Peru |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Peru |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4, Flaggen und Wappen   |
 |
Handelsflagge – merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4, Flaggen und Wappen   |
 |
Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4, Flaggen und Wappen |
 |
Gösch – naval jack, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, Flaggenbuch 1939 |
 |
Flagge des Präsidenten – flag of the President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, Flaggenbuch 1939 |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
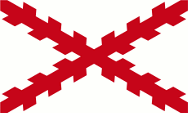 |
1542–1785, zum Spanischen Vizekönigreich Peru – to the Spanish Vice–Kingdom of Peru, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (ES)  |
 |
1785–1820, zum Spanischen Vizekönigreich Peru – to the Spanish Vice–Kingdom of Peru, Quelle/Source, nach/by: World Statesmen  |
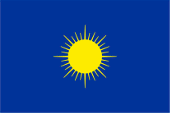 |
1820, Nationalflagge – national flag, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, World Statesmen |
 |
1820–1822, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, World Statesmen |
 |
1822, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, World Statesmen |
 |
1823–1825, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, World Statesmen |
| Die heutige Flagge Perus wurde am 25.02.1825 eingeführt. Sie zeigt drei senkrechte Streifen in Rot, Weiß und Rot. Die Nationalflagge zeigt zusätzlich den Schild des Staatswappens in der Mitte des weißen Streifens. Die Marineflagge zeigt an dieser Stelle das vollständige Staatswappen. Das Rot steht für das Blut, das für die Unabhängigkeit vergossen wurde, Weiß für Frieden und Gerechtigkeit. Die Farben der Flagge sind nicht per Gesetz festgelegt. Der Farbton des Rot scheint aus der Praxis heraus definiert zu sein, und zwar als Pantone 485. | The
today's flag of Peru was introduced on 25th of February in 1825. It shows
three vertical stripes in red, white and red. The national flag shows
further the blazon of the coat of arms in the middle of the white stripe.
The naval flag shows on this place the complete coat of arms of Peru. Red
stands for the blood which was given in the fights for the independence,
white stands for peace and justice. The colours of the flag are not defined by law. The shade of red seems to be defined by practice, as Pantone 485. |
| Die Farben gehen auf den argentinischen Generalkapitän José de San Martín (1778–1850) zurück, der im Jahre 1820 die Befreiung Chiles und Perus von der spanischen Herrschaft einleitete. Er erblickte einst eine Schar Flamingos mit roten Flügeln und weißer Brust, die über seine Soldaten der peruanischen Legion hinwegflogen, und sah darin ein günstiges Vorzeichen für seine Unternehmungen. Er wählte die Farben dieser Vögel für die Flagge seiner von Chile aus operierenden Truppen, und wenig später war sie auch beim Volk sehr beliebt. Sie war zunächst diagonal zwischen Weiß und Rot geteilt und zeigte in der Mitte ein Wappen mit der über den Anden aufgehenden Sonne. | The
colours have their roots in the Argentinian Captain General José de San
Martín (1778–1850) who initiated the liberation of Chile and Peru from the
Spanish reign in the year 1820. He saw once a swarm of flamingos with red
wings and white chest which flew over his soldiers from the Peruvian Legion.
He perceived in this a favourable omen for his ventures. He choose the
colours of this birds for the flag of his from Chile acting troops. A few
times later it was very popular in the people too. It was initially diagonally divided between white and red and showed in the middle a coat of arms with the above the Andes Mountains rising sun. |
| Im Jahre 1822 zerstritt sich José de San Martín mit dem von Norden her in das Land eindringenden Simón Bolívar (1783–1830) und verlies 1824 das Land. Möglicherweise erließ der Marquis José de Bernardo Torre-Tagle deshalb am 15.03.1822 ein Dekret, in dem die Flagge in ihrem Aussehen mehr der Flagge Argentiniens (La Plata) angeglichen wurde. In diesem Land hatte José de San Martín seinen Befreiungskampf begonnen. Die Flagge zeigte jetzt drei horizontale Streifen in den Farben Rot, Weiß und Rot mit einer strahlenden Inkasonne in der Mitte. | José de
San Martín clashed in 1822 with the from the north into the country invading
Simón Bolívar (1783–1830) and left Peru in 1824. Possibly because of that
the Marquis José de Bernardo Torre-Tagle passed a decree on 15th of March in
1822, in which the flag was assimilated in its design to the flag of
Argentina (La Plata). In that country José de San Martín started his fight
for liberation. The flag showed now three horizontal stripes in the colours red, white and red with a beaming Inca-Sun in the middle. |
| Im gleichen Jahr (nach anderen Quellen erst 1823) wurden die Streifen jedoch senkrecht angeordnet um Verwechslungen mit der Flagge Spaniens zu vermeiden. Nach den Siegen über die Spanischen Truppen im Jahre 1824 wurde am 25.02.1825 beschlossen, die Inkasonne von der Flagge zu entfernen und durch das Schild des Staatswappens von Peru zu ersetzen. | In the same year (by other sources not until 1823) the stripes however were arranged vertically to avoid confusions with the flag of Spain. After the triumphs over the Spanish troops in the year 1824 it was decided on 25th of February in 1825 to remove the Inca-Sun from the flag and to substitute it by the blazon of the coat of arms of Peru. |
| Die Flagge von Peru ist seit 1825 unverändert in Gebrauch, lediglich zwischen 1836 und 1839 unterbrochen, als Peru mit Bolivien eine Föderation bildete. Die Föderation hatte eine eigene Flagge. Sie war rot bzw. purpur und zeigte in der Mitte nebeneinander und von einem grünen Kranz umgeben die Wappen von Peru und Bolivien, oberhalb von einer Inka-Sonne dominiert. Bolivien behielt zusätzlich seine eigene Flagge. Peru wurde in Nordperu und Südperu geteilt. Nordperu verwendete weiter die bisherige Flagge von Peru, Südperu bekam eine eigene Flagge. Sie war horizontal grün-weiß gestreift und zeigte einen breiten senkrechten roten Balken am Mast, in dessen Mitte eine goldene Inkasonne platziert war, mit vier goldenen Sternen darüber. Sie standen für die vier Provinzen, aus denen Südperu gebildet wurde. |
The flag of Peru has been
in use unchanged since 1825, interrupted only between 1836 and 1839, when
Peru formed a federation with Bolivia. The federation had its own flag. It was red or purple and showed the coats of arms of Peru and Bolivia in the centre, side by side and surrounded by a green wreath, dominated above by an Inca sun. Bolivia additionally kept its own flag. Peru was divided into Northern Peru and Southern Peru. Northern Peru continued to use the previous flag of Peru, while Southern Peru got its own flag. It was horizontally striped green and white and showed a broad vertical red bar on the mast, in the middle of which a golden Inca star was placed, with four golden stars above it. They stood for the four provinces that made up Southern Peru. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (EN), Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|||
 |
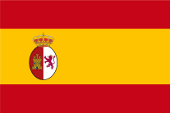
seit/since 1825, Wappen von Peru – coat of arms of Peru, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4
|
| |
| Das Staatswappen von Peru wurde, wie die Flagge, am 25.02.1825 eingeführt. Das Schild ist durch goldene Linien halbgespaltenen und geteilt. Das erste Feld zeigt ein Vikunja-Lama. Es steht für die Tierwelt des Landes. Das zweite Feld zeigt einen Chininbaum. Er repräsentiert die Pflanzenwelt. Das untere Feld zeigt ein Füllhorn. Es steht für die Bodenschätze des Landes. | The coat of arms of Peru was – like the flag – introduced on 25th of February in 1825. The blazon is semi in party per pale and party per fess by golden lines. The first field shows a Vikunja Lama. It stands for the fauna of the country. The second field shows a quinine tree. It represents the fauna. The underneath field shows a cornucopia. It stands for the mineral resources of the country. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (DE), Volker Preuß | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
Flugzeugkokarde für Marineflieger – aircraft roundel for Naval Aviation Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1250
v.Chr.–200 n.Chr. · Herausbildung lokaler Stammeskulturen (Chavin,
Cupisnique, Gallinazo, Moche, Nazca, Paracas) 1250–1450 · Herausbildung der Inka-Kultur um die Städte Machu Pichu und Cusco 1450–1530 · die Inkas erobern das gesamte Gebiet zwischen Äquator, Anden, Pazifik, und dem Kap Punta Lavapié im heutigen Chile 1531–1533 · das Reich der Inka wird von dem Spanier Francisco Pizarro erobert, Pizarro wird Statthalter und Gerneralkapitän von Peru 1535 · Francisco Pizarro Marqués de los Charcas y de los Atabillos gründet Lima 1541 · Ermordung des Francisco Pizarro 1543 · Errichtung des spanischen Vizekönigreichs Peru (ganz Südamerika außer Portugiesisch-Brasilien) 1739 · Errichtung des Vizekönigreichs Neugranada (heutiges Ekuador, Kolumbien, Panama, Venezuela) durch Abtrennung von Peru 1776 · Errichtung des Vizekönigreichs Río de la Plata (heutiges Bolivien, Paraguay, Uruguay, Nordargentinien und Rio Grande do Sul) durch Abtrennung von Peru 1780 · Aufstand der Indianer unter Tupac Amarú, dem letzten Inka 1810 · Beginn des anti-spanischen Freiheitskampfes in Südamerika (Kolumbien, Venezuela, Argentinien ...) 14.05.1811 · Proklamation der Unabhängigkeit von Spanien, Peru bleibt jedoch loyal zu Spanien 1820 · der Freiheitskämpfer José de San Martín – er hatte 1817 die spanische Herrschaft in Chile beendet – greift Peru von Süden her an 28.07.1821 · José de San Martín erobert Lima, Proklamation der Unabhängigkeit von Spanien 1822 · der Freiheitskämpfer Simón Bolívar – er hatte 1819 die spanische Herrschaft in Kolumbien endgültig beendet – greift Peru von Norden her an 1822 · José de San Martín und Simón Bolívar zerstreiten sich in der Frage "Monarchie oder Republik", um einen Bürgerkrieg zu vermeiden geht San Martín 1824 nach Frankreich ins Exil 1824 · Niederlagen der spanischen Truppen gegen Truppen von Simón Bolívar in der Schlacht von Junín und gegen Truppen seines Stellvertreters General Antonio José de Sucre in der Schlacht von Ayacucho (09.12.1824), faktische Unabhängigkeit Perus 1824–1825 · Diktatur des Simón Bolívar 1825 · Oberperu trennt sich als Bolivien mit Simón Bolívar als Diktator von Peru ab 1827 · Simón Bolívar wird zum Präsidenten von Peru und Bolivien gewählt, Bolívar setzt einen Stellvertreter ein und geht zurück nach Großkolumbien wo er kurz darauf gestürzt wird 1828–1835 · Peru versinkt in Kriegen mit Bolivien, Ekuador, Argentinien und Chile, Bürgerkrieg 1835 · Invasion durch Bolivien, Ende der Anarchie 1835–1839 · Peruanisch-Bolivianische Konföderation 1879–1883 · Salpeterkrieg gegen Chile, Peru muss die Provinz Tarapacá sowie die Gebiete um Tacna und Arica an Chile abtreten 1929 · Peru erhält das Gebiet um Tacna von Chile zurück 1930–1933 · Diktatur des Obersten L. Sánchez Cerro 1933–1939 · Diktatur des Generals Oscar Benavides 1948–1956 · Diktatur einer Militärjunta unter Manuel Orída 1962–1963 · Diktatur des Generals Pérez Godoy 1965–1966 · kommunistischer Partisanenkrieg 1968–1975 · Diktatur einer Militärjunta unter General Alvarado 1975 · die Indianersprache Ketschua wird Amtssprache (neben Spanisch) 1981 · Beginn des kommunistischen Partisanenkriegs der Bewegung "Sendero Luminoso" (Leuchtender Pfad) 1992 · Festnahme von Guzman, dem Führer des "Sendero Luminoso" 1995 · Grenzkrieg mit Ekuador 1996 · Festnahme von Camilo Santos Vera, dem neuen Führer des "Sendero Luminoso" |
| 1250
B.C.–200 A.D. · evolution of locally tribal cultures (Chavin, Cupisnique,
Gallinazo, Moche, Nazca, Paracas) 1250–1450 · evolution of the Inca-Culture around the cities Machu Pichu and Cusco 1450–1530 · the Inca conquer the whole area between equator, Andes Mountains, Pacific Ocean and Cape Punta Lavapié in the today’s Chile 1531–1533 · the Empire of the Inca becomes conquered by the Spaniard Francisco Pizarro, Pizarro becomes Governor and Captain Gerneral of Peru 1535 · Francisco Pizarro Marqués de los Charcas y de los Atabillos founds Lima City 1541 · assassination of Francisco Pizarro 1543 · establishment of the Spanish Vice-Kingdom of Peru (whole South America except Portugese Brazil) 1739 · establishment of the Vice-Kingdom of New Granada (today’s Ecuador, Colombia, Panama, Venezuela) by separation from Peru 1776 · establishment of the Vice-Kingdom of Río de la Plata (today’s Bolivia, Paraguay, Uruguay, Northern Argentina and Rio Grande do Sul) by separation from Peru 1780 · revolt of the Indians under Tupac Amarú, the Last Inca 1810 · onset of the anti-Spanish liberation fights in South America (Colombia, Venezuela, Argentina ...) 14th of May 1811 · proclamation of the independence from Spain, but Peru stands loyally to Spain 1820 · the liberation-fighter José de San Martín – in 1817 he finished the Spanish reign in Chile – attacks Peru from the south 28th of July 1821 · José de San Martín conquers Lima City, proclamation of the independence from Spain 1822 · the liberation-fighter Simón Bolívar – in 1819 he ultimately finished the Spanish reign in Colombia – attacks Peru from the north 1822 · José de San Martín and Simón Bolívar conflict in the question "monarchy or republic", to avoid a civil war San Martín exiles in 1824 to France 1824 · defeats of the Spanish troops against troops of Simón Bolívar in the battle of Junín and against troops of his Deputy General Antonio José de Sucre in the battle of Ayacucho (9th of December 1824), effective independence of Peru 1824–1825 · dictatorship of Simón Bolívar 1825 · Upper Peru separates as Bolivia from Peru with Simón Bolívar as dictator 1827 · Simón Bolívar is elected as president of Peru and Bolivia, Bolívar deploys an deputy and goes back to Great Colombia where he becomes overthrowed short times thereafter 1828–1835 · Peru goes under in wars against Bolivia, Ecuador, Argentina and Chile, civil war 1835 · invasion by Bolivia, end of the anarchy 1835–1839 · Peruvian-Bolivian confederation 1879–1883 · Saltpeter War against Chile, Peru has to cede the Province of Tarapacá as well as the areas around the towns of Tacna and Arica to Chile 1929 · Peru gets back from Chile the area around Tacna 1930–1933 · dictatorship of the Colonel L. Sánchez Cerro 1933–1939 · dictatorship of the General Oscar Benavides 1948–1956 · dictatorship of a military junta under Manuel Orída 1962–1963 · dictatorship of General Pérez Godoy 1965–1966 · communist partisan war 1968–1975 · dictatorship of a military junta under General Alvarado 1975 · the Indian language Quechua becomes an official language (besides Spanish) 1981 · onset of the communist partisan war of the Movement "Sendero Luminoso" (Glowing Path) 1992 · capture of Guzman, the leader of the "Sendero Luminoso" 1995 · frontier war with Ecuador 1996 · capture of Camilo Santos Vera, the new leader of the "Sendero Luminoso" |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Weltgeschichte, Wikipedia (D) |
| Der Name "Peru" geht auf das Wort "Biru" zurück, was in Ketschua – der Sprache der Inka – "Wasser" heißt. Ursprünglich war damit nur ein Fluss gemeint. Der Name wurde von den Spaniern auf das ganze Land übertragen. Die Inka nannten ihr Reich "Suyu". | The name "Peru" has its roots in the word "Biru" what in Quechua – the language of the Inca – means "water". Initially only a river was so called. That name was transfered by the Spaniards over the whole country. The Inca called their empire "Suyu". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen | |