mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Seychelles
- presidial republic
- own names:
– English: Republic of Seychelles
– French: République des Seychelles
– Creole: Republik Sesel
- other names:
– French: Séchelles
– German: Seschellen
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World






Flag of the President,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World





1794–1976,
Union Flag → quasi National flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






1865–1976,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations






1882–1903,
Mauritius,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1903–1961,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
LadyofHats, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons




1903–1961,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
LadyofHats, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons



1961–1976,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
LadyofHats, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons




1961–1976,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
LadyofHats, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons



1976–1977,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1976–1977,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
LadyofHats, CC0, via Wikimedia Common




1977–1996,
National flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1977–1996,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




The today’s flag of the Seychelles was introduced on 8th of January in 1996. It shows the five colours of blue, yellow, red, white and green radiating from the left lower canton of the flag. The flag should embody an ambitious and progressive nation. Blue stands for the heaven and the ocean, yellow for the sun and the light, red for the blood, the sweat and the tears of the people, white for right, justice and harmony, green for the agriculture and the vegetation. The colours of the flag apparently follow the following specifications in RGB: Blue = 0-63-135, Yellow = 252-216-86, Red = 214-40-40, Green = 0-122-61. These numerical values can be interpreted in Pantone colours as follows: Blue = pt 294, Yellow = pt 122, Red = pt 1795, Green = pt 356.
In the country's flag history, the Union Jack refers and points out to the former ties with United Kingdom. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. Since 1903, the sea flag of the authorities of the British Seychelles (Blue Ensign) has featured a badge showing a coastal landscape with a palm tree and a turtle and the country's motto "Finis Coronat Opus". In 1961, the badge was slightly modified: it became oval and showed the name of the country in addition to the motto in a surrounding border.
On land, the individual citizen and also the authorities represented their status as citizens or organs of the British nation, embodied in the United Kingdom, through the use of the Union Jack, then called the "Union Flag". At sea, the British citizen was thus provided with the British merchant flag, the Red Ensign. In a few cases, the citizens of a colony were allowed by the Admiralty to use their own Red Ensign with the colony's badge at sea. However, no such permission was available for the Seychelles.
The first flag of the independent Syechelles showed the colours od the two ruling parties of the country in the shape of blue and red triangles, separated by a white diagonal cross. Blue stood for the Democratic Party and red for the People's United Party. After a coup d’état of the People's United Party in the year 1977 was introduced a new flag on 5th of September in 1977. It showed the design of the party-flag of the People's United Party (today: Peoples Progressive Front), one red and one green horizontal stripe, separated by a white wave stripe, but without the rising sun. Red stood for progress, revolution and socialism, white for the strands and the Indian Ocean, green for the abundant flora of the islands.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of the World,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Volker Preuß


since 1996,
Coat of arms of the Seychelles,
Source: Corel Draw 4,
Wikipedia (EN)

1976–1996,
Coat of arms of the Seychelles,
Source: Corel Draw 4,
Wikipedia (EN)

1961–1976,
Badge of the Seychelles,
Source: Flags of the World,
LadyofHats, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons

1903–1961,
Badge of the Seychelles,
Source: Flags of the World,
LadyofHats, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons

The today’s coat of arms of the Seychelles was introduced on the occasion of the independence of the country on 27th of May in 1976. It has its roots in the in the year 1903 by the British king Edward VII. to the colony awarded badge, and shows on the shield a piece of land, on it a palm tree and beneath a giant turtle. In the background a island and a vessel. Above the shield a helmet with white-blue-red ribbons and above that a Faeton, a here living tropic bird. Supporters are two sailor-fishes. On the banner the Latin motto of the state: "Finis Coronat Opus" → "The end crowns the work". In 1996, some colour changes were made.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Volker Preuß


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
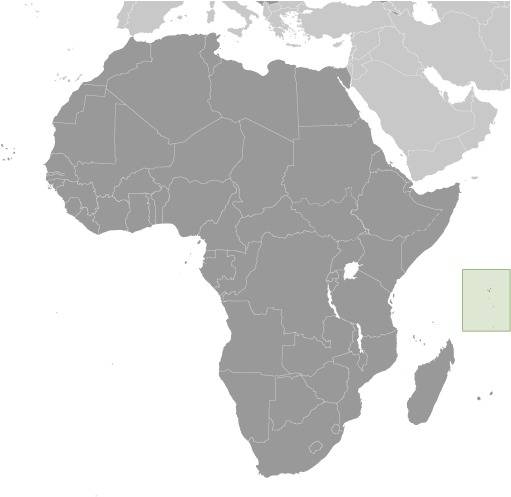
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
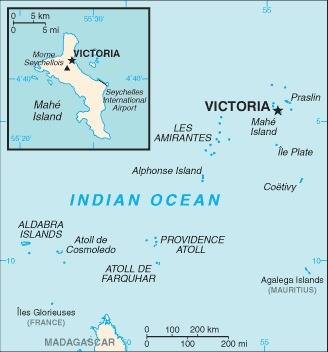
Source: CIA World Factbook
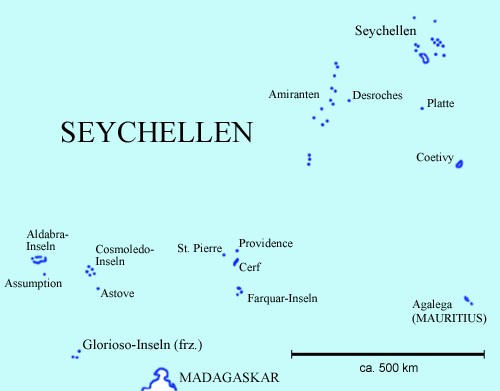
Map: Volker Preuß

Area: 176 square miles, consisting of: Seychelles Group, Amirante Islands, Assumption Island, Astove Island, Coetivy Island, Cosmoledo Islands, Providence Island, Saint Pierre Island, Cerf Island, Plate Island, Aldabra Islands and Farquhar Islands in total 115 islands, thereof 36 inhabited
Inhabitants: 99.000 (2021), thereof 91% Creoles, 4% Indians, 0,5% Madagascans, 0,5% Filipinos, 3% others, including Europeans and Africans
Religions: 76% Roman Catholic, 10% Protestants and Anglicans, 2% Hindu, 2% Muslim
Density of Population: 564 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Victoria, 26.500 inh. (2010)
official Languages: English, French, Seychellois Creole
Currency: 1 Seychellois Rupee (SCR, SR) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT + 4 h
Source:
Wikipedia (DE),
Encyclopedia Britannica Online

ca. 800 · Arabian seafarers discover the today’s Seychelles Archipelago, debark at Silhouette Island and name it "Aldabra" (The Green One)
1501 · the Portugese seafarer Vasco da Gama discovers the uninhabited islands southwestern of the today’s Seychelles Archipelago and names them "Admiral's Islands" (Amirantes), other Portuguese India-Travelers discover a little later the today’s Seychelles Archipelago and name it "As sete irmas" (The Seven Sisters), or also "Os sete irmãos" (The Seven Brethren)
1608 · the British East-India Trading Company explores and maps the uninhabited islands
1742 · Frenchman from the Île de France (Mauritius) explore the uninhabited islands
1756 · the Irish Captain Corneille Nicolas Morphey appropriates the islands for France in orders of the French King Ludvig XV. and names them by Jean Moreau de Séchelles, the royal minister of finance
1768 · the French Governor of Île de France (Mauritius), establishes with Mahé – on the likewise named island – the first housing estate on the Seychelles, installation of spice-plantations, import of black slaves from Africa
since 1770 · settlement and economic development on the islands Praslin, Silhouette, Félicité and La Digue as well as on the Amirantes Archipelago, on the Aldabra Islands an on the Farquar Islands
1794 · a British fleet appears in front of Mahé, the islands become annexed by United Kingdom, the handover prolongs until 1811, Mahé becomes renamed in Port Victoria
1812 · abolition of slavery
1814 · First Peace of Paris, End of the Coalition Wars (1813–1814) between France (Napoléon) United Kingdom, Russia, Austria, Prussia and Sweden, United Kingdom gives back some during the war occupied French colonies, but earns officially the Syechelles, that will be used from now on also as penal colony and banishment place
1882 · the Seychelles – hitherto administered from Mauritius – become a Dependence of Mauritius, get an own commissioner which however remains subordinated to the governor of Mauritius
1903 · the Seychelles become separated from Mauriritus and become a British crown colony with an own governor
1948 · the Seychelles get granted interior autonomy, election of an Island's Council
1964 · foundation of the „Seychelles People's United Party“ (SPUP) by the attorney France-Albert René, demands for independence for the Seychelles
1965 · foundation of the „Seychelles Democratic Party“ (SDP) by the attorney James Mancham, demands for a remain of the Seychelles at United Kingdom
1965 · the Aldabra Islands, the Farquar Islands, as well as the islands of Desroches, Plate and Coetivy become joined with the 1000 miles far Chagos-Archipelago to the "British Indian Ocean Territory"
1967 · first general and free elections, victory of the SDP
1970 · elections, victory of the SDP, James Mancham becomes prime minister
1974 · elections, victory of the SDP
1975 · the Seychelles get granted fully interior autonomy
28th of June 1976 · the Seychelles get granted independence within the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations, the Aldabra Islands, the Farquar Islands, as well as the islands of Desroches, Plate and Coetivy become ceded from United Kingdom to the Seychelles, James Mancham becomess president, France-Albert René becomes prime minister
7th of June 1977 · coup d’état of the People's United Party (SPUP), prime minister France-Albert René get the power as president, James Mancham goes in exile to United Kingdom
1978 · the SPUP renames in SPPF (Seychelles Peoples Progressive Front), introduction of the single-party-system
1981 · attempted coup d’état of South African mercenaries, Creole becomes recognized as official language
1991 · re-introduction of the multi-party-system
1992 · James Mancham returns to the Seychelles
1993 · constitutional reform
Source: Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

The uninhabited Seychelles-Archipelago was probably discovered in 1502 by Portuguese India-Travelers and named "As sete irmas" (The Seven Sisters), or also "Os sete irmãos" (The Seven Brethren). Already in 1501 discovered Vasco da Gama the uninhabited islands southwestern of the today’s Seychelles-Archipelago and named them "Admiral's Islands" (Amirante Islands). As the Irish Captain Corneille Nicolas Morphey appropriates the Seychelles-Archipelago for France in orders of the French King Ludvig XV. he named it by Jean Moreau de Séchelles, the royal minister of finance. The motive for that doing is not evident.
Source: www.indian-ocean.com



![]()















































