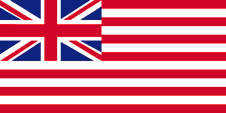
Quelle, nach: commons.wikimedia.org




1858–1946,
Union Flag → quasi Nationalflagge,
Flagge von Großbritannien,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle: Wikipedia (EN)






1867–1946,
Handelsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of all Nations






1868–1877,
Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge),
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




1868–1877,
Flagge des Gouverneurs,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



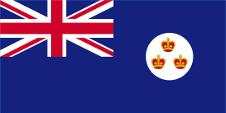
1877–1879,(?) unsicher,
Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge),
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



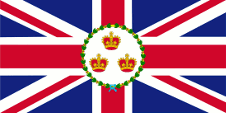
1877–1879,(?) unsicher,
Flagge des Gouverneurs,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



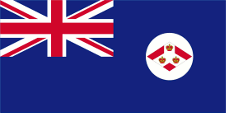
1879–1904,
Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge),
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




1879–1904,
Flagge des Gouverneurs,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



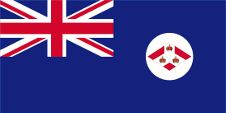
1904–1925,
Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge),
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



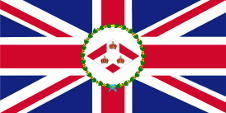
1904–1946,
Flagge des Gouverneurs,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



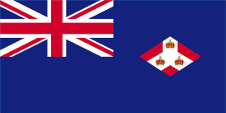
1925–1946,
Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge),
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Als die Kolonie der Straits Settlements im Jahre 1826 durch die Britische Ostindienkompanie geschaffen wurde, wurde hier deren Flagge bzw. der britische Union Jack verwendet. Die Flaggen der Ostindienkompanie zeigten seit Anfang des 17. Jahrhunderts weiße und rote Streifen, um deren Schiffe besser von anderen britischen Schiffen zu unterscheiden. Im Jahre 1867 wurden die Straits Settlements eine britische Kronkolonie. Für diese wurde eine Flagge eingeführt, wie sie damals in britischen Kolonien üblich war. Großbritannien hatte in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem eingeführt, in dem:
• Kriegsschiffe einen sogenannten "White Ensign" (Marineflagge), eine weiße Flagge oft mit durchgehendem roten Georgskreuz und mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke,
• Handelsschiffe einen "Red Ensign" (auch "Civil Ensign" → Bürgerflagge genannt, die eigentl. Handelsflagge), eine rote Flagge mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke, und
• Dienstschiffe einen "Blue Ensign" (Regierungsflagge → die eigentliche Staatsflagge), eine blaue Flagge mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke führten.
Seit 1865 durften Schiffe von Kolonialregierungen einen Blue Ensign mit einem Badge (Abzeichen) im fliegenden Ende führen. Das Badge der Straits Settlements war ein roter Rhombus mit einer weißen Deichsel, auf die drei Kronen aufgelegt waren. Diese standen für die drei Besitzungen Pinang, Malakka und Singapur. An Land repräsentierten der einzelne Bürger und auch die Behörden ihren Status als Bürger oder Organe der britischen Nation, verkörpert im United Kingdom, durch die Verwendung des Union Jack, dann „Union Flag“ genannt. Zur See war somit für den britischen Bürger die britische Handelsflagge, der Red Ensign (Rote Flagge) vorgesehen. In einigen wenigen Fällen wurde den Bürgern einer Kolonie durch die Admiralität erlaubt, auf See einen Red Ensign mit dem Badge der Kolonie zu verwenden.
Quelle:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flags of the World,
Volker Preuß


1868–1877,
Emblem (Badge) der Straits Settlements,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

1877–1879,(?) unsicher,
Emblem (Badge) der Straits Settlements,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

1879–1904,
Emblem (Badge) der Straits Settlements,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World
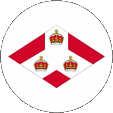
1904–1925,
Emblem (Badge) der Straits Settlements,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World
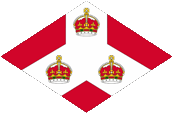
1904–1925,
Emblem (Badge) der Straits Settlements,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

1874–1942,
Wappen der Straits Settlements,
Quelle: Xavi Garcia, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons

Als die Kolonie der Straits Settlements im Jahre 1826 durch die Britische Ostindienkompanie geschaffen wurde, wurde hier deren Flagge bzw. der britische Union Jack verwendet. Die Flaggen der Ostindienkompanie zeigten seit Anfang des 17. Jahrhunderts weiße und rote Streifen, um deren Schiffe besser von anderen britischen Schiffen zu unterscheiden.
An Land, bis 1864 auch zur See, repräsentierten der einzelne Bürger und auch die Behörden ihren Status als Bürger oder Organe des United Kingdom, durch die Verwendung des Union Jack, "Union Flag" genannt. Im Jahre 1867 wurden die Straits Settlements eine britische Kronkolonie. Für diese wurde eine Flagge eingeführt, wie sie damals in britischen Kolonien üblich war.
Großbritannien hatte in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem eingeführt, in dem:
• Kriegsschiffe einen sogenannten "White Ensign" (Marineflagge), eine weiße Flagge oft mit durchgehendem roten Georgskreuz und mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke,
• Handelsschiffe einen "Red Ensign" (auch "Civil Ensign" → Bürgerflagge genannt, die eigentl. Handelsflagge), eine rote Flagge mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke, und
• Dienstschiffe einen "Blue Ensign" (Regierungsflagge → die eigentliche Staatsflagge), eine blaue Flagge mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke führten.
Seit 1865 durften Schiffe von Kolonialregierungen einen Blue Ensign mit einem Badge (Abzeichen) im fliegenden Ende verwenden. Für alle anderen Zwecke war ab diesem Zeitpunkt an Land ausschließlich der britische Union Jack zu verwenden und zur See die übliche rote britische Handelsflagge, der "Red Ensign". Wenn die britische Admiralität der Kolonie die entsprechende Erlaubnis erteilt hatte, durften Handelsschiffe und private Seeleute dieser Kolonien einen Red Ensign mit dem Bagde führen. Dies war für die Straits Settlements nicht der Fall. Die jeweiligen Regierungen sollten entsprechene Bagdes zur Verfügung stellen.
Ein solches Badge war oft eine auf einer Scheibe platzierte regionale landschaftliche Darstellung, zeigte oft Schiffe, historische Begebenheiten oder konnte auch nur eine Art Logo sein. Sehr oft zeigte ein Badge zusätzlich den Namen des Landes oder auch einen Wahlspruch. Einige Besitzungen hatten aber auch schon von Anfang an ein Wappen, bzw. erhielten über die Jahre eine eigenes Wappen und das Badge wurde abgeschafft. Um ein weitgehend einheitliches Erscheinungsbild im fliegenden Ende der Flaggen zu gewährleisten, wurden Wappen und auch andere Symbole auf einer weißen Scheibe in der Größe der früheren Badges dargestellt. Es gab hier aber auch Ausnahmen, denn einige Kolonien verwendeten diese weiße Scheibe nicht, und platzierten ihr Wappen oder auch nur das Wappenschild - manchmal auch vergrößert - direkt auf das Flaggentuch. Schon in den 40-er Jahren wurde dazu übergegangen die weißen Scheiben zu entfernen und das Wappen direkt zu platzieren oder vergrößert dazustellen. Dieser Umstellungsprozess erfolgte allmählich, nirgendwo gleichzeitig und vollständig. In einigen britischen Besitzungen sind bis heute Flaggen mit der weißen Scheibe in Gebrauch, in anderen nicht mehr und in einigen Gebieten gibt es beide Varianten nebeneinander. Das Badge der Straits Settlements war ein roter Rhombus mit einer weißen Deichsel, auf die drei Kronen aufgelegt waren. Diese standen für die drei Besitzungen Pinang, Malakka und Singapur.
Quelle: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flags of the World, Volker Preuß

interaktive Landkarten
Straits Settelements ca. 1906:
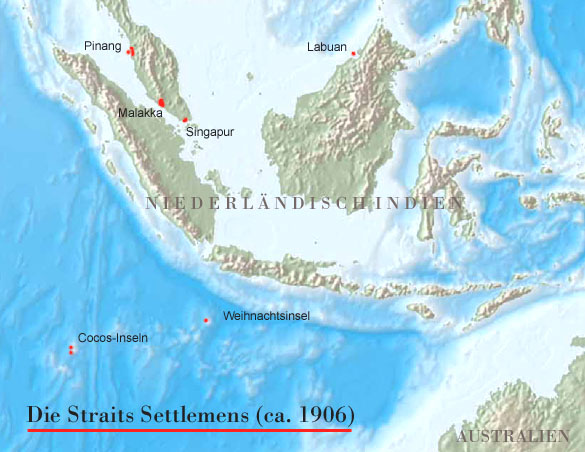
Quelle/Source: Freeware, University of Texas Libraries, modyfied by: Volker Preuß
Die Bundesstaaten Malaysias:
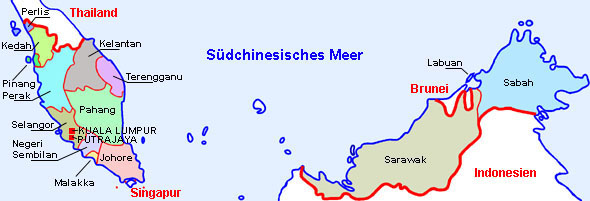
Landkarte/Map: Volker Preuß, nach/to Malaysia? → hier klicken – click here
Halbinsel Malaya:
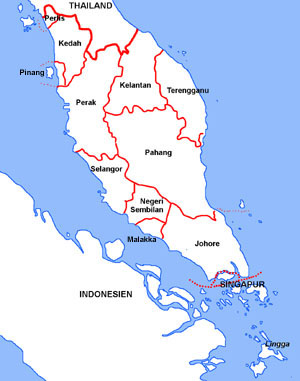
Landkarte/Map: Volker Preuß

Fläche: 3.742 km² (1887)
Einwohner: ca. 536.000 (1887)
Bevölkerungsdichte: 143 Ew./km² (1887)
Hauptstadt: Singapur, 172.993 Ew. (1881)
Amtssprache: Englisch
sonstige Sprachen: Malaiisch, Chinesisch
Währung: 1 Sovereign = 4 Crown = 8 Half Crown = 10 Florin = 20 Shilling = 60 Groat = 240 Penny = 960 Farthing = 1 Pfund Sterling
Zeitzone: MEZ + 7 h
Quelle: RetroBib Retrobibliothek, Volker Preuß

1609 · der englische Seefahrer William Keeling entdeckt die Kokosinseln
1641 · Eroberung Malakkas durch die Niederländer
1643 · der englische Seefahrer William Mynors entdeckt die Weihnachtsinsel
1685 · die Britische Ostindienkompanie erwirbt die Besitzung Benkulen an der Südküste Sumatras
1786 · der Sultan von Kedah ruft gegen Siam (Thailand) die Britische Ostindienkompanie zu Hilfe, Francis Light besetzt die Insel Pinang und baut sie zu einem Stützpunkt aus
1795 · Eroberung Malakkas durch die Britische Ostindienkompanie
1800 · die Britische Ostindienkompanie erwirbt das Festland gegenüber von Pinang (Provinz Wellesley)
1818 · erneute Eroberung Malakkas durch die Niederländer
1819 · Sir Stamford Raffles von der Britischen Ostindienkompanie (East India Company) errichtet auf der Insel Singapur eine Handelsniederlassung
1824 · britisch-niederländischer Vertrag von London zur Abgrenzung der Interessensphären im Bereich des malaiischen Archipels, die Britische Ostindienkompanie erhält Malaya und den Norden der Insel Borneo (das heutige Singapur, Malaysia und Brunei), die Niederlande erhalten das heutige Indonesien, Gebietsaustausch: die Britische Ostindienkompanie tritt Benkulen an die Niederlande ab, die Niederlande treten Malakka an die Britische Ostindienkompanie ab
03.08.1824 · Sir Stamford Raffles und John Crawfurd erwerben die Insel Singapur vom Sultan von Lingga für die Britische Ostindienkompanie
14.08.1826 · Singapur wird mit Pinang und Malakka zur Kolonie "Straits Settlements" unter der Oberhoheit der Britischen Ostindienkompanie zusammengeschlossen, Verwaltungssitz ist Gerorgetown auf Pinang
1832 · der Verwaltungssitz der Straits Settlements wird von Pinang nach Singapur verlegt
1841 · der Sultan von Brunei muss die britische Oberhoheit über sein Land anerkennen, die Insel Labuan ist zu diesem Zeitpunkt ein Bestandteil des Sultanats Brunei
1857 · die Kokosinseln werden von der Britischen Ostindienkompanie in Besitz genommen
1858 · die Verwaltung der Straits Settlements geht auf Britisch-Indien über
01.04.1867 · die Straits Settlements werden britische Kronkolonie
1870 · die Verwaltung der Kokosinseln geht auf den Britischen Gouverneur von Ceylon (Sri Lanka) über
1873 · die Britische Ostindienkompanie wird aufgelöst
1886 · die Kokosinseln werden den Straits Settlements angegliedert
1888 · Großbritannien errichtet sein Protektorat über das Sultanat Brunei
1888 · die Weihnachstinsel wird von Großbritannien in Besitz genommen und den Straits Settlements angegliedert
1906 · Labuan wird vom Sultanat Brunei abgetrennt und den Straits Settlements angegliedert
1912 · Labuan wird wieder aus den Straits Settlements ausgegliedert
1942–1945 · die Straits Settlements sind im Zweiten Weltkrieg durch japanische Truppen besetzt
01.04.1946 · das Ende der Straits Settlements: Pinang und Malakka werden der Malaiischen Union (Malaya) angeschlossen, Singapur wird eine eigene britische Kronkolonie, die Kokosinseln und die Weihnachtsinsel werden Singapur angeschlossen, Labuan kommt an Britisch-Nordborneo
01.10.1958 · die Verwaltung der Weihnachtsinsel geht auf Australien über
31.08.1963 · Großbritannien gewährt Singapur die Unabhängigkeit
16.09.1963 · Proklamation des Königreiches Malaysia durch Zusammenschluss der Malaiischen Föderation (Malaya) mit den ehemaligen britischen Kolonien Sarawak, Sabah (Nordborneo) und Singapur. Brunei lehnte den Beitritt ab und verblieb bei Großbritannien
09.08.1965 · Singapur verlässt die Föderation Malaysia
1982 · Bildung des Bundesterritoriums Labuan
Quelle: Wikipedia (EN), World Statesmen
![]()