mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Dominion of Canada
- parliamentary monarchy with the British monarch as chief of state
- own names:
- English: Dominion of Canada
- French: Dominion du Canada
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• Administrative Structures
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National, merchant, state flag and naval jack,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4






Common flag of the armed forces,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)




since 2013,
Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wim Schuurmann in Vlag! Nr. 13 & Wikipedia (EN)




since 2016,
Flag of the army,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




since 1982,
Flag of the air force,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




Naval jack of the coast guard,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Governor General of Canada



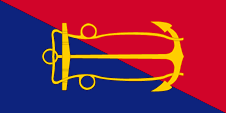
Flag of the Naval Board,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Gouvernor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1962–2022,
Flag of the Queen,
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by: Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen






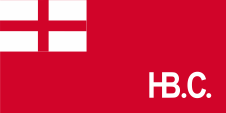
1682–1707,
Flag of the Hudson’s Bay Company,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN),
canadashistory.ca




1707–1801,
Flag of the Hudson’s Bay Company,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN),
canadashistory.ca



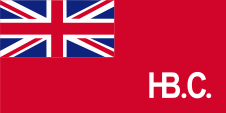
1801–1965,
Flag of the Hudson’s Bay Company,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN),
canadashistory.ca




1841–1922,
The Royal Union Flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1870–1922,
State flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




1892–1922,
National- und Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




1922–1957,
State flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




1922–1957,
National- und Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




1957–1965,
State flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




1957–1965,
National- und Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




The today's flag of Canada was officially hoisted for the first time on 15th of February in 1965. It consists in three vertical stripes in red, white and red in ratio 1:2:1. The white stripe carrys in the middle a red maple leaf. The flag portrays the position of Canada between the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean, which border the country in the west and in the east. The maple leaf is as Canadian symbol in use leastways since one hundred years and is nowadays the national landmark of Canada. The colours red and white became declared to the official colours of the country Canada by a royal patent from 21st of November in 1921. The red of the flag of Canada is precisely defined and is interpreted as CMYK 0/100/100/0 or Pantone 485. If the flags follow British specifications, the following also apply here: blue = Pantone 280, red = Pantone 186. On 5th of May in 2013 Canada had introduced a new naval flag. It corresponds to the to date valid naval jack. Until the introduction of the current flag in 1965, Canada followed the British Ensign system. Prior to that time, the national flags were plain blue or red ensigns, a single-coloured flag bunting with a representation of the flag - the British Union Jack - in the upper corner. The Union Jack indicated the ties to United Kingdom. The ensign system is still used today for official flags, the flags of the armed forces or government departments. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty.
Source:
Wim Schuurmann in Vlag! Nr. 13,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt


Coat of arms of Canada,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4

The Canadian coat of arms was adoped in the today's form on the 21st of November in 1921, likewise the colours of the country, by a royal patent of King George V. The blazon is quartered and shows the heraldry of England (three golden lions on red), Scotland (red lion on gold), Ireland (golden harp on blue) and France (three golden lilies on blue). Those four countries are the original home of a big part of the Canadian population. Until 1921 there were the coats of arms of four provinces in the quads. In the lower top of the blazon are to see three maple leafs. Its colour was changed not until the year 1957 from green into red. Shield holders are the British lion and the Scottish unicorn. The motto in the blue motto ribbon is: "A MARI VSQVE AD MARE" → "From Ocean to Ocean".
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt


1946–1965,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

since 1965,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
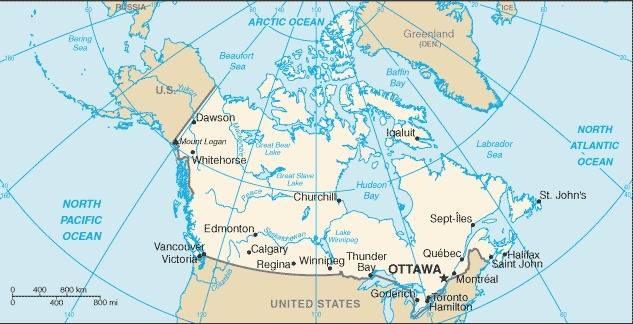
Source: CIA World Factbook
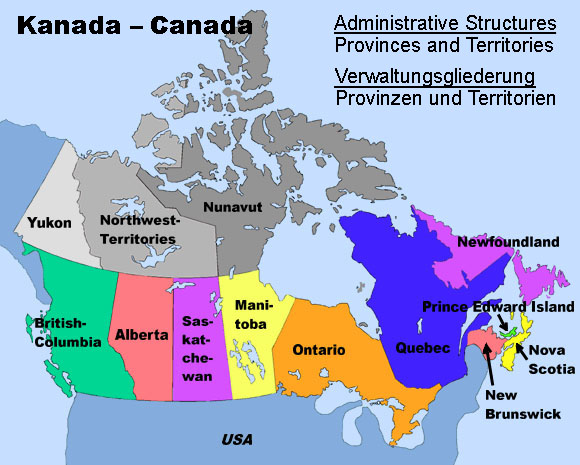
Map: Volker Preuß

Area: 3.855.085 square miles
Inhabitants: 37.000.000 (2021), thereof 32.3 % Canadians, 18.3 % Anglo-Canadians, 13.9 % Scots, 13.6 % French Canadians, 13.4 % Irish, 9.6 % German, 5.1 % Chinese, 4.4 % native Indians (mostly Cree), 4.0 % Indians, 4.0 % Ukrainians, 3.2 % Dutch, 3.1% Poles
Religions: 39% Roman Catholic, 24% Protestant, 3% Muslim, 1% Jewish, 24% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 10 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Ottawa (to 1854 Bytown), 934.243 inh. (2016)
official Languages: English, French
other Languages: German, Italian, Chinese, Cree, Eskimo (Inuktitut)
Currency: 1 Canadian Dollar (CAD, can$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 3,5 to – 8 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook


ca. 30000 years B.C. · first settlement by native tribes
ca. 1000 · Normans reach the Canadian eastern coast
1497 · Giovanni Caboto (John Cabot), an Italian seafarer in the services of England discovers Labrador, Newfoundland and Cape Breton
1534–1535 · the Frenchman Jacques Cartier explores the Saint-Lawrence-Stream and appropriates the land on both sides for France, but an attempt of colonization near the today's City of Québec failes initially
16th cent. · England, Portugal and Spain exercise fishing rights and establish momentaryly fishery bases
1576 · Martin Frobisher, an English seafarer, discovers the coast of Baffin Island
17th cent. · expeditions under Henry Hudson, William Baffin and Robert Bylot
1603–1606 · expedition of colonization by Samuel de Champlain, first settlements arise
1608 · Champlain founds Québec, summary of all French possessions in the today's Canada as "New France"
1663 · New France becomes a French crown colony
1670 · English furriers establish the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), the HBC colonizes in the afteryears whole Canada between New France, the Rocky Mountains, Labrador and the northern rand of the Hudson Bay
1679–1682 · the Frenchman La Salle explores the Great Lakes and the river Mississippi
17th–18th cent. · French colonization of the region around the Great Lakes and along the river Mississippi (Louisiana), the region northern of the Great Lakes is named Canada
1713 · Peace of Utrecht, France has to cede the today's New Brunswick, Nova Scotia and the Island of Newfoundland to United Kingdom
1763 · Peace of Paris, France has to cede all its north american possessions to United Kingdom (British Northern America), except St. Pierre and Miquelon
1775–1776 · defence of diverse attacks by anti-British rebels from New England
1783 · immigration of 35 000 loyal US-Americans
1812–1814 · defence of diverse attacks of troops of the USA
1824 · Newfoundland becomes a British crown colony
1840 · union of the provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Québec and Ontario in one colony (Kanada) with an own constitution
1855 · Newfoundland becomes a British Dominion (colony with own parliament)
1867 · establishment of the Confederation of Canada (Dominion of Canada – with an own parliament) because of demands for autonomy, confederation by the four founding provinces New Brunswick, Québec, Ontario and Nova Scotia
1869 · the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) cedes all their territorial rights and prerogatives to the British Dominion of Canada
1870 · formation of the Northwest-Territories from the former properties of the HBC, Rupertsland and Northwestern Territories, the Arctic Islands come under direct British administration
1870 · establishment of the Province of Manitoba by dividing of the Northwest Territories
1871 · British Columbia becomes a Canadian province
1876 · establishment of the Keewatin Territory by dividing off the Northwest Territories
1880 · incorporation of the Arctic Islands into the Northwest Territories
1881 · enlargement of the Province of Manitoba by annexation of territories of the Keewatin Territory
1882 · enlargement of the Province of Ontario in the northwest by annexation of parts of Western Rupertsland
1883 · establishment of the Territories Alberta, Athabaska, Saskatchewan and Assiniboia by dividing off the Northwest Territories
1895 · establishment of the District of Franklin and the District of Mackenzie within the Northwest Territories, establishment of the Ungava Territory on Labrador, of the Yukon Territory in the outer northwest by dividing off the Northwest Territories
1898 · enlargement of the Province of Quebéc in the northwest by annexation of parts of the Ungava Territory
1905 · incorporation of Keewatin as district in the Northwest Territories, Alberta and Saskatchewan get enlarged by annexion of Assiniboia and Athabaska and joined as provinces into the Dominion of Canada
1912 · enlargement of the Province of Ontario by annexation of the leftovers of Western Rupertsland, enlargement of the Province of Quebéc by annexation of the leftovers of the Ungava Territory, once again enlargement of the Province of Manitoba by annexation of the southern regions of the District of Keewatin
1914–1918 · First World War, the Dominion of Canada has to give troops for United Kingdom
1925 · extension of the borders of the Northwest Territory as sector's frontiers towards the North Pole
1st of December 1931 · Statute of Westminster, United Kingdom grants Canada full military sovereignty as well in foreign policy
1934 · Newfoundland is administrated by United Kingdom again because of economical problems
1939–1945 · the British Dominion Canada intervenes on the side of United Kingdom and the USA in the Second World War, the USA build military bases in the British Dominion of Newfoundland
1949 · Canada is founding member of the NATO, dissolution of the British control over the constitution thereby extension of the rights of the Canadian parliament
31st of March 1949 · Newfoundland joines after a plebiscite to the State of Canada as 10th province, the USA military bases stay
1950–1953 · Canada is committed on the sides of the USA in the Korean War
1968 · foundation of the Franko-Canadian and separatist Party of Québec (Parti Québécois, PQ) to achieve a full separation from Canada
1976 · victory of the Parti Québécois in Québec, demands for Québec`s independence, French becomes official language in Québec
1980 · plebiscite for independence in Québec (justly rejected)
1982 · new constitution, United Kingdom disclaims for all by British laws given power over Canada
1990 · demands for Québec`s independence
1995 · plebiscite for independence in Québec (justly rejected)
1st of April 1999 · establishment of the Eskimo Nunavut Territory with an own regional government by dividing off the Northwest Territories at the cost of the District of Keewatin, of nearly the whole District of Franklin and of large parts of the District of Mackenzie
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte,
Wikipedia (D)

The name of the country goes back to the Indians from the tribe of the Irkoese. In their language,
kanata means "village" or "settlement ." The French researcher Jacques Cartier transferred the directions to a
kanata to the whole area, which succeed successfully and very quickly as the name for the region.
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Wikipedia (D)


![]()

























































