mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of the Congo
- presidial republic with multi-party-system
- own name: Republique du Congo
• Flag
• Historical Flag
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
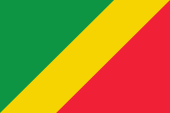
since 1959,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source: Wikipedia (D)







1969–1991,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4




The today's flag of Congo Brazzaville was already adoped in 1959. In the year 1969 it was abolished for the red flag and on 10th of June 1991 it was re-introduced again. The flag is green and red and is splited by a broad diagonal to the right side ascending yellow stripe. The combination of the colours green, yellow and red are the pan-african colours: Perhaps in 1900 was the beginning of the Panafrica-Movement, wich wants to emphasize the commons of all people with black skin. For the political unity of Africa stands the colour-triad green-yellow-red, wich used many african countries in their flags after the independence. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the origin apply the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent state in Africa. The colour green stands for nature, fruitfulness and peace, yellow for the wealth of the country and red stands for the struggle for freedom and even for the peaceful cohabitation of all peoples. There is no definition of the colors of the flag, only the color values that were deposited by the International Olympic Committee on the occasion of the 2012 Olympics: green = Pantone 355, yellow = Pantone 109, red = Pantone 32. Congo Brazzaville used during the rule of the PCT (Congolese Worker`s Party) between the 30th of december in 1969 and the 10th of June in 1991 the party-flag of the PCT, a red flag with the emblem of the state in the upper staff quadrant. Model was the flag of the Soviet Union. The red symbolized the struggle for freedom and the socialism. The colour red symbolized the struggle for freedom and socialism. The yellow star was an expression of the hope for a better future. The at the lower end crossed hammer and hoe stood for the workers and peasants, the green palm fronds for the will for peace.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen-Atlas Erde


1963–1969 and since 1991,
Coat of arms of Congo-Brazzaville,
Source: Corel Draw 4

1969–1991,
Coat of arms of Congo-Brazzaville,
Source: Corel Draw 4

The today's coat of arms was already in use between 1963 and 1969. It shows a golden shield with a red lion (the nation), which carryes a torch (freedom). In the background a green wave-line (Congo River). Supporters are two black elephants. They symbolize power and dignity and stand on a tree trunk. The shield is crowned by a stylized forest, representing am important economical factor. In a golden circlet the name of the country. Below the shield in a golden banner the motto of the country in red letters: "Unité, Travail, Progres" → "unity, work, progress". Between 1969 and 1991 was in use as coat of arms of the state an emblem, which had its roots in the socialistic PCT party. The yellow star was an expression of the hope for a better future and stands for the leading role of the only legal party (PCT). The yellow star was an expression of the hope for a better future. The at the lower end crossed hammer and hoe stood for the workers and peasants, the green palm fronds for the will for peace. The motto of the state in the white banner was: "Travail, Democratie, Paix" → "Work, Democracy, Peace".
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt


since 1991,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1969–1991,
Aircraft Roundel,
People's Republic of the Congo,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
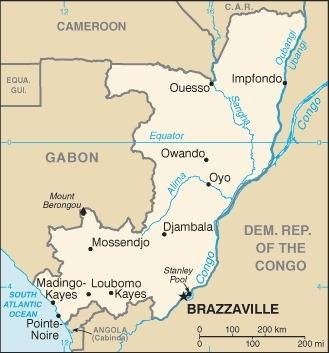
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 132.046 square miles
Inhabitants: 5.546.307 (2022), thereof 40% Kongo (Bantu), 25% Teke (Bantu), 12% Mboshi (Bantu), 11% Kuyu (Bantu), 1% Pygmies and Europeans
Religions: 33% Roman Catholic, 20% Protestant, 26% other Christians, 2% Muslim, 11% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 42 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Brazzaville, 1.827.000 inh. (2014)
official Language: French
other Languages: Lingála, Kituba ...
Currency: CFA-Franc BEAC (XAF) = 100 Centimes
Time Zone: GMT + 1 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

ca. 1400 · nascence of the Kingdom of Congo near the mouth of the Congo River, on the territory of the today's northern Angola and the southern Congo Brazzaville
1482 · the Portugese seafarer Diego Cão discovers the mouth of the Congo River
1488 · the Portugese seafarer Bartolomëu Diaz as well achieves the mouth of the Congo River, the Kingdom of Congo gets christianized in the afteryears and developes to a Portugese zone of influence
1512–1570 · Portugal submits the coast of the Congo Empire, northern the Congo River separates the people of Fiote with its Kingdom of Loango from the Congo Empire, in the hinterland northern the Congo River arises the Kingdom of Teke
1880 · the French explorer Count Pierre Savorgnan de Brazza travels in the region around the Congo River, comes to an agreement about a treaty of protection between France and the Kingdom of Teke and he founds the town Brazzaville
1883 · the Kingdom of Loango becomes a French protectorate
1886 · the Kingdoms of Teke and Loango get joined to the French Protectorate of Middle Congo
1888 · Middle Congo gets joined with French-Gaboon
1891 · Middle Congo - Gaboon gets declared to the Colony of French Congo
1910 · French Congo becomes a component of the Colony of French Equatorial Africa, now consisting of the territories Gaboon, Middle Congo (today Congo Brazzaville), Ubangi-Shari (today Central Africa) and Chad
1946 · French Equatorial Africa becomes an overseas territory, in the four territories they establish parliaments
1958 · Middle Congo becomes autonomy within the French Community
15th of August in 1960 · Middle Congo becomes independent under the name Congo Brazzaville
1963 · coup d'état
1964 · single-party-system
1969 · coup d'état, socialistic constitution, Congo Brazzaville becomes renamed in People's Republic of the Congo
1977 · coup d'état
1979 · coup d'état
1990 · re-establishment of democracy, multi-party-system
1991 · rename of the country in Republic of the Congo
1992 · new constitution, elections
1997 · coup d'état, civil war
1999 · armistice
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

"Cong" means in the language of the Bantu "Mountain". Obviously the name "Mountain" was given by the indigenous people for the whole river, indeed, its source is in the Mountains. The both Congos get popularly and officially differentiated by the supplement "Republic" or "Democratic Republic". This is not functional, because such designation could change very quickly and moreover they do not reflect the state-legal realities. The adjustment to differentiate the both Congos by attach of the name of the capital it wide spreaded, far purposefuller and is proven in the past.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()













