mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag
![]()



















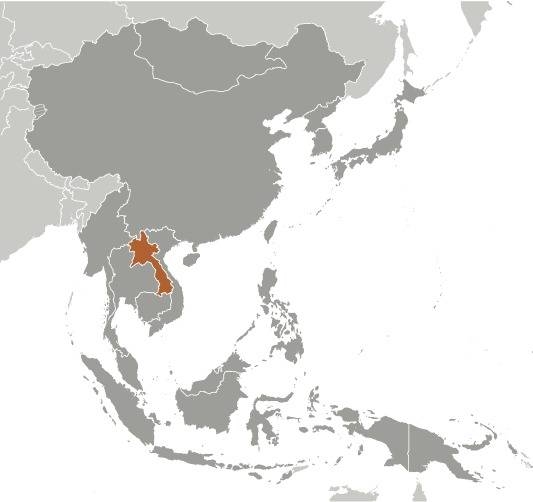
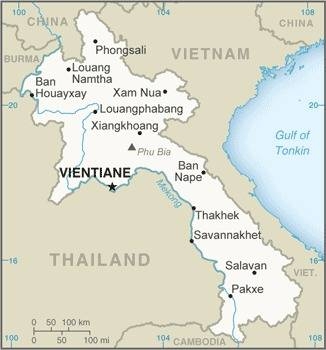
13th cent. · the Thai nation of the Lao immigrates
1353 · Prince Fa Ngum establishes the Laotian Kingdom og Lan Tshang (Lane Xang)
1641 · the Hollander Gerrit van Wuysthof explores the country as first European
1707 · Lan Tshang disintegrates into the Kingdoms of Champasak, Luang Prabang and Vientiane
1778 · Siam (Thailand) conquers the Kingdom of Champasak
1779 · Siam (Thailand) conquers the Kingdom of Luang Prabang
1828 · Siam (Thailand) conquers the Kingdom of Vientiane
1893 · France purchases from Siam (Thailand) all territories eastern the Mekong River as well as Champasak and Luang Prabang, establishes the French protectorate and summarizes all the territories under the denomination Laos
1917 · Laos becomes subordinated the General Government of Indochina
1940 · Second World War, Japan occupys Laos, France retires, Japan centralizes the country
1941 · Siam (Thailand) occupies all Laotian territories western the Mekong River
15th of April 1945 · Japan dismisses Laos as a satellite state formally in independence
12th of October 1945 · proclamation of the independence by national forces
March 1946 · intervention of French troops, establishment of the French protectorate including the territories western the Mekong River
1947 · new constitution, Laos stays French protectorate
19th of July 1949 · Laos becomes independent as a kingdom in the framework of the French Community, what means granting of internal autonomy
1950 · communist Viet-Minh troops from Vietnam start invasion in Laos and occupy until 1954 perhaps the half of the country
21st of July 1954 · Genf Indochina Conference, Laos becomes independent, all foreign troops have to leave the country, the communist guerilla continues the struggle
22nd of March 1955 · foundation of the communist LPF-Party
1958 · open civil war under influence of the USA and the Soviet Union
1961 · Genf Laos Conference, agreement between the war camps
1962 · the communist LPF-Party and its armed sprig "Pathet Lao" begin the civil war again
1971 · the Second Vietnam War expands into Laos
1973 · armistice in Laos
May 1975 · the communist LPF-Party and its guerilla troop "Pathet Lao" seize the power
2nd of December 1975 · abolition of the monarchy, proclamation of the Democratic People's Republic, foundation of the state's party LPRP out of the LPF-Party
1984–1986 · frontier quarrels with Vietnam
14th of August 1991 · new constitution
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97
The name "Laos" goes back to the Thai nation of the "Lao", which settles in this country in the 13th century.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen
The Kingdom of Champasak existed as an independent state between 1713 and 1778. After the conquest by Siam (1778), it belonged as a viceroyalty to Siam, but was little more than a province. Siam ceded the country to France in 1893. The monarchy did not end until 1946 by renunciation of the throne. Source: Wikipedia (DE)
The Kingdom of Luang Prabang existed as an independent state between 1707 and 1779. After the conquest by Siam (1779), it belonged as a viceroyalty to Siam. Luang Prabang submits itself to under the protection of France in 1877. Siam ceded the country to France in 1893. The monarchy did not end until 1949, by renunciation of the throne, but the last king, Sisavang Vong, became king of the newly created kingdom of Laos in 1959. Source: Wikipedia (DE)

1713–1904,
flag of Champasak,
Source: SodacanThis W3C-unspecified vector image was created with Inkscape. [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons

![]()

![]()
Luang Prabang
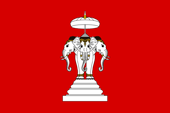
1707–1949,
flag of Luang Prabang,
Source: SodacanThis W3C-unspecified vector image was created with Inkscape. [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons

![]()

![]()
Vientiane

1707–1828,
flag of Vientiane,
Source: SodacanThis W3C-unspecified vector image was created with Inkscape. [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons

![]()

The Kingdom of Vientiane existed as an independent state between 1707 and 1828. After the conquest by Siam (1828), the kingdom was abolished. Siam ceded the area to France in 1893.
Source: Wikipedia (DE)