mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag
![]()





























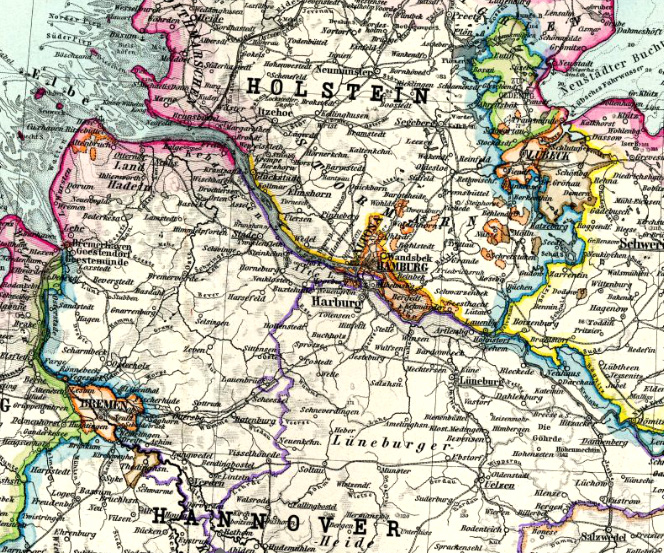
about Christ's birth · in the region settle Germanic tribes, possibly Saxons
375 · Hun invasion, the beginning of the Great Transmigration (Migration Period), migration of the old Germanic tribes into the Roman Empire, moving up of other Germanic tribes towards the Roman border, the Saxons migrate to England and in the Weser River Region, in the now deserted area (Germania Slavica) immigrate Slavs, into the region around today's Luebeck immigrate from the 7th century Slavs from the tribe of the Obodrites
819 · foundation of Liubice (Old-Luebeck) by the Slavic tribe of the Obodrites
900 · in the East Frankish Kingdom forme out five tribal duchies (Saxony, Bavaria, Swabia, Franconia and Lorraine), the beginning of the eastward expansion into Germania Slavica between the rivers Saale/Elbe and the Oder/Neisse, the Elbe river becomes crossed to the north-east, and about 960 the Baltic Sea and the Oder River are reached, the Obodrites become annexed to the Mark (Margraviate) of Hermann Billung
1093 · Liubice becomes the residence of a Slavic prince
1127 · Liubice is destroyed by the Slavic tribe of the Ranen
1143 · foundation of Luebeck by earl Adolf II. of Holstein
1160 · Luebeck becomes a bishopric and gets granted the city rights
1189 · Luebeck comes to the Duchy of Saxony
1192 · Luebeck comes to Holstein
1201–1225 · under Danish rule
1226 · incorporation of Old-Luebeck (est. ca. 1100)
1226 · levied to an Free Imperial City by emperor Friedrich II.
ca. 1280 · establish of the Hanseatic League
1361· the City of Visby on Gotland, until now the capital of the Hanseatic League, is conquered by the Danish King Waldemar IV., the seat of the Hanseatic League is moved to Luebeck
14th–16th cent. · powerful economical and cultural influence in the Baltic Sea area
1563–1570 · Nordic War (Hanse and Denmark against Sweden), Sweden achieves
1570 · peace of Stettin, the political importance of Luebecks ends
1669 · last Hanse congress in Luebeck
1792, 1796, 1800 and 1805 · invasions of French revolutionary troops under Napoleon in the German Empire, the German Empire subjectes and becomes territorially transformed
1803 · German Mediatisation (Reichsdeputationshauptschluss), transformation of the territorial partition of the German Empire, ecclesiastical possessions become confiscated, old princely territories and free cities become confiscated or dissolved or annexed to old or new principalities, the number of sovereign authorities and territorial entities of the empire is thus reduced from 300 to 60
1806 · occupation by French troops under Napoléon
12th of July in 1806 · Napoleon forces the creation of the Rhine Confederation, an alliance of sixteen southern and southwestern German states under French protectorate
1st of August 1806 · the states of the Rhine Confederation declare themselves sovereign and resign from the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation
6th of August in 1806 · Emperor Franz II. lays down the crown of the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation, the empire ends
1810 · Luebeck is annexed by France
1811 · withdrawal of the French
October 1813 · Napoleon's defeat at Leipzig, the Rhine Confederation begins to fall apart, Napoleon and his troops withdraw behind the Rhine River, restoration of the Free and Hanseatic City of Luebeck
1814–1815 · Congress of Vienna, reconstruction of Europe after the era of Napoleon, the ownership and the administrative partitions in the former German Empire become restored, but not the sovereignty of the ecclesiastical countries, their possessions become transferred to old or new principalities, the 39 remaining German states – in this way Luebeck too – become organized in a loose association, the German Confederation
1866 · German War (civil war), Prussia and its allies against Austria and its allies, Prussia wins, Luebeck is on the side of Prussia, join of the North German Confederation
1st of January in 1868 · selling of the claims in the mutual government of Bergedorf with
Hamburg to Hamburg
1868 · joining of the Customs Association
1871 · joining of the German Empire
1933–1934 · Luebeck cedes (like all German states) its exclusive pilitical rights to the government of the empire, the territorial structure of the German Empire countries become replaced by the Gau structure of the NSDAP, the countries become meaningless, finally on 30th January in 1934 by the 'Law on the rebuilding of the empire'
26th of January in 1937 · Greater Hamburg Act, the territory of the City of Hamburg becomes significantly increased at the expense of the Prussian territory, in exchange Prussia annexes the city of Luebeck, the (since 1934 marginal) sovereignty of the city ends, it becomes affiliated to the Gau of Schleswig-Holstein
1949 · the town belongs to Schleswig-Holstein
Source:
RetroBib Retrobibliothek,
Wikipedia (D),
Historisches Deutschland,
World Statesmen,
Jürgen Kaltschmitt
