




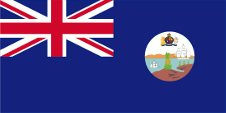
1871–1958,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




today's flag of Leeward Islands Cricket Team,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




The flag of the Leeward Islands was a so called "Blue Ensign", a dark blue flag with a flag depiction – the British Union Jack – in the upper left staff quadrant. The Union Jack pointed to the connections to
United Kingdom. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The Leeward Islands became awarded an own badge in the year 1871. It showed a pineapple at a coast with two ships. The separate colonies of the Leeward Islands had however mostly used their own "Blue Ensigns" with an own badge. The flag of the Leeward Islands was only used by the government of the colony. To this day, the Leeward Islands have their own common cricket team, which includes Saint Kitts, Nevis, Anguilla, Montserrat, British Virgin Islands, Sint Maarten, US Virgin Islands. The flags of some of these countries are united on the flag of the Leeward Islands Cricket Team.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of the World


Badge,
Source, by:
Flags of the World

The Leeward Islands became awarded an own badge in the year 1871. It showed a pineapple at a coast with two ships.
Source:
Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of the World

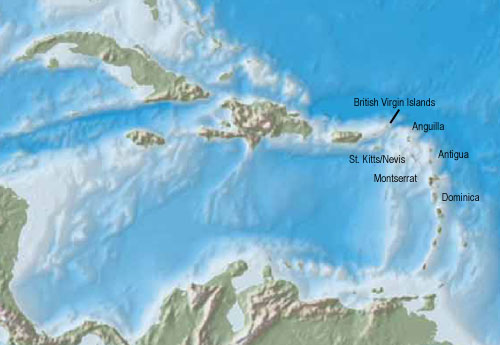
Interactive Map of the Leeward Islands:
Quelle/Source: Freeware,
University of Texas Libraries, modyfied by:
Volker Preuß

Area: 404 square miles (1939), thereof the today's states and colonies: British Virgin Islands, Anguilla, St. Kitts/Nevis, Montserrat, Antigua, Dominica (only to 1939)
Inhabitants: ca. 92.700 (1939)
Density of Population: 229 inh./sq.mi. (1939)
Main Place: Saint John's (on Antigua) 10.000 inh. (1960)
official Language: English
Currency: Pound Sterling (GBP)
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Quelle/Source:
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

1671 · establishment of the colony of the British Leeward Islands (by unification of the possessions of British Virgin Islands, Anguilla,
St. Kitts, Nevis, Montserrat, Antigua, Dominica)
1816 · dissolution of the colony
1833 · re-establishment of the colony
1871 · introduction of federal structures with limited self administration for the separate islands "Federal Colony of the Leeward Islands"
1939 · Dominica becomes excorporated out of the colony of the Leeward Islands
and affiliated to the colony of the British Windward Islands
1956 · rename in "Territory of the Leeward Islands"
1958 · the Leeward Islands become a part of the Federation of the West Indies
1st of January 1960 · dissolution of the colony in several self-contained colonies: 1.) British Virgin Islands, 2.) St. Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla, 3.) Montserrat, 4.) Antigua
Source:
Wikipedia (EN),
World Statesmen

The name "Leeward Islands" means "the leeward placed islands" (on the from the direction of the wind turned avay side). In this way the in the northern Lesser Antillas placed islands are called until today. The name has its roots in the trade winds of this geographical latitudes. In German they are called "Inseln über dem Wind" (Islands above the Wind).
Source: Volker Preuß


![]()
















![]()
![]()
