Malawi |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Malawi |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
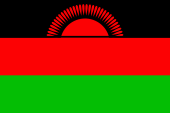 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4, Flags of the World   |
 |
Präsidentenflagge – flag of the president, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
1893–1914, British Central Africa Protectorate, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1914–1953, Njassaland / Nyasaland, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1953–1963, Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1964–2010, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4, Flags of the World   |
 |
2010–2012 (Mathurika), Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
| Die anlässlich der Unabhängigkeit Malawis am 06.07.1964 eingeführte Flagge zeigt drei waagerechte Streifen in Schwarz, Rot und Grün, mit einer aufgehenden roten Sonne im schwarzen oberen Streifen. Die Sonne hat 31 Strahlen, ein Hinweis darauf, das Malawi als 31. Staat Afrikas unabhängig wurde. | The on the occasion of the independence of Malawi on 6th of July in 1964 hoisted flag shows three horizontal stripes in black, red and green with a rising red sun in the black upper stripe. The sun has 31 rays, a hint for the fact, that Malawi became independent as the 31st state of Africa. |
| Diese Flagge wurde am 01.06.2012 erneut gehisst. Sie war schon einmal in Verwendung, und zwar vom 06.07.1964 bis 31.07.2010. Präsident Bingu wa Mathurika hatte zwischenzeitlich – und ohne besonderen Grund – eine andere Flagge eingeführt, die jedoch in der Bevölkerung keine Akzeptanz gefunden hat. Als Mathurika im April 2012 starb, sah man keine Veranlassung mehr die "Mathurika-Flagge" zu verwenden, und man kehre am 01.06.2012 zur alten Flagge von 1964 zurück. | The today's flag of Malawi was re-hoisted on 1st of June in 2012. It was already in use, from the 6th of July in 1964 to 31st of July in 2010. President Bingu wa Mathurika had in the meantime - and for no particular reason - introduced another flag, but this has found no acceptance among the population. When Mathurika died in April 2012, they saw no reason to use the "Mathurika Flag" linger, and they returned to the old flag from 1964 on 1st of June in 2012. |
| Die "Mathurika-Flagge" basierte auf der im Jahre 1964 anlässlich der Unabhängigkeit eingeführten Flagge, zeigte jedoch einige Änderungen, wobei die Bedeutung der Farben und die Symbolik beibehalten wurden. Sie zeigte drei waagerechte Streifen in Rot, Schwarz und Grün, und in der Mitte der Flagge erschien eine weiße Sonne mit 45 Strahlen. | The "Mathurika Flag" was based
on the in 1964 on the occasion of Independence introduced flag and did show
some changes, but the meaning of the colors and symbols have been retained.
|
| Rot steht für das für die Unabhängigkeit vergossene Blut, Schwarz für den afrikanischen Kontinent, Grün für die Wälder und Felder von Malawi. Die Sonne symbolisiert die Hoffnung auf eine neue und erfolgreiche Entwicklung in Afrika. Sie drückt damit den Gedanken des "Kwacha" aus, der Dämmerung eines neuen Zeitalters. Mit den Farben der Flagge von Malawi hat es – außer beim Schwarz – so seine Schwierigkeiten. Die Farbtöne werden in "British Standard Colours" angegeben, die sich nicht ohne weiteres in andere Farbsysteme übertragen lassen. Die Flaggendarstellungen auf dieser Seite orientieren sich von daher farblich an den Farben der Flagge, die auf der Webseite des UNO-Botschafters von Malawi verwendet worden sind. | Red
stands for the blood shed for independence, black for the African continent,
green for the forests and fields of Malawi. The sun symbolizes the hope for a new and successful development in Africa. It expresses the idea of "Kwacha", the dawn of a new era. With the exception of black, the colours of the Malawi flag have their difficulties. The colours are given in "British Standard Colours", which cannot easily be transferred to other colour systems. The colours of the flags on this page are therefore based on the colours of the flag used on the website of the UN Ambassador of Malawi. |
| Die heutige Nationalflagge von Malawi basiert auf der Flagge der Malawi-Kongress-Partei (MCP), die seit der Erlangung der Unabhängigkeit bis 1994 die einzige Partei des Landes war. Die Parteiflagge der MCP geht auf die von Marcus Garvey erfundene schwarze Befreiungsflagge zurück, und wurde 1953 eingeführt. Die Präsidentenflagge ist rot mit einem goldenen (britischen) Löwen, ähnlich dem im Mittelteil des Wappens. Auf einem goldenen Schriftband darunter der Landesname: "MALAWI". | The
today's
national flag of Malawi is based on the flag of the Malawi Congress Party
(MCP), which was since the achievement of the independence until 1994 the
only party of the country. The party flag of the MCP has its roots in the by
Marcus Garvey created black Liberation Flag and was introduced in 1953. The president's flag is red with a golden (British) lion, similar that in the middle part of the coat of arms. Below on a golden banner the name of the country: "MALAWI". |
| Die Farbenkomination aus Rot, Schwarz und Grün wird Garvey-Farben genannt. Es sind die Farben, die Markus Garvey 1917 für die Flagge der United Negro Improvement Association schuf und die in diesen Farben gestreift war. Er war ein Befürworter der "Zurück nach Afrika"-Bewegung und sah in diesen Farben diejenigen eines Staates für Schwarze, der in Afrika entstehen sollte. Die Farben wurden dann aber in den USA und der Karibik als diejenigen der Black-Power-Bewegung bekannt, fanden aber in Afrika nur wenig Zuspruch. Trotzem wird auch diese Farbenkombination manchmal als panafrikanische Farben bezeichnet. | The combination of the colours red, black and green is named Garvey-colours. They are those colours who created Markus Garvey in 1917 for the flag of the United Negro Improvement Association, which was striped in this colours. He was a supporter of the "Back-to-Africa"-Movement and saw in them the colours of a state for Blacks, which should be accomplished in Africa. But the colours get known in the USA and in the Caribic as the colours of the Black-Power-Movement, and get in Africa few persuasion. Nevertheless this colour-combination is sometimes named as Panafrican Colors. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen-Atlas Erde, Wikipedia (EN), Flags of the World, UNO, www.touring-afrika.de | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
seit 1964, Wappen von Malawi – coat of arms of Malawi, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
| Das Staatswappen von Malawi wurde am 30.06.1964 von Königin Elisabeth II. verliehen. Es zeigt auf dem Schild die Sonne aus dem Wappen der einstigen Kolonie Njassaland, einen Löwen als Vertreter der Tierwelt und der ehemaligen Kolonialmacht, und Wellenlinien als Symbol für den Malawisee. Als Schildhalter fungieren ein Löwe und ein Leopard. Auf dem Helm, der das Wappen krönt, ein Adler als weiterer Vertreter der Fauna des Landes. Das Schild ruht auf einem Gebirge, dem Mlanjemassiv. Unterhalb ein Schriftband mit dem Motto des Landes: "Unity and Freedom" → "Einheit und Freiheit". | The coat
of arms of Malawi was awarded by Queen Elisabeth II. on 30th of June in
1964. It shows on a shield the sun from the coat of arms of the former
colony Njassaland, a lion as deputy of the fauna and of the former colonial
might, and waves as symbol for the Malawi Sea. As shield supporters act a lion and a leopard. On the helmet – which crowns the coat of arms – an eagle as further deputy of the country's fauna. The shield rests on mountains, the Mlanje Massive. Below a banner with the motto of the country: "Unity and Freedom". |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (DE) | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
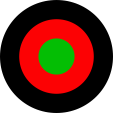 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 16./17.
Jahrhundert · Königreich Maravi 1875 · Einrichtung schottischer Missionsstationen, Beginn der Kolonialisierung durch Großbritannien 1891 · Errichtung des britischen Protektorats (Nyasaland Districts) 1893 · Umbenennung in "British Central Africa Protectorate" (Britisch-Zentralafrika) 1907 · offizielle Einführung des Namens Njassaland 1953 · Bildung der Zentralafrikanischen Föderation (Föderation Rhodesien und Njassaland) zusammen mit Rhodesien (heute Sambia und Simbabwe) 1963 · Aufhebung der Zentralafrikanischen Föderation 1959 · antikoloniale Unruhen, Verfassung 1962 · innere Autonomie 06.07.1964 · Unabhängigkeit 1966 · Umbenennung in Malawi, Proklamation der Republik, Einführung des Einparteiensystems 1971 · Präsidialdiktatur 1992 · Unruhen 1993 · nach Volksentscheid Einführung des Mehrparteiensystems |
| 16th/17th
century · Kingdom of Maravi 1875 · establishment of Scottish mission stations, beginning of the colonization by United Kingdom 1891 · establishment of the British protectorate (Nyasaland Districts) 1893 · rename in "British Central Africa Protectorate" 1907 · official introduction of the name Nyasaland 1953 · formation of the Central African Federation (Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland) together with Rhodesia (nowadays Zambia and Zimbabwe) 1963 · dissolution of the Central African Federation 1959 · anti-colonial riots, constitution 1962 · internal autonomy 6th of July 1964 · independence 1966 · rename in Malawi, proclamation of the republic, introduction of the single-party-system 1971 · presidial dictatorship 1992 · riots 1993 · after plebiscite introduction of the multi-party-system |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) |
| Der Name "Malawi" geht auf das mittelalterliche "Königreich Maravi" zurück. Der frühere Name "Njassaland" bezieht sich auf das Yao-Wort "nyasa", was "See" heißt, womit der Malawisee / Njassasee gemeint war. | The name "Malawi" has its roots in the medieval "Kingdom of Maravi". The former name "Nyasaland" refers to the Yao word "nyasa", meaning "lake", what was the Lake Malawi / Lake Nyasa. |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß, Wikipedia (DE) | |