
The today’s flag of Zimbabwe was introduced on 18th of April in 1980. It shows seven narrow horizontal stripes in green, yellow, red, black, red, yellow and green, and on the pole a white, black-bordered triangle with a yellow (golden) bird on a red star in the middle. The designing of the flag has its roots in the design of the flag of the ZANU-Party, which consists of concentric fields in the colours green, yellow, red and black from outside to inside. White stands for the peace which the black government formerly aimed for with the white minority. Red, yellow and green are the Panafrican Colours, and the black points out to the black majority within the nation. The red star stands for internationalism and socialism. The colours of the present flag were summarised by the Southern African Vexillological Assosiation on 18th of April in 1980, namely: Red = Pantone 185, Yellow = Pantone 123 and Green = Pantone 348. In the years prior to this, the colours of the flags were subject to the usual British determinations, e.g. Red = Pantone 186, Blue = Pantone 280, Azure = Pantone 549 and Green = Pantone 357.
Green, yellow and red are even known as the "Panafrican colors": Perhaps in 1900 was the beginning of the Panafrica-Movement, wich wants to emphasize the commons of all people with black skin. The colour-triad green-yellow-red, wich used many african and even american countries in their flags after the independence, stands for the political unity of Africa, of all black People. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the origin apply the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent state in Africa. The golden bird is called Zimbabwe Bird or even Flash Bird. Golden reproductions of that on an pedestal sitting bird were found in 1888 in the legendary ruin-city of Zimbabwe (20 km southeastern of Fort Victoria). The Zimbabwe Bird is since 1924 a part of the heraldry of Rhodesia.
A few years after the arrival of the British, the country became a protectorate of the British South Africa Company (BSAC) in 1893, and its flag was used until 1923. The flag of the BSAC showed the British Union Jack with the emblem of the BSAC in the middle of the flag on a white disk. The emblem showed a golden lion which held an elephant tusk in its right paw. It stood on a red-golden torus. Below the shortcut of the company: B.S.A.C. On 1st of October 1923 Southern Rhodesia became a British crown colony with limited self-administration (Dominion), and that got awarded on 11th of August 1924 an own coat of arms. The shield of the coat of arms became – like sometimes usual in British colonies – added as badge into the flying end of the blue British official flag. On land, the individual citizen and also the authorities represented their status as citizens or organs of the British nation, embodied in the United Kingdom, through the use of the Union Jack, then called the "Union Flag". At sea, the British citizen was thus provided with the British merchant flag, the Red Ensign. In a few cases, the citizens of a colony were allowed by the Admiralty to use their own Red Ensign with the colony's badge at sea. However, no such permission was available for Southern Rhodesia.
United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. That badge was for Southern Rhodesia the blazon of the in 1924 awarded coat of arms. It was single-coloured green with a golden pickaxe in it. In the head of the shield a red lion between two thistles.
In the year 1953 Northern Rodesia became united with Southern Rhodesia and Nyasaland to the Central African Federation. The federation got an own flag, a Blue Ensign with the coat of arms of the federation in the flying end. The federation was dissolved on 31st of December in 1963 and Northern Rodesia became independent on 24th of October in 1964. Before the disintegration of the federation they had already prepared for the forthcoming own independence in Southern Rhodesia and already adoped a new flag on 8th of April in 1964. It showed the design of the flag of the British colony between 1924 and 1953 but the dark blue of the bunting in the blue ensign was displaced by pale blue as a sign for the independence. On 11th of November in 1968 was adoped a new flag, which should show clearlyer and better the separation from United Kingdom. It showed three vertical stripes in green, white and green and in the middle the coat of arms. Green stood for the hope and white for peace.
On 1st of June in 1979 was proclaimed the Republic of Simbabwe-Rhodesia and on the 2nd of September in 1979 was adoped a new flag. The blacks were now participated in the government and the new flag got a more colorful and more African design. It showed three horizontal stripes in red, white and green and on the leech a some broader black stripe which was separated from the rest of the flag by a narrow white line. In the upper part of the black stripe appeared a golden Zimbabwe Bird. But the Republic of Zimbabwe-Rhodesia became internationally not recognized. On 17th of April in 1980 was then proclaimed the Republic of Zimbabwe – which became internationally recognized – and on 18th of April in 1980 was introduced the today's flag.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flags of the World,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
SAVA,
Volker Preuß


Coat of arms of Zimbabwe,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1924–1953, 1963–1980,
Coat of arms of Southern Rhodesia,
Source: Corel Draw 4

1953–1963,
Blazon of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland,
Source, by: Flags of the World

The today’s coat of arms was – like the flag – inroduced on 18th of April in 1980. It shows a green shield with a reproduction of the ruins of the ancient city of Zimbabwe. In the head of the shield a silvery field with seven blue wave lines. The green stands for the natural richness which the fruitful soil of the country could produce. The blue waves stand for the vital water. Behind the shield a gun and a hoe. They should represent the transformation from struggle to productive work. Above the shield - ahead of a red five-pointed star a golden-green torus which stands for the mineral resources and the natural richness. On the torus s golden Zimbabwe Bird. The golden bird is called Zimbabwe Bird or even Flash Bird. Golden reproductions of that on an pedestal sitting bird were found in 1888 in the legendary ruin-city of Zimbabwe (12,5 miles southeastern of Fort Victoria). The Zimbabwe Bird is since 1924 a part of the heraldry of Rhodesia. Supporters are two Kudu antelopes. The blazon rests on a golden pedestal on which were presented the products of the country: grain-ears, cotton and corn. Quite below a silvery banner with the motto of the country: Unity, Freedom, Work. The coat of arms of British Southern Rhodesia was awarded to the country on 11th of August in 1924 and was valid for Rhodesia over the end of the colonial times until the 17th of April in 1980. It showed a single-coloured green shield with a golden pickaxe in it. The pickaxe stood for the mining industry and the color green for the at that time exceedingly productive and fruitful agriculture. In a silvery head of the shield was placed a red lion between two thistles. The lion and the thistles derive from the personal coat of arms of Cecil Rhodes, the founder and sponsor of the country. Above the shield was placed a helmet with golden and green blankets, on it a golden-green torse with a golden Zimbabwe Bird. Supporters of the shield had been two Sable Antelopes. The shield was placed on a green pedestal with a silvery banner. In it the Latin motto of the country: "Sit nomine digna" → "May it be worthy that name " A reminiscence to the name of Cecil Rhodes. In the times of the Central African Federation – between the years 1953 and 1963 Northern Rhodesia was united with Southern Rhodesia and Nyasaland – was in use the coat of arms of the federation. This consisted of a twice divided shield and its three parts were separated from each other by a "swallow tail cut". In the head of the shield a sun (Nyasaland), in the middle part a red lion (Southern Rhodesien) and in the lower part of the shield silvery wave-lines on black ground (Northern Rhodesia). The "swallow tail" – a kind of gearing – should express the close connexion of the three parts of the country.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Wikipedia (EN),
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Volker Preuß


1939–1954,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)
1954–1963,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

1963–1970,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)
1970–1980,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

since 1980,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
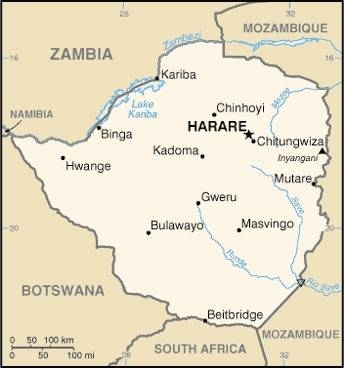
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 150.871 square miles
Inhabitants: 15.418.674 (2022), thereof 82% Shona, 14% Ndebele, 0,5% Asian and Indian, 0,22% Afrikaner (Rhodesians)
Religions: 69% Protestant, 8% Roman Catholic, 7% other Christian, 4% Animist, 0,7% Muslim, 10% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 102 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Harare (Salisbury), 2.013.048 inh. (2020)
official Languages: Chewa, Chibarwe ,English ,Kalanga ,Koisan,Nambya ,Ndau, Ndebele, Shangani, Shona, Sotho, Tonga, Tswana, Venda, Xhosa, Zimbabwean sign language
Currencies (since 2009):
• 1 Euro (EUR, €) = 100 Cent
• 1 US-Dollar (USD, $) = 100 Cent
• 1 Pound Sterling (£) = 100 Pence
• 1 South African Rand (R) = 100 Cents
• 1 Pula (BWP, P) = 100 Thebe
• 1 Australian Dollar ($A, A$, AU$, AUD) = 100 Cents
• 1 Renminbi Yuan (RMB) = 10 Jiao = 100 Fen
• 1 Indian Rupee (INR, iR) = 100 Paise
• 1 Yen (JPY, ¥) = 100 Sen
Currency (1980–2009): 1 Simbabwe-Dollar (Z§) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT + 2 h
Source: Wikipedia (EN)

Middle Ages · settlement by from the north immigrating Bantu tribes (Ndebele and Shona)
1100 · nascence of the city of Simbabwe with the legendary stone buildings
14th–15th century · to the Bantu Kingdom of Monomotapa
1837 · nascence of an Matabele-Kingdom, war against the Mashona
February 1888 · the Kingdom of the Matabele becomes as "Matabeleland" a protectorate of the British South Africa Company (BSAC)
Oktober 1888 · the British name the country "Zambesia"
1889 · the territory of the Mashona becomes as "Mashonaland" a protectorate of the British South Africa Company (BSAC)
1893 · Matabele revolt
1894 · Matabeleland and Mashonaland become summarized to "South Zambesia"
1895 · South Zambesia and North Zambesia (the today’s Zambia) become united to the Protectorate of "Rhodesia", immigration of european settlers
1896–1897 · Matabele- and Mashona revolt
1st of October 1923 · Southern Rhodesia becomes a British crown colony with limited self administration by the european settlers
1st of August 1953 · Northern Rhodesia, Southern Rhodesia and Nyasaland become merged to the "Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland" (also named Central African Federation), the by Europeans ruled Southern Rhodesia dominated in the afteryears the federation, against that arises waxing resistance in Northern Rhodesia
1960 · establishment of the ANC (African National Council), immediate interdiction
1961 · establishment of the Matabele-ZAPU-Party (Zimbabwe African People's Union)
1963 · establishment of the Mashona-ZANU-Party (Zimbabwe African National Union)
31st of December 1963 · Northern Rhodesia leaves the Central African Federation, dissolution of the federation
24th of October 1964 · Northern Rhodesia becomes independent as "Republic of Zambia"
11th of November 1965 · Southern Rhodesia declares as "Rhodesia" its independence from United Kingdom (internationally not recognized), the UNO decided to boycott Rhodesia, infliction of the state of emergency
1966 · ZANU and ZAPU start the armed struggle
2nd of March 1970 · new constitution, Rhodesia leaves the Commonwealth of Nations and becomes a republic
1976 · ZANU and ZAPU operate together in the Patriotic Front
1979 · new constitution, common and equal suffrage (with special rights for the whites), elections
1st of June 1979 · proclamation of the Republic of Zimbabwe-Rhodesia under Premier Abel Muzorewa (internationally not recognized)
10th to 21st of December 1979 · Zimbabwe-Conference in London, Lancasterhouse Agreement, negotiations between Zimbabwe-Rhodesia, United Kingdom and the Patriotic Front about cease fire, constitution and elections
12th of December 1979 · Zimbabwe-Rhodesia becomes for a momentarily period of time a British colony again
17th of April 1980 · independence, proclamation of the Republic of Zimbabwe
1987 · change of constitution, the fo whites reserved seats in the parliament become abolished, unification of the parties ZANU and ZAPU to the ZANU-PF-Party, election of Robert Mugabe to president, introduction of the single-party-system
25th of July 1990 · end of the state of emergency
1991 · economical reforms, deep social crisis
1992 · start of the expropriation of the white inhabitants
1992 · establishment of the opposition party "United Front"
1993 · corruption scandal in the government
1997 · expropriation of 1734 farms of white inhabitants, 4,6 millions hectare of arable land become divided, decline of the agricultural production, supply crisis
2000 · President Mugabe declares the white Zimbabweans to state enemies, hundreds of farms of white inhabitants become besieged and burned down, the farmers become interned and partially lynched, the land becomes divided
2001 · further decline of the agricultural production, hunger
2002 · Zimbabwe begs the UNO for food-help
2007 · the last 500 white farmers are asked to leave the country
2014 · President Mugabe declares that whites are not allowed to own land in Zimbabwe
2015 · President Mugabe sends out requests to evicted white farmers to come back
2016 · Zimbabwe asks for US$ 1.5 billion in food aid to prevent famine
2017 · Zimbabwe asks white farmers to come back to the country
14th of November in 2017 · Military coup, Mugabe resigns after impeachment trial on 21st of November
2018 · new president Mnangagwa declares Zimbabwe is lost without the white Farmers
2019 · Zimbabwe pays compensation to returning white farmers
Source: Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (EN),
World Statesmen,
reddit.com

The name of the country "Zimbabwe" derives from the about 12,5 miles southeastern of Fort Victoria situated legendary ruin-city. Its name was given by the Matabele Bantu. It means "houses made of stone". The former name "Rhodesia" resp. "Southern Rhodesia" has its roots in the British colonial politician Cecil John Rhodes (1853–1902) the founder and sponsor of the country.
Source: Atlas der wahren Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()





































![]()
