mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- 1712–1918 Principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont
- former country of the German Empire
- 1st of May in 1929 incorporated to Hesse-Nassau
• Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Cockade
• Numbers and Facts
• History

ca. 1830 to 1849,
Flag of the country (Colours of the country),
ratio = 2:3,
Reconstruction,
Source, by: Cockade




1848/49 to 1929,
Flag of the country (Colours of the country),
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




1848/49 to 1929,
Presumed official flag (state flag)
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (D)



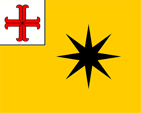
to ca.1849,
Flag of the Prince,
ratio = 4:5,
Source, by: Deutsche Wappen Rolle,
Flags of the World




ca.1900–1918,
Flag of the Prince,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Neubecker 1933




The country's colors of Waldeck correspond to the colors of the German tricolor in the revolution year of 1848. This seems to be a contradiction, on the one side a monarchical state and on the other side the flag of the liberals and democrats.
The black-red-golden flag of the German Confederation was not only adoped for Germany, a lot of sovereigns accepted a constitution and adoped likewise the black-red-golden flag for their country. The constitution for the German Confederation was never undersigned, because Prussia especially opposed all democratic ambitions and eliminates step by step all in 1848 reached rights. The black-red-golden flag got there even banned. In other countries of the German Confederation just not. Waldeck is only one exemple for this.
The time before 1848 is largely hidden in the dark as far as the national colors and flags are meant. A blue, white and red cockade has survived, from which a flag could theoretically be reconstructed. A blue-white-red tricolor in the colors of the coat of arms and corresponding to the taste at that time. It is not known whether such a flag really existed.
The colours of the German states are (called Landesfarben, are often derived from the colours of the coats of arms, and used as cockades, as well as flags), were formed – especially in the German inland countries – rather late, often after the French Revolution and the following wars of liberation. In the period from ca. 1815 to ca. 1830, this process was finally completed in all German states.
The flag of the prince was originally monochrome yellow with a black star in the middle, the image of the coat of arms of the Principality of Waldeck, and a white upper corner with a red anchor-cross in it, the image of the coat of arms of the Principality of Pyrmont. Both principalities were in one hand from 1631 and formed together the principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont, as it was called right with a long name. The flag appears to have been decommissioned in the transition phase to black, red and gold. Hugo G. Ströhl, the author of the book "Deutsche Wappen Rolle", writes around 1897 that this flag is no longer used and that the prince, on request at the princely court, would no longer use a special flag, only the national colors black, red and gold. According to other sources (Ottfried Neubecker, 1933) a new princely standard seems to have been introduced around 1900, a (like the national flag) horizontally striped flag in black, red and gold but in the middle red stripe appears the middle coat of arms of the principality.
The black, red and golden flag with the Waldeck Star in the middle has been handed down and can still be admired in the museum today. It can only be assumed that it is a distinguishing feature, perhaps to differentiate the official flag (used by offices and authorities) from the common colors of the country (Landesfarben).
Source: Volker Preuß,
Flags of the World,
Deutsche Wappen Rolle,
Jens Hild


Lesser coat of arms of the Principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont,
Source, by: Deutsche Wappen Rolle

Middle coat of arms of the Principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont,
Source, by: Flags of the World, Neubecker 1933

Shield of the greater coat of arms of the Principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont,
Source, by: Deutsche Wappen Rolle

The central elements of the heraldry of the Principality of Waldeck are a black star on gold, the image of the coat of arms of the Principality of Waldeck, and a red anchor-cross on silver, the image of the coat of arms of the Principality of Pyrmont. Both principalities were in one hand from 1631 and formed together the principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont, as it was called right with a long name. The greater coat of arms (mantle with crown, shield with shield holders and 5 helmets with crests and mantling, motto-banner) showed a shield that was twice parted per pale and twice parted per fess, with a golden heart-shield with the Waldeck Star on it. The first and ninth fields showed the anchor-cross of Pyrmont, in the second and eighth field appeared on silver three red escutcheons (County of Rappoltstein), the third and seventh fields showed on silver three golden-crowned black eagle-heads (Dominion of Hohenack), the fourth field showed on blue one golden-crowned silvery lion (Dominion of Tonna, County of Gleichen) and the sixth field showed on silvery background covered with blue shingles a golden-crowned red lion (Dominion of Geroldseck). The middle coat of arms showed the mantle with crown and the shield of the greater coat of arms, the lesser coat of arms showed the mantle with crown and a parted per pale shield with the heraldry of Waldeck and Pyrmont.
Source: Volker Preuß,
Deutsche Wappen Rolle


1807–1848,
Cockade of the Principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont,
Source, by: Jürgen Kaltschmitt
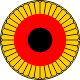
1848–1919,
Cockade of the Principality of Waldeck-Pyrmont,
Source, by: Jürgen Kaltschmitt
From 1807 the cockade showed the color-combination of blue-white-red, derived from the colors of the coat of arms. Despite the very French appearance, the colors were left unchanged even after the crossing Waldecks on the side of the Allies in the year 1813. In the revolutionary year of 1848, the cockade and also the flag were changed to black-red-gold (which are also derived from the coat of arms) and consistently maintained until the end of the country in the year 1929.
Source: Jürgen Kaltschmitt, nach P. Bunde, Brigadeuniformtafel Nr. 235, Herzogenrath 2010

Read here:
Informations, history and facts about the theme "Cockades".
Cockade

Area: 433 square miles
Inhabitants: 61.700 (1910)
Density of Population: 142 inh./sq.mi. (1910)
Capital: Arolsen
Currency to 1875: 1 Taler = 30 Silbergroschen = 360 Pfennige
Currency 1875–1924: 1 Mark = 100 Pfennig
Currency 1924–1929: 1 Reichsmark (RM) = 100 Reichspfennig (Rpf.)
Source: Der Michel,
Wikipedia (D)

1189 · the Counts of Schwalenberg purchase the castle of Waldeck
1631 · annexation of the county of Pyrmont
1712 · elevation of the county to a principality
1807 · joining to the Rhine Confederation
1815 · joining to the German Confederation
1866 · in the brother war on the hands of Prussia, joining to the North German Confederation, Prussia takes over the administration of the country
1871 · joining to the German Empire
1918 · fall of the monarchy in Prussia, formation of the Free State of Waldeck
30th of November in 1921 · annexation of the region of the former County of Pyrmont to the Prussian Province of Hannover
1st of May in 1929 · affiliation of the region of the former county of Pyrmont to the Prussian Province of Hessen-Nassau, Waldeck expires
Source: Wikipedia (D),
RetroBib Retrobibliothek,
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Discovery '97,
Volker Preuß







![]()






















