mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Haiti
- zone of US-american influence
- own name: République d'Haïti
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National and merchant flag,
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN), Corel Draw 4




State and naval flag,
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN), Corel Draw 4





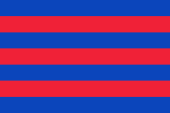
Naval jack,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




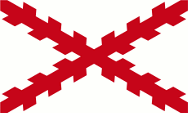
16./17th cent.,
Haiti belongs to the Spanish sphere of influence,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)




1697–1790,
State flag and royal standard of France,
Source, by:
Flaggen Enzyklopädie





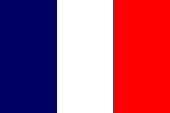
1790–1803,
Flag of France,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4





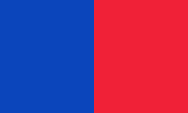
1803–1805,
National flag,
under Toussaint l'Ouverture,
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen




1805–1806,
National flag,
under Dessalines,
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen




1808–1820,
North Haiti,
National flag,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1808–1964, (1808–1820, South Haiti)
National flag,
first under Boyer,
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen



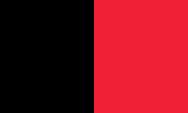
1964–1986,
Merchant flag,
Source, by:
Flaggen und Wappen




1964–1986,
National flag,
Source, by:
Flaggen und Wappen




The today's flag of Haiti was hoisted up for the first time on 21st of June in 1964 and was reintroduced on 25th of February in 1986. It exists in two horizontal stripes in the colours blue and red. About the meaning of the colours there are different opinions:
• Blue and red should symbolize each the win freedom and the new time.
Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen
• Blue stands for the african heritage, and red for the struggle for independence.
Source: Flaggen-Atlas Erde
• Blue stands for the blacks and the mulattoes, red stands for the in the fight for freedom given blood.
Source: Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt
• The first blue-red flag of Haiti was vertical striped (1803), and was created by the remove of the white stripe of the French Tricolour.
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen
• Blue represents the blacks, red the mulattoes.
Source: Das farbige Flaggenlexikon
The Haitian history was marked by confrontations between blacks, whites, and mulattoes. The whites were almost killed already in the uprising of 1791. The others followed in 1805. The struggle continued between blacks and mulattoes. The blacks used red and black flags, the colors stood for "liberty or death". The mulattos had blue and red flags in use, the same colours that Toussaint l'Ouverture already used in 1803, but its flag should have worn the inscription "Liberte ou la Mort" ("Liberty or Death"). But that is unlikely, and was probably not common, because such flags with inscriptions had been very difficult to produce. The time of the Duvalier dictatorship, between 1964 and 1986, the blue-red was replaced by a black-red flag – as it has been used since 1805, and later in North Haiti – to emphasize the African heritage of the country. The colors of the flag (including the coat of arms image) are defined as follows: blue = Pantone 293, red = Pantone 032, green = Pantone 355, brown = Pantone 125, yellow = Pantone 102, grey = Pantone 430. Today is the coat of arms (placed within a white rectangle) only to find in the middle of the state and naval flag.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen,
The Observers Book of Flags,
Wikipedia (D),
Flags of the World


since 1986,
Coat of arms of Haiti,
Source, by:
Flags of the World,
Corel Draw 4

1964–1986,
Coat of arms of Haiti,
Source, by:
Flaggen und Wappen,
Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms of Haiti was designed in 1807, and was changed until today only in litte details. The today's version from the 25th of February in 1986 shows on green meadow a palm tree as well as a weapon trophy with anchors, and to the right and to the left on every side per three national flags. In the foreground id to see a white saying-ribbon with the motto "L'Union fait la Force" ("unity makes strong"). Between 1964 and 1986 the coat of arms showed black-red flags and the Liberty-Cap on the top of the palm tree was lacking.
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen

Location:
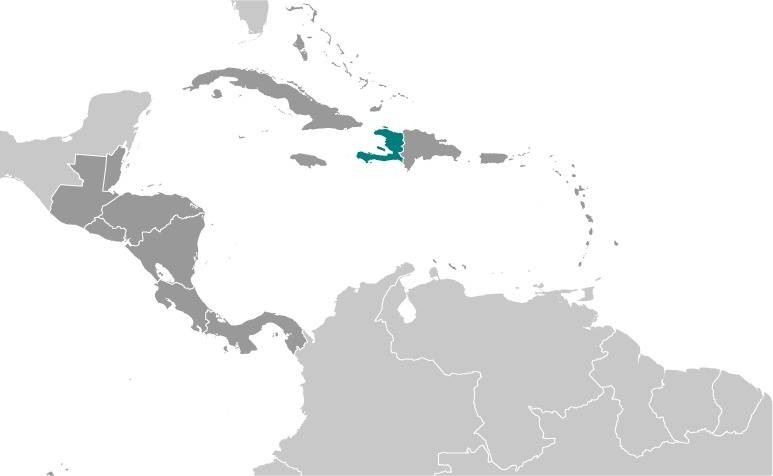
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
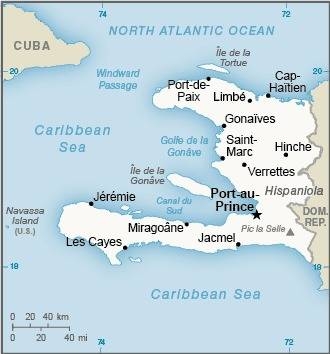
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 10.714 square miles
Inhabitants: 11.400.000 (2020), thereof 95% Afro Americans, 5% Mulattos
Religions: 55% Roman Catholic, 30% Protestant, 10% non religious
Density of Population: 1.064 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Port-au-Prince, 1.275.000 inh. (2018)
official Languages: Haitian Creole, French
Currency: 1 Gourde (HTG, Gde.) = 100 Centimes
Time Zone: GMT – 5 h
Source: World Statesmen, Wikipedia (D)

5th of December 1492 · the Spanish seafarer Christoph Columbus discovers that island on which Haiti and the Dominican Republic are today situated, and names it "La Isla Española", and appropriates it for Spain
1494 · start of the Spanish colonization
1496 · foundation of Santo Domingo (today capital of the Dominican Republic), the name of that town gets later taken over for the whole island
1500 · crown colony "Santo Domingo" under a by the Spanish King installed gouverneur
1505 · import of the first black slaves as substitute for the vanishing native Indians
17th cent. · pirates (Buccaneer and Flibusteer) settle down on the coast of the island, especially on the near Tortuga Island (Île de la Tortue), the pirates in the western part of the island stand thereby under French protection
1697 · Peace of Rijswijk, Spain has to cede the western part of the island (Saint Domingue) to France, in this way partition of the island
1791 · anti colonial revolt of the black slaves and the Mulattos in Saint Domingue under Toussaint l'Ouverture, assassinantin of the most Europeans
1794 · abolition of the slavery
1801 · Toussaint l'Ouverture becomes president of Haiti (former Saint Domingue), capture of the Spanish eastern part of the island (Santo Domingo) by the insurgents
1802 · military intervention by France, Toussaint l'Ouverture comes in French imprisonment, Dessalines gets to the successor of Toussaint l'Ouverture
1803 · Anti-French riotings, the insurgents strike the French invasors
1st of January in 1804 · Dessalines declares Haiti irrevocably for independent from France and lets proclaim itself as emperor Jacob I. of Haiti, once more intervention by France (in the east of the island)
1805 · Haiti conquers again Santo Domingo (the east of the island), the today's Dominican Republic
1806 · emperor Jakob I. gets assassinated, Blacks and Mulattos turn against each other, civil war, anarchy
1808 · Santo Domingo, the today's Dominican Republic, comes under Spanish rule again
1808 · in the south of the island arises a Mulatto republic under General J. P. Boyer
1811 · in the north lets the Black Henri Christophe crown itself for king
1820 · the southern state captures the kingdom of the Blacks in the north
1821 · the Spanish part of the island (Santo Domingo) declares its independence from Spain (Independent State of Spanish Haiti)
1822 · Santo Domingo joins the state Haiti
1843 · overthrow of J. P. Boyer by insurgent Blacks
1844 · revolt of the Mulattos in the initially Spanish part of the island, those separates as independent Republic of Santo Domingo from Haiti (→ Dominican Republic)
1844–1915 · civil war and permanent agitations in Haiti
1915 · military intervention by the USA, Haiti becomes a protectorate of the USA
1934 · withdrawal of the US-troops
1957–1971 · military dictatorship under François Duvalier
1971–1986 · military dictatorship under Jean-Claude Duvalier
1988–1990 · military government under General P. Avril
1990 · Jean-Bertrand Aristide gets elected for president
1991 · military coup d'état, Aristide goes in exile
1994 · military intervention of the USA
1995 · Arisitide gets re-appointed as president again, but at the elections get René Preval elected for president
2000 · elections, Aristide gets elected for president, withdrawal of the US-troops
2004 · Aristide gets banished by an insurrection
2004 · the country is occupied by an international intervention force (USA, France, Chile and later even Brazil), formation of a government under Latortue
from 2006 · elections, changing governments and presidencies
7th of July in 2021 · assassination of President Moïse
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (D)

The name "Haiti" comes from the Araucanian word "ahiti", which translated means "mountainous". So called the Araucanian Indians (Arawaks) once the entire island. When Columbus on the 5th of December 1492 discovered the island – on which today are placed the states Haiti and Dominican Republic – he named it "La Isla Española" (the Spanish Island), in the course of time it became "Hispaniola". The name is in use until today, although locals sometimes use the word "Kiskeya". Another name for the island was "Santo Domingo", by the in 1496 founded city. In the French part of the island it became "Saint Domingue".
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Wikipedia (D)


![]()























