Kuba |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Kuba |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
National-, Handels- und Marineflagge – national, merchant and naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D)   |
 |
Gösch – jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
Flagge des Präsidenten – flag of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)  |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
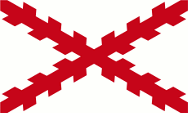 |
1538–1785, Flagge Königreich Neu-Spanien – flag of the Kingdom of New Spain, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1785–1821, Flagge Vize-Königreich Neu-Spanien – flag of the Vice-Kingdom of New Spain, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1821–1898, Flagge Spanisch-Amerika – flag of Spanish America, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die Flagge Kubas zeigt ein gleichschenkliges rotes Dreieck am Flaggenmast, mit weißem fünfzackigen Stern darin, ansonsten fünf Querstreifen in Blau und Weiß. | The flag of Cuba shows an isosceles red triangle on the flagstaff with a white five-pointed star in it, otherwise five transverse stripes in blue and white. |
| Sie wurde im Jahre 1849 – im Vergleich zu heute farblich umgekehrt – von dem venezoelanischen General Narciso López in seinem Neu Yorker Exil und in ihrer heutigen farblichen Gestaltung von dem kubanischen Dichter Miguel Teurbe Tolon für Kuba entworfen. Die Flagge wurde erstmals bei dem großen anti-spanischen Aufstand im Jahre 1850 benutzt, und am 20.05.1902 erstmals offiziell als Nationalflagge gehisst. | It was
created for Cuba in the year 1849 – in comparison to nowadays with inverted
colours – by the Venezuelan General Narciso López in his New York exile and
in it's today's arranging of colours by the Cuban poet Miguel Teurbe Tolon.
The flag was in use for the first time at the great Anti-Spanish riot in the year 1850, and officially hoisted as national flag for the first time on the 20th of May in 1902. |
| Das rote Dreieck ist ein Emblem freimaurerischer Herkunft, das für Freiheit, Gleichheit und Brüderlichkeit steht, und für das im Unabhängigkeitskampf vergossene Blut. Die drei blauen Streifen stehen für die damaligen Provinzen des Staates, Weiß für Reinheit, Gleichheit und Frieden, und der weiße Stern (La Estrella Solitaria) ist ein Symbol für Freiheit und Gleichheit, und sollte ursprünglich ausdrücken, dass den USA ein neuer Staat hinzugefügt werden sollte. Auch das Rot, Weiß und Blau sind eindeutige Bezüge auf die "Stars and Stripes". Die Flagge Kubas ist verwandt mit der Flagge von Puerto Rico. Die Buntfarben sind heute unter anderem in Pantone PMS definiert, als Rot = pt 186, Blau = pt 2765. | The red
triangle is an emblem of Masonic origin, which stands for freedom, equality
and brotherliness, und for the in the struggle for independence given blood.
The three blue stripes stand for the then provinces of the state, white
stands for purity, equality and peace, and the white star (La Estrella
Solitaria) is a symbol for freedom and equality, and should initially
express that there has to add a new state to the USA. Red, white and blue
are also clear references to the "Stars and Stripes". The flag of Cuba is related with the flag of Puerto Rico. The chromatic colors are nowadays among others defined in Pantone PMS, as red = pt 186, blue = pt 2765. |
| Während des anti-spanischen Aufstandes des Jahres 1868 wurde von Carlos Manuel de Céspedes eine andere Flagge benutzt. Sie zeigte zwei waagerechte Streifen in Weiß und Blau sowie eine rote quadratische Oberecke mit einem weißem fünfzackigen Stern darin. Sie ist noch heute auf Kuba sehr beliebt und wird von der kubanischen Marine als Gösch verwendet. | During
the Anti-Spanish riot of the year 1868 was in use an other flag by Carlos
Manuel de Cespedes. It showed two horizontal stripes in white and blue as well as a red square upper staff quadrant with a white five-pointed star in it. It is still today very popular in Cuba and is in use by the Cuban navy as jack. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Flags of the World | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
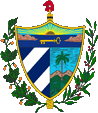 |
Wappen von Kuba – coat of arms of Cuba, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Staatswappen ist ein Entwurf des Dichters Miguel Teurbe Tolon und zeigt im Schildhaupt, mittels einem goldenen Schlüssel (aus Wappen von Havanna) unter der aufgehenden Sonne, die Lage der Insel. Darüber, als Freiheitssymbol, eine phrygische Mütze über einem Liktorenbündel, als Symbol der Autorität. Im gespaltenen Schild finden sich links Schrägbalken in Blau und Silber, und rechts eine Palmenlandschaft, als Symbol für die Agrarstruktur. | The coat
of arms is a design of the poet Miguel Teurbe Tolon and shows in the head of
the shield the position of the island by using a golden key (from the coat
of arms of Havana) below the rising sun. Above that, as symbol for freedom,
a Phrygian Cap above a Liktor's Bundle as symbol of the authority. In the
vertically halved shield are to the left slope bars in blue and silver, and on the
right a palm tree scenery as symbol for the agrarian structures. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
1955–1959, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1959–1962, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
seit/since 1962, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Die Lage des Landes – position of the Country: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| Vorzeit ·
Besiedelung durch die karibischen Indianerstämme der Guanahatabey, der
Siboney und der Taino 1492 · Entdeckung durch Christoph Kolumbus 1500 · Entdeckung des Inselcharakters des Landes durch Juan de la Cosa 1509 · Umsegelung von Kuba durch Ocampo 1511 · spanische Kolonisierung durch Diego de Velázquez, Ausrottung der karibischen Urbevölkerung bis 1532 1523 · Einfuhr von Sklaven für die Plantagenwirtschaft 1850 · anti-spanischer Aufstand 1868 · Ende des Sklavenhandels 1868–1878 · anti-spanischer Bürgerkrieg unter der Führung von Carlos Manuel de Céspedes, Sieg der Spanier 1895 · anti-spanischer Bürgerkrieg, tausende Todesopfer in spanischen Konzentrationslagern 1898 · rätselhafte Explosion des US-amerikanischen Kriegsschiffs „Maine“ vor Havanna, US-amerikanische Militärintervention, spanisch-US-amerikanischer Krieg, Frieden von Paris: Spanien muss sein Kolonialreich – und damit Kuba – zum größten Teil an die USA abtreten, die USA richten auf Kuba Militärstützpunkte ein (Guantanamobucht) 1901 · neue Verfassung 20.05.1902 · Kuba wird formell unabhängig 1906–1909 · US-amerikanische Militärintervention 1919–1924 · US-amerikanische Militärintervention 1925–1933 · Diktatur des Präsidenten Gerardo Machado 1940 · neue Verfassung 1933–1959 · Herrschaft von General F. Batista y Zaldivar 1953–1959 · Guerillakrieg der Revolutionsbewegung des Fidel Castro 01.01.1959 · Sturz von General Batista 1960 · Beginn der Wirtschaftsblockade durch die USA 1961 · Versuch einer Invasion durch Exilkubaner in der Schweinebucht (Playa Girón) 1962 · Stationierung sowjetischer Raketen, Kuba-Krise 1976 · neue Verfassung, Kuba entsendet Truppen nach Angola 1977 · Kuba entsendet vorübergehend Truppen nach Äthiopien 1991 · Abzug der kubanischen Truppen aus Angola 1992 · Verfassungsrevision 1993 · Abzug der sowjetisch/russischen Truppen aus Kuba 1994 · schwere Wirtschaftskrise in Kuba, viele Kubaner flüchten in die USA 1996 · Verschärfung der US-Sanktionen gegen Kuba durch das US-amerikanische Helms-Burton-Gesetz, die UNO verurteilt in einer Resolution das Embargo der USA gegen Kuba 1998 · Lockerung der US-Sanktionen 2014 · Lockerung der US-Sanktionen 2018 · Verschärfung der US-Sanktionen 2019 · neue Verfassung |
History: |
| distant
past · settlement by the Caribbean Indian tribes of the Guanahatabey, the
Siboney and the Taino 1492 · discovery by Christoph Columbus 1500 · discovery of the island's character of the country by Juan de la Cosa 1509 · sail round Cuba by Ocampo 1511 · Spanish colonization by Diego de Velázquez, eradication of the Caribbean natives until 1532 1523 · import of slaves for the plantation agriculture 1850 · Anti-Spanish riot 1868 · end of the slave trading 1868–1878 · Anti-Spanish civil war under the leadership of Carlos Manuel de Céspedes, victory of the Spanish 1895 · Anti-Spanish civil war, thousands of victims in Spanish concentration camps 1898 · mysterious explosion of the US-American warship „Maine“ before Havana, US-American military intervention, Spanish-US-American war, peace of Paris: Spain has to cede it's colonial empire – and in this way Cuba – to the bigest part to the USA, the USA install military bases on Cuba (Guantanamo Bay) 1901 · new constitution 20th of May 1902 · Cuba becomes formally independent 1906–1909 · US-American military intervention 1919–1924 · US-American military intervention 1925–1933 · dictatorship of the president Gerardo Machado 1940 · new constitution 1933–1959 · rule of General F. Batista y Zaldivar 1953–1959 · guerilla war of the revolutionar movement of Fidel Castro 1st of January 1959 · overthrow of General Batista 1960 · starting with the economical blockage by the USA 1961 · trial to invade by exile Cubans in the Hog Bay (Playa Girón) 1962 · deploy of soviet missiles, Cuba Crisis 1976 · new constitution, Cuba sends troops to Angola 1977 · Cuba sends momentarily troops to Ethiopia 1991 · withdrawal of the Cuban troops from Angola 1992 · constitutional revision 1993 · withdrawal of the Soviet/Russian troops from Cuba 1994 · heavy economical crisis in Cuba, many Cubans take refuge in the USA 1996 · aggravate of the US sanctions against Cuba by the US-American Helms-Burton Law, the UN condemns in a resolution the embargo of the USA against Cuba 1998 · US sanctions eased 2014 · US sanctions eased 2018 · tightening of US sanctions 2019 · new constitution |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97, Weltgeschichte |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Die Bezeichnung "Kuba" geht auf den Namen der Insel zurück, wie er von den karibischen Ureinwohnern verwendet wurde: "Cubanascnan". Er geht auf das Wort "Cubagua" zurück, was soviel heißt wie: "Ort, an dem man Gold findet". Kolumbus, der Insel 1492 entdeckte, hatte ihr zunächst den Namen "Juana" (Name der damaligen spanischen Prinzessin) gegeben, später jedoch "Fernandina" ('Ferdinand' war der Name des damaligen spanischen Königs) verwendet. Letztlich übernahm er jedoch die Bezeichnung der Eingeborenen. | The
denomination "Cuba" goes back to the name of the island how it was in use by
the Caribbean natives: "Cubanascnan". This goes back to the word "Cubagua",
what mens something like this: "place where is to find gold". Columbus, who discovered the island in 1492 gave it initially the name "Juana" (name of the then Spanish princess), but later he used "Fernandina" ('Ferdinand' was the name of the then Spanish king). However, in the end he used the denomination of the natives. |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |