mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Part of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
- other name: Albion
• Flags
• historical Flags
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag and of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

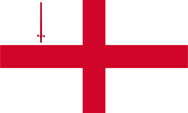
Flag of England,
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen





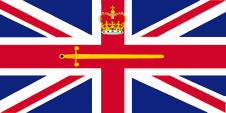
Flagge of the Lord High Commissioner of England,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations



Flag of the City of London,
the historical core of the capital,
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by:
Flags of all Nations







11th to 15th century,
Banner of the king of England,,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




Flag of the English Kingship,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)





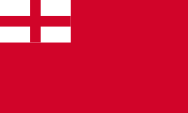
1606–1649, State flag,
1634–1649, Naval flag
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN)





1634–1707,
Merchant flag for vessels from England,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN)






1634–1707,
Merchant flag for vessels from Scotland,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN)






1649–1651,
Flag of the Commonwealth of England,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN)






1651–1658,
Flag of the Commonwealth of England,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN)






1658–1660,
State und naval flag,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN)






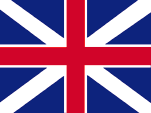
1660–1707,
State und naval flag,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN)







Coat of arms of England,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)
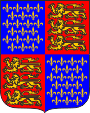
1340–1395,
Coat of arms of the English Kingship,
Edward III.
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)
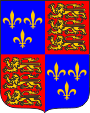
1399–1603,
Coat of arms of the English Kingship,
e.g. Henry IV.
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)

The flag of England shows the red george's cross on white ground. St. George is the patron saint and national saint of England. The flag arised in the 15th century, and complemented resp. displaced the hitherto valid lion's banner of the king as national symbol. The three golden, striding and here seeing lions (better leopards) on red ground go back to the king of England, Richard I. "lion heart", who instead of one or two leopards showed three leopards in his coat of arms since the year 1195. The leopards were probably brought on the British Islands by the Normana in the year 1066. The coat of arms of the duke of the Normandy showed nevertheless two of this leopards on red ground. As a grandson of King Philip IV., who died in 1314, the English King Edward III. raised a claim to the French throne, and named himself 'King of France' from 1340. In this way he added his coat of arms with the lions by the golden lilies on a blue background. The claim to the French throne was supported by all the successors of Edward III. until George III. from the house of Hanover, and the lilies remained as a part of the coats of arms of the English and British kings until 1801.
Source: Wikipedia (DE)

 Read here:
Read here:
A flag affair!
"From a royal banner-throw to being held hostage". The problems of Richard I. (the Lionheart), King of England, with an unloved flag!

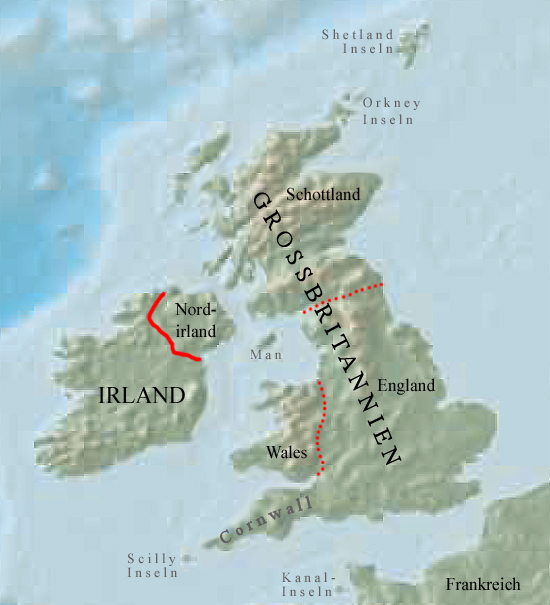
Source: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries, modyfied by: Volker Preuß

Area: 50.345 square miles
Inhabitants: 55.977.178 (2018)
Density of Population: 1.112 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: London, 8.961.989 inh. (2019)
official Language: English
Time Zone: Greenwich Meantime = CET – 1 h
Source: Wikipedia (DE)

ca. 600 B.C. · immigration of celtic tribes on the British islands
55/54 B.C. · first Roman attacks
43 · the Roman Empire conquers the region of the today's England
85 · Britain becomes Roman province
120–128 · construction of the Hadrian bulwark against Scotland
195 · the Hadrian bulwark gets overrun
200–400 · frequent riotings of the celtic British against the Roman
from ca. 400 · withdrawal of the Roman legions, in the following years immigration of the Germanic tribes of the Angles, Saxons and Jutes, which were later summarized under the term Anglo-Saxons
450–500 · fights of the celtic British and Saxon against the Piktes and Scotes, ousting of the celtic British by the Saxon, formation of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of Sussex, Wessex, Essex, Kent, East Anglia, Mercia and Northumbria
825 · unification of Wessex, Sussex, Kent and Mercia under king Egbert of Wessex
865 · Danish invasion: Essex, East Anglia and parts of Mercia become Danish possession until 954 → Danelaw
1016 · the Dane Knut the Grand enforces his election to the king of England
1019 · Knut the Grand becomes king of Denmark after the death of his brother
1050 · ultimate end of the Danish rule
1066 · the Saxon Harald II. becomes king of England
1066 · the invading Normans conquer the Saxons in the battle near Hastings and establish their power in England
1169 · beginning of the conquest of Ireland by the Kingdom of England
1265 · foremost English parliament
1284 · conquest of Wales
1297 · establishment of a first Irish Parliament, the conquest of Ireland by the Kingdom of England is essentially complete
1338–1453 · Centenarian War in France for demands of the English king at the French throne
1455–1485 · Rose wars between the house of Lancaster (badge: red rose) and the house of York (badge: white rose)
1603 · the house of Tudor vanishes with Elisabeth I.
1603 · personal union between Scotland and England under Jakob I. from the house of Stuart
1649 · execution of the king Karl I.
1649–1654 · England is a republic under Oliver Cromwell
1654 · re-introduction of the monarchy
1707 · constitutional unification of England and Scotland to the United Kingdom
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Discovery '97,
Wikipedia (DE)

The name of England comes from the Old English word "Engaland" (first mentioned in 1014) meaning "Land of the Angles". The Angles were a Germanic tribe that, along with the Saxons and Jutes, conquered and settled the country from the 5th century. Another and older name is "Albion", but it referred to the whole island. In modern times it is primarily used poetically for England. It goes back to a mention in the "Corpus Aristotelicum" in the 4th century BC. and may derive from the Latin word "albus" (white), a reference to the white cliffs of Dover.
Source: Wikipedia (DE)


![]()

















































 Read here:
Read here:
