England |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
England |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
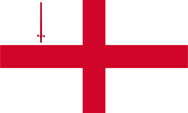
Flagge von England – flag of England, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen   |
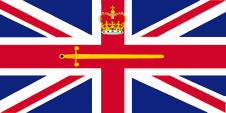 |
Flagge des Lord High Commissioner von England – flag of the Lord High Commissioner of England, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source: Flags of all Nations   |
 |
Flagge der City of London, des historischen Kerns der Hauptstadt – flag of the City of London, the historical core of the capital, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source: Flags of all Nations    |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
11. bis 15. Jahrhundert – 11th to 15th century, Banner des Königs von England – banner of the king of England, Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
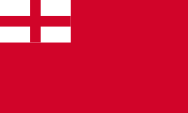
Flagge des englischen Königtums – flag of the English kingship, Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN)    |
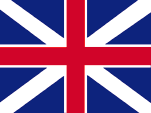 |
1606–1649, Staatsflagge – state flag, 1634–1649, Marineflagge – naval flag, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1634–1707, Handelsflagge für Schiffe aus England – merchant flag for vessels from England, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1634–1707, Handelsflagge für Schiffe aus Schottland – merchant flag for vessels from Scotland, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1649–1651, Flagge des Commonwealth von England – flag of the Commonwealth of England, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1651–1658, Flagge des Commonwealth von England – flag of the Commonwealth of England, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1658–1660, Staats- und Marineflagge – state and naval flag, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1660–1707, Staats- und Marineflagge – state and naval flag, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (EN) |
| Wappen – Coat of arms: | |
 |
Wappen von England – coat of arms of England, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
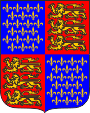 |
1340–1395, Wappen des englischen Königtums – coat of arms of the English kingship, Eduard III. – Edward III., Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
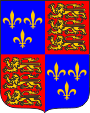 |
1399–1603, Wappen des englischen Königtums – coat of arms of the English kingship, z.B. Heinrich IV. – e.g. Henry IV., Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE) |
| Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge und des Wappens: | Meaning/Origin of the Flag and of the Coat of Arms: |
| Die Flagge Englands zeigt das rote Georgskreuz auf weißem Grund. St. Georg ist Schutzpatron und Nationalheiliger von England. Die Flagge kam im 15. Jahrhundert auf, und ergänzte bzw. verdrängte das bisherige Löwenbanner des Königs als Nationalsymbol. Die drei goldenen, schreitenden und hersehenden Löwen (besser Leoparden) auf rotem Grund gehen auf den König von England, Richard I. "Löwenherz" zurück, der anstelle von einem oder zwei Leoparden ab 1195 drei Leoparden in seinem Wappen zeigte. Die Leoparden sind wahrscheinlich durch die Normannen im Jahre 1066 auf die Britischen Inseln gebracht worden. Das Wappen des Herzogs der Normandie zeigte immerhin zwei dieser Leoparden auf rotem Grund. |
The flag of England shows the red george's cross on white ground. St. George
is the patron saint and national saint of England. The flag arised in the
15th century, and complemented resp. displaced the hitherto valid lion's
banner of the king as national symbol. The three golden, striding and here seeing lions (better leopards) on red ground go back to the king of England, Richard I. "lion heart", who instead of one or two leopards showed three leopards in his coat of arms since the year 1195. The leopards were probably brought on the British Islands by the Normana in the year 1066. The coat of arms of the duke of the Normandy showed nevertheless two of this leopards on red ground. |
| Der englische König Eduard III. erhob als Enkel des 1314 verstorbenen französischen Königs Philipp IV. Ansprüche auf den französischen Thron und nannte sich ab 1340 'König von Frankreich'. Dazu ergänzte er sein Löwenwappen um die goldenen Lilien auf blauem Grund. Der Anspruch auf den französischen Thron wurde von allen Nachfolgern von Eduard III. bis zu Georg III. aus dem Haus Hannover aufrecht erhalten, und die Lilien blieben bis zum Jahr 1801 Bestandteil der Wappen der englischen und britischen Könige. |
As a grandson of King Philip IV., who died in 1314, the English King Edward
III. raised a claim to the French throne, and named himself 'King of France'
from 1340. In this way he added his coat of arms with the lions by the
golden lilies on a blue background.
The claim to the French throne was supported by all the successors of Edward III. until George III. from the house of Hanover, and the lilies remained as a part of the coats of arms of the English and British kings until 1801. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) | |
|
Lesen Sie hier: Eine Flaggen-Affäre! "Vom königlichen Bannerwurf zur Geiselhaft". Die Probleme von Richard I. (Löwenherz), König von England, mit einer ungeliebten Flagge! |
 |
|
Lesen Sie hier: Hintergründe, Geschichte und Fakten zum Thema "Der Löwe in der Heraldik". Ausführungen, Varianten, Entwicklung, sowie Panther und Leoparden. |
 |
Landkarte – Map: |
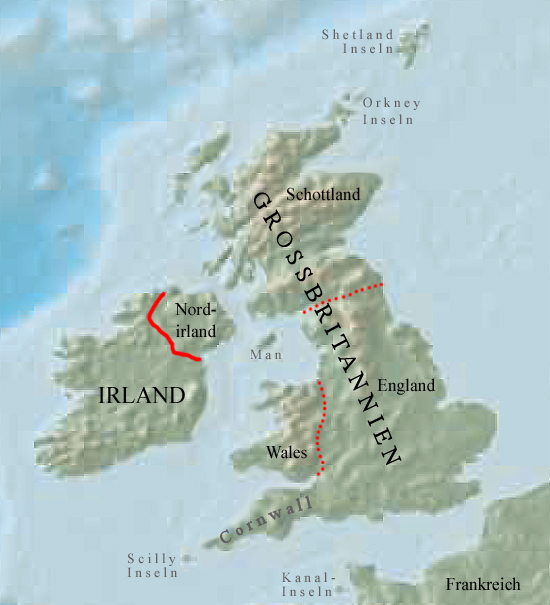 Quelle/Source: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries, modyfied by: Volker Preuß |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ca. 600 v.Chr. · Einwanderung keltischer Stämme auf die
Britischen Inseln 55/54 v.Chr. · erste römische Angriffe 43 · das Römische Reich erobert das Gebiet des heutigen England 85 · Britannien wird römische Provinz 120–128 · Bau des Hadrianswalls gegen Schottland 195 · der Hadrianswall wird überrannt 200–400 · häufige Aufstände der keltischen Briten gegen die Römer ab ca. 400 · Abzug der römischen Legionen, in den Folgejahren Einwanderung der germanischen Stämme der Angeln, Sachsen und Jüten, die später unter dem Begriff Angelsachsen zusammengefasst wurden 450–500 · Kämpfe der keltischen Briten und Sachsen gegen die Pikten und Scoten, Verdrängung der keltischen Briten durch die Sachsen, Bildung der angelsächsischen Königreiche Sussex, Wessex, Essex, Kent, Ostanglien, Mercien und Nordumbrien 825 · Vereinigung von Wessex, Sussex, Kent und Mercia unter König Egbert von Wessex 865 · Däneninvasion: Essex, Ostanglien und Teile von Mercia werden bis 954 dänischer Besitz → Danelaw 1016 · der Däne Knut der Große erzwingt seine Wahl zum König von England 1019 · Knut der Große wird nach dem Tod seines Bruders auch König von Dänemark 1050 · Endgültiges Ende der Dänenherrschaft 1066 · der Sachse Harald II. wird König von England 1066 · die einfallenden Normannen besiegen die Angelsachsen in der Schlacht von Hastings und Errichten ihre Herrschaft in England 1169 · beginnende Eroberung von Irland durch das Königreich England 1265 · erstes englisches Parlament 1284 · Eroberung von Wales 1297 · Einrichtung eines ersten irischen Parlaments, die Eroberung von Irland durch das Königreich England ist im Prinzip abgeschlossen 1338–1453 · Hundertjähriger Krieg in Frankreich um Ansprüche des englischen Königs auf den französischen Thron 1455–1485 · Rosenkriege zwischen dem Haus Lancaster (Wappen: rote Rose) und dem Haus York (Wappen: weiße Rose) 1603 · mit Elisabeth I. stirbt das Haus Tudor aus 1603 · Personalunion zwischen Schottland und England unter Jakob I. aus dem Hause Stuart 1649 · Hinrichtung des Königs Karl I. 1649–1654 · England ist Republik unter Oliver Cromwell 1654 · Wiedereinführung der Monarchie 1707 · staatsrechtliche Vereinigung von England und Schottland zu Großbritannien |
|
ca. 600 B.C. · immigration of celtic tribes on the British
islands 55/54 B.C. · first Roman attacks 43 · the Roman Empire conquers the region of the today's England 85 · Britain becomes Roman province 120–128 · construction of the Hadrian bulwark against Scotland 195 · the Hadrian bulwark gets overrun 200–400 · frequent riotings of the celtic British against the Roman from ca. 400 · withdrawal of the Roman legions, in the following years immigration of the Germanic tribes of the Angles, Saxons and Jutes, which were later summarized under the term Anglo-Saxons 450–500 · fights of the celtic British and Saxon against the Piktes and Scotes, ousting of the celtic British by the Saxon, formation of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of Sussex, Wessex, Essex, Kent, East Anglia, Mercia and Northumbria 825 · unification of Wessex, Sussex, Kent and Mercia under king Egbert of Wessex 865 · Danish invasion: Essex, East Anglia and parts of Mercia become Danish possession until 954 → Danelaw 1016 · the Dane Knut the Grand enforces his election to the king of England 1019 · Knut the Grand becomes king of Denmark after the death of his brother 1050 · ultimate end of the Danish rule 1066 · the Saxon Harald II. becomes king of England 1066 · the invading Normans conquer the Saxons in the battle near Hastings and establish their power in England 1169 · beginning of the conquest of Ireland by the Kingdom of England 1265 · foremost English parliament 1284 · conquest of Wales 1297 · establishment of a first Irish Parliament, the conquest of Ireland by the Kingdom of England is essentially complete 1338–1453 · Centenarian War in France for demands of the English king at the French throne 1455–1485 · Rose wars between the house of Lancaster (badge: red rose) and the house of York (badge: white rose) 1603 · the house of Tudor vanishes with Elisabeth I. 1603 · personal union between Scotland and England under Jakob I. from the house of Stuart 1649 · execution of the king Karl I. 1649–1654 · England is a republic under Oliver Cromwell 1654 · re-introduction of the monarchy 1707 · constitutional unification of England and Scotland to the United Kingdom |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Weltgeschichte, Wikipedia (DE) |
| Der Name von England kommt vom vom altenglischen Wort "Engaland" (erstmals erwähnt im Jahre 1014), was "Land der Angeln" bedeutet. Die Angeln waren ein germanischer Stamm, der, zusammen mit den Sachsen und Jüten, das Land ab dem 5. Jahrhundert eroberte und besiedelte. Ein weiterer und älterer Name ist "Albion", der sich aber auf die ganze Insel bezog. Er wird in der modernen Zeit vor allem dichterisch für England benutzt. Er geht auf eine Erwähung im "Corpus Aristotelicum" im 4. Jahrhundert v. Chr. zurück und ist möglicherweise auf das lateinische Wort "albus" (weiß) zurückzuführen, ein Verweis auf die weißen Klippen von Dover. | The name of England comes from the Old English word "Engaland" (first mentioned in 1014) meaning "Land of the Angles".
The Angles were a Germanic tribe that, along with the Saxons and Jutes, conquered and settled the country from the 5th century. Another and older name is "Albion", but it referred to the whole island. In modern times it is primarily used poetically for England. It goes back to a mention in the "Corpus Aristotelicum" in the 4th century BC. and may derive from the Latin word "albus" (white), a reference to the white cliffs of Dover. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) | |