mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Free County of Burgundy, also called: Upper Burgundy
- historical region in today's France
- former county and province
• Flag
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map of the historical Regions in France
• Explanations about the Regions
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

• Flag of Franche-Comté – drapeau de la Franche-Comté
• 1960–2016, unofficial flag of Franche-Comté Region
– drapeau officieux de la région Franche-Comté,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)






The flag of Franche-Comté is a scutcheon-flag, its design is the image of the coat of arms of Franche-Comté. The with this associated heraldry shows a blue bunting, covered with golden tiles, and in the middle a red armored golden lion with a crown. The in 1960 created Region of "Franche-Comté" has no official flag. In the between 1960 and 2016 existing Region of "Franche-Comté" was an unofficial flag in use, which showed the historic heraldry of Franche-Comté.
Source:
Volker Preuß, Wikipedia (D)


Coat of arms of Franche-Comté
– blason de Franche-Comté,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)

The coat of army of Franche-Comté shows a blue bunting, covered with golden tiles, and in the middle a red armored golden lion with a crown. There also exist reproductions without the crown. Probably the coat of arms goes back to the 12th century.
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Volker Preuß

The historical, French Regions:
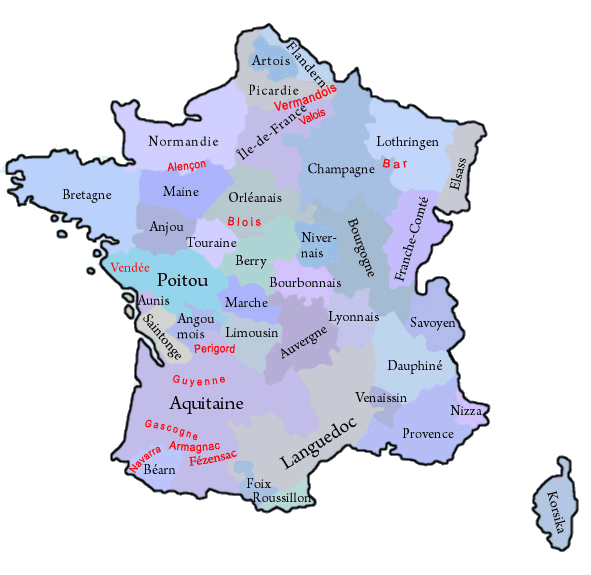
in black: governorate and province in 1776,
in red: former county, province oder governorate
Map: Volker Preuß

The until the French Revolution existing provinces (or governorates) have been historically grown structures, which had their roots oftenly in former fiefdoms of the French crown, historic counties and duchies. They oftenly existed for hundreds of years and had preserved regionality (e.g. cultural particularities and regional languages). On the occasion of the French Revolution such phenomena were of course not desirable, and as part of their bloody and violent egalitarianism any regional references were eliminated. Shortly after the French Revolution the provinces were dissolved and France became divided into many départements, which should have approximately the same size and the same status. The départements were named after rivers or mountains, to use never and in no circumstances the name of an old province. However, there was no success in cutting the connections of the people of France to their respective regions, so that administrative regions were re-created in 1960, to have a better control in regional administrative processes. In this way became départements, which were placed in a historical province, administratively grouped to an oftenly historically named region. The resulted structures coincide only approximately with the boundaries of the old provinces. In the strictly centralist France any regionality is avoided, so that even the official flags of these regions mostly look like flags of companies, unloving, unhistorical, technocratic and modernistic, and these flags should not be a subject of any lexical considerations here. Only in a few of that regions, exist official flags which remember the historical models. But, even the existence of these today's regions is douptful, because in 2014 was passed a territorial reform valid from the year 2016, that reduces the number of the existing regions by merging to nearly the half. However, there exist unofficial flags in nearly all of these regions, which should remember the old provinces and the old heraldry.
Wikipedia Link to the regions of France:
click or tap here
FOTW Link to the regions of France:
click or tap here
Source: Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (D),
Volker Preuß

antiquity · settlement by Celtic tribes, the largest of them are the Sequans
58 B.C. · Roman conquest, the area comes to the provinces of Gallia Lugdunensis and Germania Superior, for a time it was an own province as Maxima Sequanorum, in the last days of the Roman Empire, the province was called Germania Tertia
52 B.C. · an uprising of the Gauls under Vercingetorix is suppressed
4th/5th century A.D. · the Burgundians come from the region between the Oder River and Vistula River and invade into the Roman Empire, settle on the Middle Rhine near Worms and plunder neighboring Roman settlement areas
436 · the Kingdom of Burgundy in the Middle Rhine area is shattered by Huns in Roman service
443 · the surviving Burgundians get settled by the Romans in the area of Lake Geneva and the today's Savoy
443–500 · establishing of the Kingdom of Burgundy (Burgundia), territorial expansions
534 · conquest of the Kingdom of Burgundy by the Franks, today's Burgundy comes to the Frankish Empire, the area will remain as part of empire with its own administration
870 · at the division of the Frankish Empire (Treaty of Meersen) arises the West Frankish Kingdom, the East Frankish Kingdom, and the Frankish Kingdom of Italy – Burgundy gets divided, the north (Upper Burgundy) comes to the West Frankish Kingdom, the south (Lower Burgundy) comes to the Frankish Kingdom of Italy
877 · Lower Burgundy separates from Italy
879 · Boso of Vienne is king of Lower Burgundy
880 · by the division of the Frankish Empire (Treaties of Verdun and Ribbemont) arises the West Frankish Kingdom (later France), the East Frankish Kingdom (later German Empire), the Kingdom of Italy, the Kingdom of Upper Burgundy (under Rudolf the Welf), the Kingdom of Lower Burgundy persists, and formerly Burgundian territories in the northwest come as "Regnum Burgundiae" to the West Frankish Kingdom too
920–1016 · Regnum Burgundiae develops to a duchy of France, which adopts the name Burgundy (=> Duchy of Burgundy)
951 · Upper Burgundy and Lower Burgundy become united to the Kingdom of Burgundy, under Conrad III. of Upper Burgundy, this country is also called Arelat
1016 · the King of France, Robert II. (from the House of Capet) conquers the Duchy of Burgundy
1031 · Robert II., passes the Duchy of Burgundy as an appanage to Robert, his second son, he founds the dynasty of the Senoir Line of the House of Burgundy, which will reign until 1361
1033 · the Kingdom of Burgundy (Arelat) comes as an inheritance to the German Empire, the Roman-German Emperor Conrad the Elder is elected in Peterlingen (Payerne) to the king of Burgundy, but in subsequent years, the country is divided into several counties (County of Provence, County of Venaissin, County of Savoy, County of Dauphiné, Franche-Comté), the last king of Burgundy is the Emperor Charles IV., who was enthroned in 1365
10th century · the Counts of Mâcon consolidate and extend their possessions in the region, which were inherited to Otto Wilhelm from the House of Burgundy-Ivrea, he called himself first Count of Burgundy, the Counts of Burgundy belonged to the kingdom of Burgundy and were in this way vassals of the Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire of German Nation
1156 · Beatrix of Burgundy marries Emperor Frederick I. (Barbarossa), as a dowry she brings the County of Burgundy in marriage, so the country comes to the House of Hohenstaufen
1169 · Emperor Frederick I. separates the County of Burgundy from the Kingdom of Burgundy, and renames it to Palatinate of Burgundy
1200 · the Palatine of Burgundy comes by marriage to Otto II. of Merania (House of Andechs)
1248 · after the extinction of the house of Andechs the county the Palatine of Burgundy comes to the Counts of Chalon
1316 · the Palatine of Burgundy comes by marriage to Philip V., King of France, and in this way to the French crown
1322 · death of Philip V., the Palatine of Burgundy comes as a heir to the House of Burgundy (Senior Line of the House of Burgundy), instead of the term Palatine appears the name of Free County (Freigrafschaft), Free County means in French: Franche-Comté
1361 · death of Duke Philip I. of Burgundy, extinction of the Senior Line of the House of Burgundy, Franche-Comte goes as heir to Margaret of Flanders
1369 · Philip II. of Valois (the Bold) marries Margaret, the daughter and heiress of Artois, Nevers, Flanders and the Franche-Comté, he is the founder of the Junior Line of the House of Burgundy, which ruled to 1482 in the Duchy of Burgundy
1444 · the County of Moempelgard (Montbéliard) comes to Wuerttemberg
1477 · Battle of Nancy, defeat against Lorraine, death of Duke Charles the Bold
11th of February in 1477 · Mary of Burgundy, daughter of Charles the Bold, can get the inheritance as Duchess of after she has to make concessions to the estates (Large Privilege), in the same year she marries the later emperor of the Holy Roman Empire, Maximilian of Habsburg, Ludwig XI. – the King of France – terminates the Duchy of Burgundy and other Burgundian owned areas as completed fiefs, they come to the french crown
1493 · Treaty of Senlis, Charles VIII., King of France, gives back the Free County of Burgundy to Emperor Maximilian I. (House of Habsburg), because it is a fief of the German Empire, Franche-Comte comes in this way to the House of Habsburg
1512 · the House of Habsburg and the Helvetian Confederation declare neutrality for Franche-Comte
1555 · Franche-Comte comes to the Spanish line of the House of Habsburg
1618–1648 · Thirty Years War in the German Empire, France occupies in 1618, among others, the Free County of Burgundy
1668 · Louis XIV., King of France, occupies Franche-Comte
1674 · Louis XIV., King of France, invades and occupies the Free County of Burgundy
1678 · Peace of Nijmegen, the Franche-Comté is ceded to France, the country comes to the French crown, the capital is moved from Dole to Besançon
16th to 18th century · Franche-Comté (as part of the French crown) becomes a province, the country is involved in the civil administration of the Kingdom of France and has a governmental administration
1776 · the already in the 14th century created governorates of the civil administration of the kingdom of France become committed to a number of 39, and correspond in this way to the number of provinces, in previous years could any provinces be summarized in one governorate
1789 · French Revolution, the governorates (provinces) become abolished, Franche-Comté is divided into departments (mainly Doubs, Jura, Haute-Saône and after 1871 even the Territoire de Belfort)
1790/1793 · French troops occupie the County of Moempelgard (Montbéliard)
1796 · Peace of Paris, Wuerttemberg cedes Moempelgard (Montbéliard) to France
1960 · reintroduction of regions in France, formation of the Region of Franche-Comté with Besançon as capital, nearly within the historic boundaries, just by integrating the departments of Doubs, Jura, Haute-Saône and Territoire de Belfort
2016 · the Franche-Comté region merges with the Burgundy region (Bourgogne) in the new, larger region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Meyers Konversationslexikon

Mömpelgard – Montbéliard

Coat of arms of Montbéliard – blason de Montbéliard,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)

The name "Franche-Comté" is to translate as "Free County", a name that first appeared in the 14th century for the Palatinate of Burgundy. Presumably the name comes from the fact that after the extinction of the House of Andechs and the marriage of the heir-daughter of the subsequent House of Châlon with Philip V., King of France, the ties to the German Empire were lost temporarily in 1316 (to 1477).
Source:
Volker Preuß


![]()








