
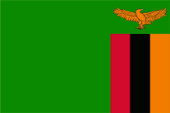
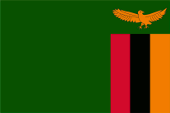
Die Flagge Sambias wurde anlässlich der Unabhängigkeit erstmals am 24.10.1964 gehisst. Das Design und auch die Farben der Nationalflagge von Sambia sind im National Flag and Armorial Ensigns Act vom 4. Juni 1965 beschrieben: Die Flagge ist grün mit einem orangefarbenen Adler im Flug über einem rechteckigen Block aus drei vertikalen Streifen, die von links nach rechts in Rot, Schwarz und Orange gefärbt sind; mit den Gesamtabmessungen 3:2; und nach folgenden Farbvorgaben: "Spectrum Green" British Colour Council Farbton Referenz 100, "Union Jack Red" British Colour Council Farbton Referenz 210, "Jet Black" British Colour Council Farbton Referenz 220, "Spectrum Orange" British Colour Council Farbton Referenz 57. Diese Farbtöne sind heute nicht mehr anwendbar. Die Farbtöne die heute verwendet werden, lassen den Schluss zu, dass es sich neben Schwarz um folgende Farben handeln könnte: Grün = Pantone 363, Rot = Pantone = 186, Orange = Pantone 716. Im Jahre 1996 wurde die Flagge Sambias leicht modifiziert. Der ursprünglich in der Flagge verwendete dunkle Grünton wurde durch ein helleres Grün ersetzt und der Adler wurde der Gestalt des Adlers im Wappen des Landes angepasst. Die Flagge basiert auf den Farben der Vereinigten Nationalen Unabhängigkeitspartei (United National Independence Party – UNIP), welche das Land in die Freiheit geführt hat, jedoch wurde das Gelb durch Orange ersetzt. Grün steht für Wälder und Felder, Rot für Freiheitskampf und Fortschritt, Schwarz für das Volk von Sambia, Orange für den Reichtum an Kupfer. Bis 1924 war Nordrhodesien im Besitz der Britisch-Südafrikanischen Gesellschaft (BSAC), und kein britisches Hoheitsgebiet. Die Flagge der BSAC zeigte den britischen Union Jack mit dem Logo der BSAC in der Mitte der Flagge auf einer weißen Scheibe. Das Logo zeigte einen goldenen Löwen der einen Elefanten-Stoßzahn in seiner rechten Pranke hielt. Er stand auf einem rot-goldenen Wulst. Darunter das Kürzel der Company: B.S.A.C. Im Jahre 1924 wurde Nordrhodesien britisches Protektorat. Man hat keine spezielle Dienstflagge eingeführt. Es wurde nur der britische Union Jack verwendet. Im Jahre 1939 wurde endlich ein Blue Ensign eingeführt. Er zeige im fliegenden Ende das 1927 verliehene Wappen. Im Jahre 1953 wurde Nordrhodesien mit Südrhodesien und Njassaland zur Zentralafrikanischen Föderation zusammengeschlossen. Die Föderation hatte eine eigene Flagge, einen Blue Ensign mit dem Wappen der Föderation im fliegenden Ende. Die Föderation wurde 1963 aufgelöst und Nordrhodesien wurde 1964 unabhängig.
Quelle:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


1927–1953,
Wappenschild von Nordrhodesien,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

1953–1963,
Wappenschild der Föderation Rhodesien und Njassaland,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

seit 1965,
Wappen von Sambia,
Quelle: Corel Draw 4

Das heutige Staatswappen wurde am 19.02.1965 eingeführt. Es zeigt einen schwarzen Schild mit weißen Wellenlinien, der von zwei Landesbewohnern gehalten wird, links ein Mann und rechts eine Frau. Oberhalb des Wappens zwei Hacken und ein orangefarbener Adler. Der Schildfuß zeigt üppige grüne Vegetation und einen Maiskolben. Darunter, in einem Spruchband, das Motto des Landes: "One Zambia, one Nation" → "Ein Sambia, eine Nation". Die Wellenlinien und der Adler gehen auf das 1927 verliehene Wappen des Protektorats Nordrhodesien zurück. Auf dem Kolonialwappen hielt er jedoch noch einen Fisch in seinen Fängen. Die Wellenlinien im Schild symbolisieren die Viktoriafälle. Die Werkzeuge über dem Schild verweisen auf den Mineralreichtum. der Adler gilt als Symbol der Freiheit und Unabhängigkeit, aber er symbolisiert auch Fähigkeit sich über die Probleme des Landes zu erheben. In der Zeit der Zentralafrikanischen Föderation, in der Nordrhodesien mit Südrhodesien und Njassaland zwischen 1953 und 1963 zusammengeschlossen war wurde das Wappen der Föderation verwendet. Dieses bestand aus einem zweimal geteilten Schild, dessen drei Teile durch einen Schwalbenschwanzschnitt voneinander getrennt waren. Im Schildhaupt eine Sonne (Njassaland), im Mittelteil ein roter Löwe (Südrhodesien) und im Schildfuß silberne Wellenlinien auf schwarzem Grund (Nordrhodesien). Der Schwalbenschwanzschnitt – eine Art Verzahnung – soll die enge Verbindung der drei Landesteile verdeutlichen.
Quelle:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Volker Preuß


Flugzeugkokarde,
Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)

Lage:
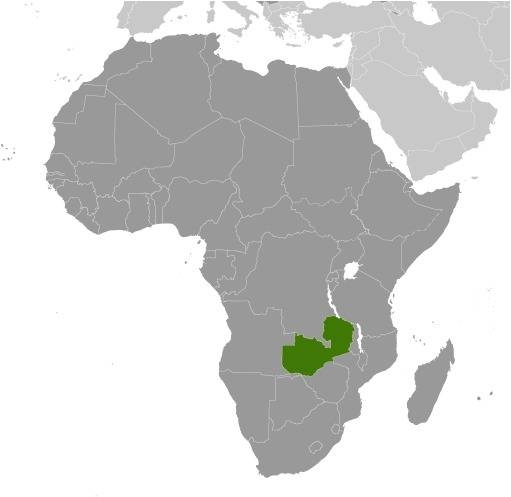
Quelle/Source: CIA World Factbook
Landkarte des Landes:
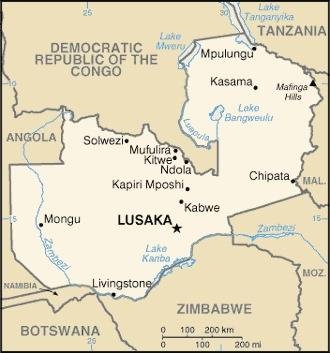
Quelle/Source: CIA World Factbook

Fläche: 752.614 km²
Einwohner: 19.610.769 (2022), davon 21% Bemba (Bantu), 14% Tonga (Bantu), 8% Tumbuka (Bantu), 7% Nyanja-Chewa (Bantu), 6% Rotse/Lozi (Bantu), und weitere bis zu 60 Völker und Stämme der Bantu, und ferner 100.000 Chinesen, 20.000 Europäer (meist Briten)
Religionen: 75% Protestanten, 20% Katholiken, 2% Animisten, 2% Nicht-Religiöse
Bevölkerungsdichte: 26 Ew./km²
Hauptstadt: Lusaka, 2.204.059 Ew. (2022)
Amtssprache: Englisch
sonstige Sprachen: Bantu-Sprachen
Währung: 1 Kwacha (K, Kw, ZMW) = 100 Ngwee
Zeitzone: MEZ + 1 h
Quelle:
Wikipedia (DE),
Wikipedia (EN)

17.–18. Jahrhundert · Besiedlung durch Bantustämme
ca. 1750 · der Norden heutigen Sambia (Nordrhodesien) wird vom Lundareich unterworfen, am oberen Sambesi bildet sich das Barotsereich
1798 · der portugiesische Entdecker Lacerda durchzieht von Mosambik aus das Gebiet des heutigen Sambia (Nordrhodesien)
1831–1832 · der portugiesische Forscher Monteiro duchzieht von Mosambik aus das Gebiet des heutigen Nordostsambia (Nordostrhodesien) und erreicht den Merusee
1840 · das Barotsereich wird von den aus Südafrika kommenden Makololo erobert und übernommen
1852–1853 · der portugiesische Händler Silva Porto duchzieht von Angola aus das Gebiet des heutigen Sambia (Nordrhodesien) und erreicht Mosambik, erste Durchquerung Zentralafrikas
1853 · der britische Forscher David Livingstone besucht Nariele, die Hauptstadt des Barotsereiches
1854–1856 · der britische Forscher David Livingstone besucht den Sambesi und entdeckt die Victoriafälle
1860–1861 · der britische Forscher David Livingstone besucht erneut den Sambesi
1866–1873 · der britische Forscher David Livingstone besucht das heutige Nordostsambia (Nordostrhodesien) und entdeckt die Quellen des Kongo und den Bangwelosee
1884–1885 · die portugiesischen Forscher Capello und Ivens duchziehen von Angola aus Zentralafrika und erreichen den Merusee, das Ziel war die Schaffung einer möglichen Landverbindung zwischen Portugiesisch-Angola und Portugiesisch-Mosambik zu prüfen
1889 · Gründung der Britischen Südafrika-Gesellschaft (British South Africa Company - BSAC) auf Initiative des britischen Politikers Cecil Rhodes, mit dem Ziel die nördlich des Flusses Transvaal gelegenen Gebiete zu erwerben und zu kolonisieren
1890 · Cecil Rhodes kommt den Portugiesen zuvor und erwirbt im Auftrag der BSAC große Ländereien nördlich und südlich des Flusses Sambesi
1891 · Königin Victoria von Großbritannien erteilt der BSAC die Konzession zur Erschließung des Landes
23.01.1894 · Bildung der BSAC-Privatkolonie "Nordsambesia" (einschließlich des Protektorats Barotseland)
03.05.1895 · die BSAC vereinigt "Nordsambesia" mit "Südsambesia" (heutiges Südrhodesien / Simbabwe) zum "Protektorat Rhodesien"
29.01.1900 · die BSAC-Verwaltung des Landes wird wieder zwischen Nordrhodesien (ehem. Nordsambesia) und Südrhodesien (ehem. Südsambesia) getrennt, Nordrhodesien wird in Nordwestrhodesien und Nordostrhodesien geteilt
1902 · Eröffnung der Blei- und Zink-Minen von Broken Hill (Kabwe)
1905–1910 · die Kap-Kongo-Eisenbahn wird gebaut und durchquert Rodesien in Nord-Süd-Richtung
17.08.1911 · Nordwestrhodesien und Nordostrhodesien werden von der BSAC wieder zu Nordrhodesien vereinigt
25.11.1918 · General Lettow-Vorbeck - der Kommandeur der deutschen Kolonialarmee - kapituliert auf Befehl der deutschen Regierung mit seinen Truppen in Abercorn
01.10.1923 · Südrhodesien wird britische Kronkolonie mit eingeschränkter Selbstverwaltung
26.04.1924 · Nordrhodesien wird britisches Protektorat
1931 · Beginn des Kupferabbaus
01.08.1953 · Nordrhodesien, Südrhodesien und Njassaland werden zur "Föderation Rhodesien und Njassaland" zusammengefasst (auch Zentralafrikanische Föderation), das von Europäern beherrschte Südrhodesien dominierte in den Folgejahren die Föderation, wogegen sich in Nordrhodesien zunehmend Widerstand formierte
1955 · große Bergarbeiterstreiks
März 1959 · Verhängung des Ausnahmezustands
1961 · Verfassungskonferenz von London
1962 · Parlamentswahlen, neue Verfassung, Regierungsbildung
31.12.1963 · Nordrhodesien tritt aus der Zentralafrikanischen Föderation aus, Auflösung der Föderation
22.01.1964 · Nordrhodesien wird innere Autonomie gewährt (Selbstverwaltung)
Mai 1964 · Verhandlungen über eine Entschädigung der BSAC bei der bevorstehenden Verstaatlichung der Bergbauminen
24.10.1964 · Nordrhodesien wird als "Republik Sambia" unabhängig
1968 · erste Wahlen nach der Unabhängigkeit
1969 · teilweise Verstaatlichung des Kupferbergbaus
1972 · Sambia wird präsidialer Einparteienstaat, die Staatspartei ist die UNIP
1973 · neue Verfassung, Verstaatlichung des Kupferbergbaus
1975 · Enteignung alles privaten Landbesitzes
1988 · Beginn einer wirtschaftlichen Krise, Reformdruck
1990 · Zulassung von Oppositionsparteien
1991 · freie Wahlen, neue Verfassung (Mehrparteiensystem)
Oktober 1997 · Putschversuch des Militärs
1998 · Verbot der meisten Oppositionsparteien
2020 · Sambia ist vorübergehend zahlungsunfähig
Quelle:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (DE)

Der Name "Sambia" geht auf den Fluss "Sambesi" zurück. Bereits 1894 wurde dem Land von den Briten der Name "Sambesia" gegeben, allerdings setzte sich schon 1895 der Name "Rhodesien" durch, der sich sich auf Cecil Rhodes, den großen Förderer des Landes bezieht.
Quelle: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()



















![]()
