St. Kitts/Nevis |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
St. Kitts/Nevis |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
seit/since 1983, National- und Handelsflagge, national and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of all Nations   |
 |
seit/since 1983, |
 |
seit/since 1983, Flagge des Generalgouverneurs – flag of the Governor General, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
Nevis: |
|
 |
Flagge von Nevis – flag of Nevis, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of all Nations |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
|
|
|
Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts): |
|
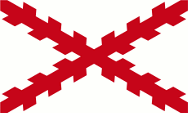 |
16./17. Jhd./cent., Die Inseln gehören zum spanischen Machtbereich – The islands belong to the Spanish sphere of influence, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
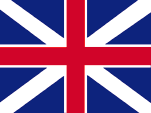 |
1620–1649, Flagge des Commonwealth von England, Schottland und Irland – flag of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen    |
 |
1625–1690, Flagge Frankreichs – flag of France, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Sodacan [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons  |
 |
1660–1707, Flagge des Commonwealth von England, Schottland und Irland – flag of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen    |
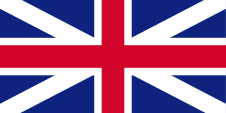 |
1707–1801, Flagge von Großbritannien – flag of United Kingdom, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen    |
 |
1801–1833, Flagge von Großbritannien – flag of United Kingdom, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)    |
|
|
|
Leeward-Inseln – Leeward Islands (1833–1958): |
|
 |
1833–1958, Union Flag → quasi Nationalflagge, Flagge von Großbritannien – flag of United Kingdom, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)    |
 |
1864–1958, |
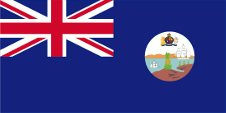 |
1871–1958, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1871–1960, Flagge des Gouverneurs – flag of the Governor, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
|
|
|
Westindische Föderation – Federation of the West Indies (1958–1962): |
|
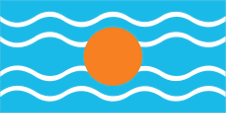 |
Flagge der Westindischen Föderation – flag of the Federation of the West Indies, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Flagge des Generalgouverneurs – flag of the Governor General, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
|
|
|
Saint Christopher, Nevis and Anguilla (1958–1967): |
|
 |
1958–1967, Union Flag → quasi Nationalflagge, Flagge von Großbritannien – flag of United Kingdom, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)    |
 |
1958–1967, |
 |
1958–1967, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1958–1967, Flagge des Gouverneurs – flag of the Governor, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1967–1971, National- und Handeslflagge – national and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1967–1971, Flagge des Gouverneurs – flag of the Governor, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
|
|
|
Saint Christopher and Nevis (1971–1983): |
|
 |
1971–1983, National- und Handeslflagge – national and merchent flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1971–1983, Flagge des Gouverneurs – flag of the Governor, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
| Die
heutige Flagge von St. Kitts und Nevis wurde von Edrice Lewis entworfen und
am 19.09.1983 anlässlich der Unabhängigkeit eingeführt. Sie zeigt einen
diagonalen, gelb gesäumten, schwarzen Streifen mit zwei weißen fünfzackigen
Sternen, ein grünes Feld links oben, und ein rotes Feld rechts unten. Das
Schwarz steht für die afrikanischen Wurzeln der meisten der Landesbewohner,
Gelb für die Sonne und Grün für die Fruchtbarkeit des Landes. Rot steht für
das Blut, das im Kampf zur Erlangung der Unabhängigkeit vergossen wurde. Die
weißen Sterne symbolisieren die beiden Inseln. Sie drücken außerdem die
Hoffnung auf Freiheit und Frieden aus. Die Farben sind wahrscheinlich nicht
definiert, das britische Verteidigungsministerium gibt in seiner Publikation
mit Vorschiftscharakter "Flags of all Nations" folgende Farben an: Grün = pt
364 c, Rot = pt 186 c, Gelb = pt 116 c. Anfänglich waren die Inseln, insbedondere St. Christopher (St. Kitts), zwischen Frankreich und England/Großbritannien umstritten. Im Vertrag von Utrecht, im Jahre 1713, bekam Großbritannien St. Christopher offiziell zugesprochen, so das ab jenem Jahr die Flagge von Großbritannien unangefochten über den Inseln wehte, die zwischen 1671 und 1816 und dann wieder ab 1833 administrativ zur britischen Kolonie der Leeward-Inseln gehörten. Die Leeward-Inseln waren somit Teil des United Kingdom, erhielten eine eigene Verwaltung und einen eigenen Gouverneur. An Land, bis 1864 auch zur See, repräsentierten der einzelne Bürger und auch die Behörden ihren Status als Bürger oder Organe des United Kingdom, durch die Verwendung des Union Jack, "Union Flag" genannt. Großbritannien hatte in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem eingeführt, in dem: • Kriegsschiffe einen sogenannten "White Ensign" (Marineflagge), eine weiße Flagge oft mit durchgehendem roten Georgskreuz und mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke, • Handelsschiffe einen "Red Ensign" (auch "Civil Ensign" → Bürgerflagge genannt, die eigentl. Handelsflagge), eine rote Flagge mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke, und • Dienstschiffe einen "Blue Ensign" (Regierungsflagge → die eigentliche Staatsflagge), eine blaue Flagge mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke führten. Seit 1865 durften Schiffe von Kolonialregierungen einen Blue Ensign mit einem Badge (Abzeichen) im fliegenden Ende verwenden. Für alle anderen Zwecke war ab diesem Zeitpunkt an Land ausschließlich der britische Union Jack zu verwenden und zur See die übliche rote britische Handelsflagge, der "Red Ensign". Wenn die britische Admiralität der Kolonie die entsprechende Erlaubnis erteilt hatte, durften Handelsschiffe und private Seeleute dieser Kolonien einen Red Ensign mit dem Bagde führen. Dies war für die Leeward-Inseln nicht der Fall. Die jeweiligen Regierungen sollten entsprechene Bagdes zur Verfügung stellen. Ein solches Badge war oft eine auf einer Scheibe platzierte regionale landschaftliche Darstellung, zeigte oft Schiffe, historische Begebenheiten oder konnte auch nur eine Art Logo sein. Sehr oft zeigte ein Badge zusätzlich den Namen des Landes oder auch einen Wahlspruch. Einige Besitzungen hatten aber auch schon von Anfang an ein Wappen, bzw. erhielten über die Jahre eine eigenes Wappen und das Badge wurde abgeschafft. Um ein weitgehend einheitliches Erscheinungsbild im fliegenden Ende der Flaggen zu gewährleisten, wurden Wappen und auch andere Symbole auf einer weißen Scheibe in der Größe der früheren Badges dargestellt. Es gab hier aber auch Ausnahmen, denn einige Kolonien verwendeten diese weiße Scheibe nicht, und platzierten ihr Wappen oder auch nur das Wappenschild - manchmal auch vergrößert - direkt auf das Flaggentuch. Schon in den 40-er Jahren wurde dazu übergegangen die weißen Scheiben zu entfernen und das Wappen direkt zu platzieren oder vergrößert dazustellen. Dieser Umstellungsprozess erfolgte allmählich, nirgendwo gleichzeitig und vollständig. In einigen britischen Besitzungen sind bis heute Flaggen mit der weißen Scheibe in Gebrauch, in anderen nicht mehr und in einigen Gebieten gibt es beide Varianten nebeneinander. Die Leeward-Inseln erhielten im Jahre 1871 ein eigenes Badge. Es zeigte eine Ananas an einer Küste mit zwei Schiffen. St. Christopher (St. Kitts), Nevis und Anguilla waren bereits 1882 innerhalb der Kolonie der Leeward-Inseln verwaltungstechnisch zu einer Kolonie vereinigt worden: Kolonie St. Christopher (St. Kitts), Nevis und Anguilla. Wahrscheinlich waren auf den einzelnen Inseln bereits eigene Siegel in Verwendung deren Bilder 1958 auf einem Wappenschild zusammengefasst wurden, als die Kolonie der Leeward-Inseln aufgelöst würde und die Kolonie St. Christopher (St. Kitts), Nevis und Anguilla eigene Hoheitszeichen verwenden durfte. Dieses Wappenschild wurde auf einer weißen Scheibe zum Badge der Kolonie, das auf einem "Blue Ensign" verwendet wurde. Das Wappenschild war dreigeteilt und zeigte die Wappenbilder der einzelnen Inseln: Kolumbus mit einem Fernrohr an Bord eines Schiffs (St. Kitts), drei Jungfrauen an einer Quelle (Nevis) und einen Eingeborenen mit seinem Boot an einer Küste (Anguilla). Gleichzeitig war die Kolonie von 1958 bis 1962 Teil der Britischen Kolonie "Westindische Föderation", ein Versuch die Verwaltung zusammenzufassen und auch den Unabhängigkeitsbestrebungen der zugehörigen Inseln und Kolonien entgegenzuwirken. Die Flagge der "Westindische Föderation" war ein hellblaues Flaggentuch mit vier waagerechten weißen Wellenlinien und einer goldenen Scheibe in der Mitte. Sie symbolisierte die Sonne über der Karibischen See. Über den Farbton des Blau ist man sich im Zweifel, es wird oft das übliche Britische Heraldikblau angenommen. Eine Zeitgenössische Beschreibung nennt jedoch ein "kaiserliches Blau" was Hellblau wäre und auch viele zeitgenössische Drucke zeigen dieses helle Blau. Am 27.02.1967 wurde durch Großbritannien innere Selbstverwaltung gewährt, und St. Kitts, Nevis und Anguilla wurden ein autonomer, mit Großbritannien assoziierter Staat. In diesem Zusammenhang wurde eine neue Flagge eingeführt, welche die Tradition der "Union Flag" und der "Blue Ensigns" beendete. Diese Flagge zeigte drei senkrechte Streifen in Grün, Gelb und Blau, und in der Mitte des gelben Streifens eine schwarze Palme mit drei Zweigen (St.Kitts, Nevis und Anguilla). Flaggen mit gleichen Farben wurden und werden auch in Grenada und in St. Vincent benutzt. Zur Unabhängigkeit am 19.09.1983 wurde dann die heutige Flagge eingeführt. Im Jahre 1971 wurde Anguilla ausgegliedert und wieder der britischen Verwaltung unterstellt und ist seit 1980 eine eigenständige Kolonie. Die Flagge von Nevis zeigt die Flagge von St. Kitts/Nevis im Obereck und im wehenden die Kontur des Vulkans Nevis Peak, der die Insel dominiert. Es gibt auch eine Variante der Flagge, die am Fuß des Vulkans einen blauen Streifen zeigt. |
The
current flag of Saint Kitts and Nevis was designed by Edrice Lewis and was
introduced on 19th of September in 1983 on the occasion of independence. It
shows a diagonal, yellow-outlined, black stripe with two white five-pointed
stars, a green field at the top left, and a red field at the bottom right.
The black represents the African roots of most of the country's inhabitants,
yellow stands for the sun and green for the fertility of the land. Red
represents the blood shed in the struggle to gain independence. The white
stars symbolize the two islands. They also express hope for freedom and
peace. The colors are probably not defined, the British Ministry of Defense states the following colors in its regulatory publication "Flags of all Nations": Green = pt 364 c, Red = pt 186 c, Yellow = pt 116 c. Initially the islands, especially Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), were disputed between France and England/United Kingdom. In the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, United Kingdom was officially awarded Saint Christopher, so that from that year on the flag of United Kingdom flew unchallenged over the islands, which became administratively part of the British Colony of the Leeward Islands between 1671 and 1816 and then again from 1833. The Leeward Islands were therefore part of the United Kingdom and received their own administration and governor. On land, and until 1864 also at sea, the individual citizen and also the authorities represented their status as citizens or organs of the United Kingdom by the use of the Union Jack, called the "Union Flag". United Kingdom had introduced a flag system in 1864 in which: • Warships use a so-called "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with a red St. George's cross throughout and with the Union Jack in the upper corner, • Merchant ships use a so-called "Red Ensign" (also called "Civil Ensign" → citizen flag, the actual merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner, and • Governmental ships use a "Blue Ensign" (flag of the government → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner. Since 1865, colonial government ships were permitted to use a Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end. From this point on, only the British Union Jack was to be used for all other purposes on land and the usual red British merchant flag, the "Red Ensign", at sea. If the British Admiralty had granted the appropriate permission to one colony, merchant ships and private sailors from this colony were allowed to use a Red Ensign with the Bagde. This was not the case for the Leeward Islands. The respective governments should provide appropriate bagdes. Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showed ships, historical events or could just be a kind of logo. Very often a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. However, some possessions had a coat of arms right from the start, or received their own coat of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. In order to ensure a largely uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk the same size as the earlier badges. But there were exceptions here, as some colonies did not use this white disk and placed their coat of arms or just the shield – sometimes enlarged – directly on the flag cloth. As early as the 1940s, the white discs were removed and the coat of arms was placed directly or enlarged. This transition process occurred gradually, never simultaneously and completely. In some British possessions flags with the white disc are still in use, in others they are no longer used and in some areas both variants exist side by side. The Leeward Islands received their own badge in 1871. It showed a pineapple on a coast with two ships. Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla had already been administratively united into one colony within the colony of the Leeward Islands in 1882: Colony of Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla. The individual islands were probably already using their own seals, the images of which were combined on a heraldic shield in 1958 when the colony of the Leeward Islands was dissolved and the colony of Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla were allowed to use their own official emblems. This heraldic shield became the colony's badge on a white disc, used on a "Blue Ensign". The escutcheon was divided into three parts and showed the heraldic images of the individual islands: Columbus with a telescope on board of a ship (Saint Kitts), three virgins at a spring (Nevis) and a native with his boat on a coast (Anguilla). At the same time, the colony was part of the British colony "West Indian Federation" from 1958 to 1962, an attempt to consolidate the administration and also to counteract the independence efforts of the associated islands and colonies. The flag of the "West Indian Federation" was a light blue flag with four horizontal white wavy lines and a golden disc in the middle. It symbolized the sun over the Caribbean Sea. There is some doubt about the color of the blue; it is often assumed to be the usual British heraldry blue. However, a contemporary description calls it an "imperial blue" which would be light blue and many contemporary prints also show this light blue. On 27th of February in 1967, United Kingdom granted internal self-government and Saint Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla became an autonomous state associated with United Kingdom. In this context, a new flag was introduced, which ended the tradition of the "Union Flag" and the "Blue Ensigns". This flag featured three vertical stripes of green, yellow and blue, and in the center of the yellow stripe a black palm tree with three branches (Saint Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla). Flags with the same colors were and are also used in Grenada and St. Vincent. The current flag was introduced on the occasion of independence on 19th of September im 1983. In 1971, Anguilla was separated and returned to British administration and has been an own colony since 1980. The flag of Nevis shows the flag of Saint Kitts/Nevis in the upper corner and in the waving end the outline of the volcano Nevis Peak, which dominates the island. There is also a variant of the flag that features a blue stripe at the base of the volcano. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flags of all Nations, Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN), Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
seit/since 1967, Wappen von Saint Kitts/Nevis – coat of arms of Saint Kitts/Nevis, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
1871–1958, Leeward-Inseln – Leeward Islands, Badge (Abzeichen) – Badge, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1958–1967, Saint Christopher, Nevis and Anguilla, Badge (Abzeichen) – Badge, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
|
Das Staatswappen von St.
Kitts und Nevis wurde am 16.02.1967 eingeführt. Das Schild zeigt in einem
blauen Schildhaupt eine Lilie, den Kopf einer Karibin und eine Tudor-Rose.
Damit wird die Geschichte der Inseln verkörpert, die in der Vergangenheit
zwischen Großbritannien und Frankreich umstritten waren. Im mittleren Teil
des Schildes, auf silbernem Grund, zwei rote Poinciana-Blüten, ein
Segelschiff und dazwischen ein roter Winkel (Sparren). Schildhalter sind
zwei Pelikane. Oberhalb des Schildes ein Helm mit gold-schwarzen Decken,
eine schwarz-blaue Wulst sowie eine Fackel, die von drei verschiedenfarbigen
Menschenarmen gehalten wird – Symbol der drei Rassen auf den Inseln. Das
Motto in dem silbernen Spruchband lautete ursprünglich "Unity and Trinity" →
"Einheit und Dreifaltigkeit". Dieses wurde zur Unabhängigkeit in "Country
above self" → "Das Land über das Selbst" geändert, ebenso wie das Schiff,
das seit 1983 anstelle von zwei Masten nur noch einen Mast hat. Das Badge (Abzeichen) der Leeward-Inseln, zu denen St. Christopher (St. Kitts), Nevis und Anguilla zwischen 1871 und 1958 gehörten, zeigte eine Ananas an einer Küste mit zwei Schiffen. St. Christopher (St. Kitts), Nevis und Anguilla waren bereits 1882 innerhalb der Kolonie der Leeward-Inseln verwaltungstechnisch zu einer Kolonie vereinigt worden: Kolonie St. Christopher (St. Kitts), Nevis und Anguilla. Wahrscheinlich waren auf den einzelnen Inseln bereits eigene Siegel in Verwendung deren Bilder 1958 auf einem Wappenschild zusammengefasst wurden, als die Kolonie der Leeward-Inseln aufgelöst würde und die Kolonie St. Christopher (St. Kitts), Nevis und Anguilla eigene Hoheitszeichen verwenden durfte. Dieses Wappenschild wurde auf einer weißen Scheibe zum Badge der Kolonie, das auf einem "Blue Ensign" verwendet wurde. Das Wappenschild war dreigeteilt und zeigte die Wappenbilder der einzelnen Inseln: Kolumbus mit einem Fernrohr an Bord eines Schiffs (St. Kitts), drei Jungfrauen an einer Quelle (Nevis) und einen Eingeborenen mit seinem Boot an einer Küste (Anguilla). |
The coat of arms of Saint
Kitts and Nevis was introduced on 16th of February in 1967. The shield shows
in a blue upper part a lily, the head of a Carib woman and a Tudor rose.
This embodies the history of the islands, which have been disputed between Britain and France in the past. In the middle part of the shield, on a silvery background, are two red poinciana flowers, a sailing ship and a red angle (chevron) between them. Supporters are two pelicans. Above the shield is a helmet with golden-black mantling, a black-blue torse and a torch held by three different colored human arms – a symbol of the three races on the islands. The motto in the silvery banner was originally "Unity and Trinity". This was changed to "Country above self" on the occasion of independence, as was the ship, which since 1983 has only one mast instead of two. The badge of the Leeward Islands, which included Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla between 1871 and 1958, showed a pineapple on a coast with two ships. Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla had already been administratively united into one colony within the colony of the Leeward Islands in 1882: Colony of Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla. The individual islands were probably already using their own seals, the images of which were combined on a heraldic shield in 1958 when the colony of the Leeward Islands was dissolved and the colony of Saint Christopher (Saint Kitts), Nevis and Anguilla were allowed to use their own official emblems. This heraldic shield became the colony's badge on a white disc, used on a "Blue Ensign". The escutcheon was divided into three parts and showed the heraldic images of the individual islands: Columbus with a telescope on board of a ship (Saint Kitts), three virgins at a spring (Nevis) and a native with his boat on a coast (Anguilla). |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN), Volker Preuß | |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1493
· der spanische Seefahrer Christoph Kolumbus entdeckt die Inseln und nennt
sie San Cristóbal (St. Christopherus, heutzutage verkürzt auf "St. Kitts")
und Santa María de las Nieves, die Inseln wurden Spanischer Besitz, jedoch
nicht kolonisiert 1620 · Inbesitznahme von Nevis durch England 1623 · Besiedlung von St. Kitts durch Engländer 1625 · Besiedlung von St. Kitts durch Franzosen 1627–1666 · St. Kitts ist zwischen England und Frankreich geteilt 1628 · Besiedlung von Nevis durch Engländer aus St. Kitts 1666–1671 · St. Kitts ist französischer Besitz 1671–1689 · St. Kitts ist zwischen England und Frankreich geteilt, der britische Besitz wird der Kolonie Leeward-Inseln angeschlossen 1689–1690 · St. Kitts ist französischer Besitz 1690 · St. Kitts wird britischer Besitz und wird wieder der Kolonie Leeward-Inseln angeschlossen 1706 · vorübergehende französische Besetzung 1713 · Vertrag von Utrecht, Großbritannien erhält St. Kitts offiziell zugesprochen 1782–1783 · vorübergehende französische Besetzung 1816 · die Kolonie Leeward-Inseln wird aufgelöst, St. Kitts wird mit Anguilla, Nevis und den Jungferninseln zusammengefasst 1833 · Neugründung der Kolonie Leeward-Inseln, bis 1958 Teil der Britischen Kolonie der Leeward-Inseln 1882 · die britischen Besitzungen St. Kitts, Nevis und Anguilla werden innerhalb der Kolonie Leeward-Inseln verwaltungstechnisch vereinigt (Kolonie St. Kitts, Nevis und Anguilla) 1958–1962 · Teil der Britischen Kolonie "Westindische Föderation" 27.02.1967 · Großbritannien gewährt innere Selbstverwaltung (Autonomie als mit Großbritannien assoziierter Staat) 1969 · Forderungen nach Unabhängigkeit auf Anguilla 1971 · Anguilla wird wieder der britischen Verwaltung unterstellt 1980 · Anguilla wird von St. Kitts/Nevis getrennt und eine eigenständige Kolonie 19.09.1983 · Großbritannien gewährt die Unabhängigkeit im Rahmen des Commonwealth of Nations, Nevis erhält jedoch eine eingeschränkte Selbstverwaltung 13.10.1997 · das Parlament von Nevis proklamiert die Unabhängigkeit der Insel, wird nicht anerkannt 10.08.1998 · eine Volksabstimmung auf Nevis für staatliche Unabhängigkeit scheitert |
|
1493
· the Spanish seafarer Christoph Columbus discovers the islands and names
them San Cristóbal (St. Christopherus, today shortend to "Saint Kitts") and
Santa María de las Nieves, the islands become a Spanish possession but were
not colonized 1620 · appropriation of Nevis by England 1623 · settlement of Saint Kitts by Englishmen 1625 · settlement of Saint Kitts by Frenchmen 1627–1666 · Saint Kitts is divided between England and France 1628 · settlement of Nevis by Englishmen from Saint Kitts 1666–1671 · Saint Kitts is French possession 1671–1689 · Saint Kitts is divided between England and France, the British possession becomes affiliated to the Leeward Islands Colony 1689–1690 · Saint Kitts is French possession 1690 · Saint Kitts becomes British possession and affiliated to the Leeward Islands Colony again 1706 · transitional French occupation 1713 · Treaty of Utrecht, United Kingdom earns Saint Kitts officially 1782–1783 · transitional French occupation 1816 · the Leeward Islands Colony becomes dissolved, Saint Kitts becomes fused with Anguilla, Nevis and the Virgin Islands 1833 · re-estbalishment of the Leeward Islands Colony, to 1958 part of the British Leeward Islands Colony 1882 · the British possessions of Saint Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla become fused within the Leeward Islands Colony (Colony of Saint Kitts, Nevis and Anguilla) 1958–1962 · part of the British colony "Federation of the West Indies" 27th of February 1967 · United Kingdom grants interior self administration (autonomy as with United Kingdom associated state) 1969 · demands for independence on Anguilla 1971 · Anguilla becomes subordinated under the British administration again 1980 · Anguilla becomes separated from Saint Kitts/Nevis and becomes a self-contained colony 19th of September 1983 · United Kingdom grants independence within the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations, but Nevis gets a limited self administration 13th of October 1997 · the parliament of Nevis proclaims the independence of the island, not recognized 10th of August 1998 · a plebiscite on Nevis for independence fails |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, World Statesmen, Wikipedia (EN) |
| Als Kolumbus im Jahre 1493 die heutige Insel St. Kitts entdeckte, nannte er sie San Cristóbal (nach anderen Quellen Isla de San Jorge). Der Name St. Christopher wird in der heutigen Zeit nur noch verkürzt wiedergegeben: "St. Kitts". | As columbus in 1493 discovered the today’s island of Saint Kitts, he named it San Cristóbal (by other sources Isla de San Jorge). The name Saint Christopher is todays only shortend in use: "Saint Kitts". |
| Als Kolumbus im Jahre 1493 die heutige Insel Nevis entdeckte, nannte er sie Santa María de las Nieves (Heilige Maria vom Schnee), weil er die Wolken am Vulkan Nevis Peak für Schnee gehalten hat. Aus "Nieves" wurde im laufe der Jahre schließlich "Nevis". | As Columbus in 1493 discovered the today’s island of Nevis, he named it Santa María de las Nieves (Saint Maria of Snow), because he thought that the clouds on the volcano Nevis Peak are snow. Through the times became "Nieves" finally to "Nevis". |
| Die Kalinago, die voreuropäischen Bewohner von St. Kitts, nannten die Insel "Liamuiga", was so viel wie "fruchtbares Land" bedeutet. | The Kalinago, the pre-European inhabitants of Saint Kitts, called the island "Liamuiga", which means "fertile land." |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN) | |