mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of The Gambia
- authoritarian presidial islamic republic
- own name: Republic of The Gambia
• today's Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Maps
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4






since 1970,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 3:4,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE),
telegraph.co.uk




Flag for ambassadors,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)




British West Afrika, West Africa Settlements:
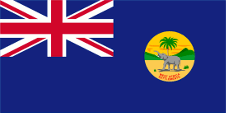
1869–1888,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)



The Colony of the Gambia:
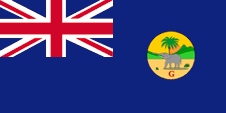
1888–1965,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)




As Gambia reached his independence on 18th of february in 1965, the today's flag was hoisted up for the first time. It shows three horizontal stripes in red, blue and green. Those are separated among themselves by narrow white stripes. The stripe width ratio is 6:1:4:1:6. The color Red embodys the sun, blue represents the river Gambia and green symbolizes the agriculture and the richness of the land, and the white stands for the peace. Previous to the independence in Gambia was in use the blue, British official flag (Blue Ensign) with an emblem in the flying part.
United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag.The governments were asked to design appropriate badges. The in 1889 introduced emblem (badge) showed an elephant with threatening gesture in front of a palm tree amid an African scenery. In the lower part of the badge was to see the inscription "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." in red. In 1888 The Gambia became an own British Crown Colony and a new badge was introduced. For this purpose, only the inscription on the old badge was changed. Instead of "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." now a "G" appeared. This badge was used until independence in 1965.
Source:
Wikipedia (DE),
Flags of the World,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Volker Preuß


Coat of arms of Gambia,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4

1869–1888,
Badge of the West Africa Settlements,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE)

1888–1965,
Badge of the Colony of the Gambia,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (DE),
Flags of the World

The today's coat of arms was awarded to Gambia on 18th of november in 1964 by the queen Elisabeth II. The badge awarded in 1889 was thus invalidated on the occasion of the country's independence. The coat of arms shows an axe and a hoe on a blue, white and green bordered shield. Above the shield a helmet with blue-yellow blankets and a palm plant. As shield holders serve two lions, each with axe and hoe. They stand for pride and dignity. Below the shield a motto ribbon with the motto of the state: "Progress, Peace, Prosperity". Axe, hoe and palm tree refer to the agricultural structures in Gambia. The both lions remember United Kingdom, the colonial power. Colonial governments have been allowed to use a badge since 1865. The governments were asked to design appropriate badges. The in 1889 introduced emblem (badge) showed an elephant with threatening gesture in front of a palm tree amid an African scenery. In the lower part of the badge was to see the inscription "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." in red. In 1888 The Gambia became an own British Crown Colony and a new badge was introduced. For this purpose, only the inscription on the old badge was changed. Instead of "WEST AFRICA SETTLEMENTS." now a "G" appeared. This badge was used until independence in 1965.
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Wikipedia (DE),
Flags of the World,
Die Welt der Flaggen

Location:
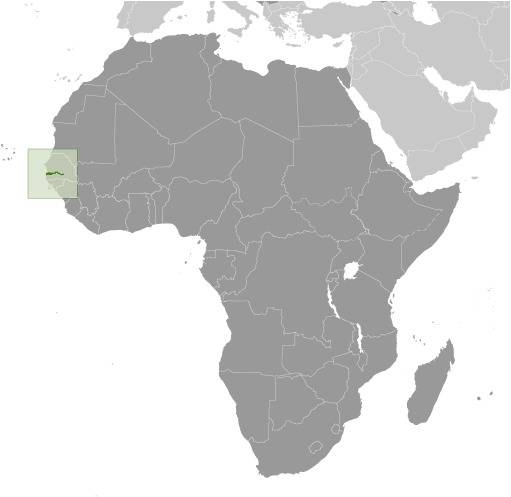
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
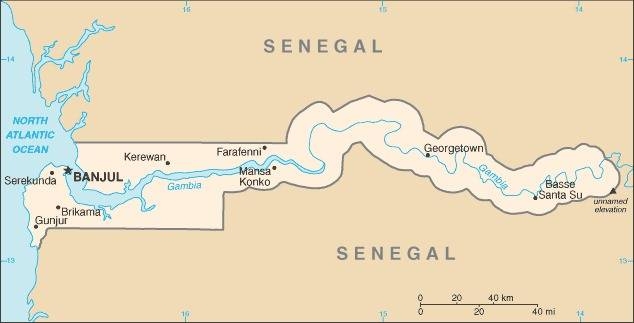
Source: CIA World Factbook
interactive Map of the Region:
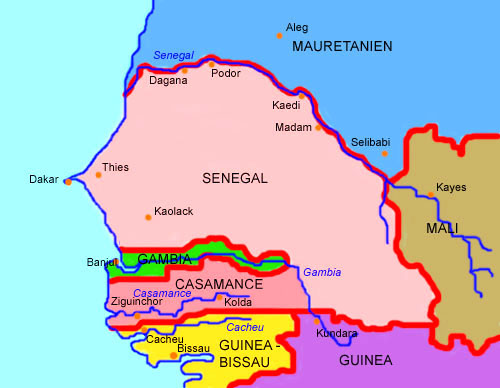
Source: Volker Preuß

Area: 4.127 square miles
Inhabitants: 2.174.000 (2020), thereof 40% Mandingo (Malinke), 19% Fulbe, 15% Wolof, 10% Jola (Diola), 9% Serahuli (Sarahole), 0,5% Europeans
Religions: 96% Muslim, 4% Christians
Density of Population: 527 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Banjul (to 1973 Bathurst), 73.000 inh. (2013)
official Language: English
other Languages: Mandingo, Fulbe, Wolof, ..., French
Currency: 1 Dalasi (D, GMD) = 100 Butut
Time Zone: GMT
Source:
Wikipedia (EN)

ca. 470 B.C. · the seafarer Hanno from Carthage visits the region
1455 · Portugese discover the mouth of the river Gambia, the region itself belongs to the Mali Empire
1588 · beginning of the English colonization, in result conflicts with France, which even claims the region
1661 · England acquires James Island and establishes Fort James trading post
1681 · France establishes the trading post of Albreda
1651–1658 · the Duchy of Courland operates a trading post on James Island
1783 · Paris Peace Treaty, Senegambia is divided between France and United Kingdom, France is given to Senegal, Gambia comes to United Kingdom and becomes later affiliated to British West Africa
1816 · United Kingdom acquires St. Mary’s Island and founds the settlement of Bathurst (from 1973 Banjul)
1857 · France cedes Albreda to United Kingdom
1888 · Gambia becomes a separate British crown colony
1963 · granting of inner autonomy
18th of February in 1965 · independence
24th of April in 1970 · proclamation of the republic, Gambia however stays in the Commonwealth of Nations
1981 · suppress of a left wingers army revolt, even with help by Senegalese troops
1982–1989 · Senegal and Gambia are connected in the Senegambia Confederation (joint military, economic and financial policy)
1994 · coup d'etat
2013 · The Gambia declares the withdrawal from the Commonwealth
2015 · Gambia is declared an "Islamic Republic"
2018 · The Gambia is admitted back to the Commonwealth after applying for membership
Source:
Wikipedia (DE),
Wikipedia (EN),
Atlas zur Geschichte

The name of the country is associated with the Gambia River, but the origin of that name is controversial.
Thesis 1: The name goes back to the Mandingo language and means "The land is the river".
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen
Thesis 2: The name goes back to the language of the Mandingo and means "Kaabu River" or "Kaabu Country". Kaabu was the Mandingo Empire, which existed from the 16th to the 19th century.
Source: Wikipedia (DE)
Thesis 3: The name goes back to a translation error made in the 16th century on James Island. The interpreter did not say the name of the country to a question of Portuguese seafarers, but he told his own name: "Kambi". And so became James Island "Kambi-yaa", what means "Kambis place", and that has been transferred to the river and to the land.
Source: Wikipedia (DE)
Thesis 4: The name goes back to the Portuguese word "câmbio", what means "exchange" or "trade".
Source: Wikipedia (DE)


![]()























