mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Kenya
- authoritarian presidial republic with multi-party-system
- own name: Jamhuri ya Kenia
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National and merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4





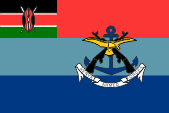
Flag of the Kenya Defense Forces,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Army,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World



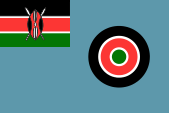
Flag of the Air Force,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)



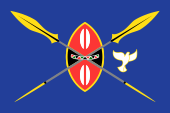
2013–2022,
Flag of the president, Uhuru Kenyatta,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Tcfc2349, CC BY-SA 4.0,
via Wikimedia Commons





1890–1895,
British East Africa,
Flag of the Imperial British East Africa Company,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1895–1921,
British East Africa,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1921–1963,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1963–1970,
Flag of the president,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)




1970–1978,
Flag of the president,
Jomo Kenyatta,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



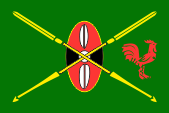
1978–2002,
Flag of the president,
Daniel Arap Moi,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



2002–2013,
Flag of the president,
Mwai Kibaki,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




Presidential colour,
presents in the military the Head of State as supreme Commander
Source, by:
Flags of the World




The flag was officially hoisted up for the first time on 12th of December in 1963 on the occasion of the independence. It has its roots in the flag of the KANU party and shows three horizontal stripes in black, red and green, each separated by a thin white stripe. The Flag shows in the middle a Massai shield and two crossed spears symbolizing the will to defend the freedom even with weapons. Shield and spears remember the saying of Jomo Kenyatta (chief of state 1964–1978) "our ancestors, which guard with this weapons our land". Black stands for the struggle for freedom, red for the Blood shed for it, Green for the vegetation of the country and white stands for Peace and Unity.
The colors red, black and green could be derived from the Garvey colors, because the color sequence of red, black and green is so named. They are those colors which were created by Markus Garvey in 1917 for the flag of the United Negro Improvement Association, which was striped in this colors. He was a supporter of the "Back-to-Africa"-Movement and saw in them the colors of a state of Blacks, which should be created in Africa. But the colors became known in the USA and in the Caribic as the colors of the Black - Power - Movement, and get in Africa only few persuasion (e.g. Malawi, Kenya, Biafra). Nevertheless this color combination is sometimes named as Panafrican Colors. Red stands for the enthusiasm and sacrifice-willingness of the people and for the in the struggle for indpendence given blood, black stands for the people and its endurance, and green for the fruitfulness of the land.
British East Africa used the British official flag (Blue Ensign) with a Badge in the flying part of the flag. It showed since 1921 a straightening (jumping) peeking red lion. In the years before was used the in 1895 introduced flag. It showed also a badge in the flying end of the flag, a golden sun with 24 rays below the British crown. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty.
With the exception of black, the colours of the Kenyan flag have their difficulties. On "Wikipedia", specifications can be found that are supposedly in the Kenya National Archives, which would be: Red = Pantone 484, Green = Pantone 7730. At "Flags of the World" similar colour specifications can be found, which would be: Red = Pantone 180, Green = Pantone 347. Both possibilities would mean a brownish red and a very light green, the flage would look like this:

In practice, these colours are not used, not even in Kenya itself. The flag images on this page are based on the colours of the flag used on the website of the UN Ambassador of Kenya and on the colour specifications of the British flag system, which are partly used in Kenya because the British Ensign system has been adopted. Thus, the air force blue would be assumed to be Pantone 549.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen-Atlas Erde,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of the World,
UNO


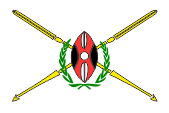
Coat of arms of Kenya,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms of the state shows on the in the colours of the country styled Massai shield an axe-swinging silvery rooster (Party-emblem of the KANU). The pedestal is Mount Kenya, on which are placed important products of the agriculture of the land. Supporters are two spear-holding lions, remembering the colonial-emblem (badge) of Kenya, a jumping lion. On the banner is placed the state-motto in Swahili, "Harambee". That means "together".
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen

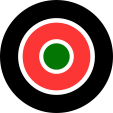
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
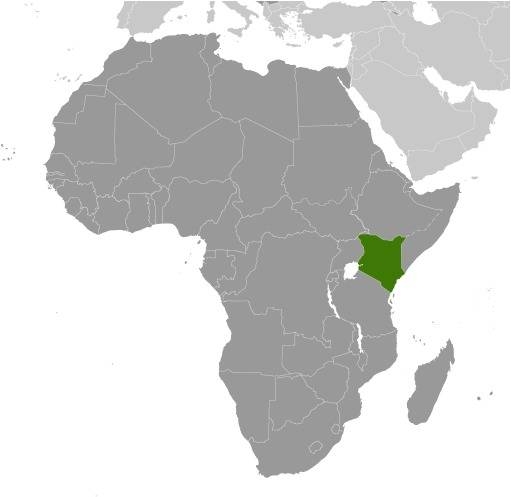
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
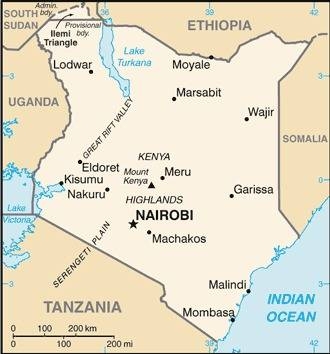
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 224.080 square miles
Inhabitants: 47.564.296 (2019), thereof 51% Bantu, 24% Nilotes, 6% Somali, 1% Indians, Pakistani, Arabs, Europeans (thereof 3.000 Germans)
Religions: 85% Christian, 11% Muslim, 0,7% Animist, 1,6% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 212 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Nairobi, 4.397.073 inh. (2019)
official Languagen: Swahili, English
other Languages: various Bantu languages
Currency: 1 Kenyan Shilling (KES, KSh) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT + 3 h
Source:
Wikipedia (EN),
Länder der Erde, Horizont - Nr. 20/1990 Artikel:"Die Auslandsdeutschen

ca. 700 · Arabs establish trade bases at the coast
1498 · the Portugese Vasco da Gama discovers the coast of Eastern Africa and embarks in the city Malindi
1505 · the Portugese conquer several coastal cities and establish trade bases in the afteryears
1696 · the Arabs banish the Portugese
1728 · the Portugese conquer several coastal cities again
1730 · the Arabs banish the Portugese once more
1837 · the Sultan of Zansibar subjects the coast of East Africa
1885 · the German Empire declares the Sultanate of Witu to a German protectorate
1887 · the Sultan of Zansibar hands the administration of the coast to the Imperial British East Africa Cooperation, United Kingdom begins with the colonization
1890 · because of the Heligoland Zansibar Treaty the German Empire has to leave the colony of German Witu
1895 · establishment of the Protectorate of British East Africa
1st of April 1905 · Uganda gets separated from British East Africa and becomes an individual colony
1920 · the hinterland of British East Africa becomes a British crown colony – the name Kenya gets used for the first time for the region, it derives from the Mount Kenya
1902–1918 · settlement by Europeans
1948 · the East African High Commision takes over – in essential parts – the administration of British East Africa
1951–1955 · Mau-Mau riotings
1960 · foundation of the KANU party
18th of may 1963 · elections, victory for the KANU
June 1963 · granting of internal self administration for British East Africa
12th of december 1963 · independence in the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations under the Premier Mzee Jomo Kenyatta
12th of december 1964 · Kenya becomes republic, but remains im the Commonwealth of Nations, Kenyatta becomes President
1969 · the opposition parties get banned
1978 · Moi becomes successor of the deceased Kenyatta
1982 · Kenya becomes one-party-state
1992 · elections within a multi-party-system
2001 · Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda agree upon the re-foundation of the in the year 1977 dissolved East African Community (EAC)
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97

The country has its name from Mount Kenya, which is 5199 meters high. The mountain was so named by its discoverer, Dr. Johann Ludwig Krapf, in 1849, because he probably misunderstood the name of the locals for the mountain "Kirinyaga" (shining mountain).
Source: Wikipedia (D)


![]()
































