: "The Federal Constitutional Court has found in consistently jurisdiction that the "German Empire" - as a subject of international law - is not extincted and the Federal Republic of Germany is not the successor, but identical with it is a subject of international law ... legal basis: BVerfGE 36, pp 1, 16;. and BVerfGE 77, p 137, 155. Source: subject of international law "German Empire" - Foreign - response - from 30th of June 2015: bundestag.de




![]()




























![]()