Quelle, nach: Flags of the World





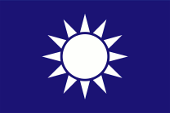
Gösch,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (EN)




Flagge der Armee,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3 (3:4, 7:8),
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Flagge für hohe Regierungsvertreter,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



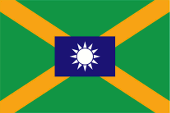
Flagge des Finanzministers,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




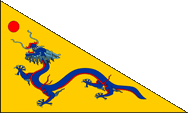
bis 1895,
Die Insel Taiwan gehört zu China,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World,
!Original:清朝政府Vector: Sodacan,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons




1895,
Flagge der "Republik Taiwan",
Seitenverhältnis = 6:7,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



1895–1945,
Die Insel Taiwan gehört zu Japan,
Seitenverhältnis = 7:10,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (EN)






1929–1986,
Flagge des Präsidenten,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




1947–1985,
Flagge des Vizepräsidenten,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




1929–1966,
Handelsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



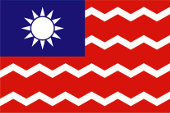
1929–1949,
Flagge der Wasserpolizei,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



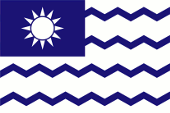
1929–1949,
Flagge der Salzverwaltung,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



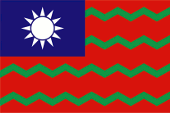
1931–1976,
Zollflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




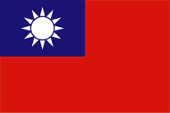
Die Flagge Taiwans ist eigentlich die Flagge der Republik China, die im Jahr 1912 als Marineflagge eingeführt wurde. Offiziell eingeführt wurde sie als chinesische Nationalflagge am 28.10.1928. Sie zeigt ein rotes Grundtuch, und trägt im blauen Obereck eine weiße zwölfstrahlige Sonne (Symbol der Guomintang-Partei). Rot ist die Nationalfarbe der Han-Chinesen, Blau symbolisiert Recht, Gleichheit und Gerechtigkeit, Weiß steht für Zusammengehörigkeit, Brüderlichkeit und Offenheit. Die Sonne symbolisiert die zwölf Doppelstunden des Tages und den Fortschritt.
Schon im Jahr 1895 hatte sich eine Reformbewegung organisiert, die chinesische Regenerationsgesellschaft. Die Flagge dieser Organisation war einfarbig blau, mit einer weißen zwölfstrahligen Sonne in der Mitte. Im Jahre 1912 wurde die nationalrepublikanische Guomindang-Partei gegründet. Die Guomindang wählten sich eine einfarbige rote Flagge mit der blauen Flagge der Regenerationsgesellschaft in der Oberecke. Die gleiche Flagge wurde schon im gleichen Jahr als chinesische Marineflagge eingeführt. In einem langen Bürgerkrieg konten sich die Guomindang im Jahre 1928 letzlich durchsetzen. Die Flagge der Guomindang wurde zur neuen Nationalflagge von China. 1937 kam es zum zweiten chinesisch-japanischen Krieg der bis 1945 andauerte. Im folgenden Bürgerkrieg, der bis 1949 dauerte, setzten sich die Kommunisten gegen die Guomindang durch und gründeten die Volksrepublik China. Die Guomindang konnten sich nach Taiwan retten, jetzt das Restgebiet der Republik China, so dass deren Flaggen auf Taiwan noch immer verwendet werden.
Aussehen und Farben der Flagge der Republik China (Taiwan) sind festgelegt in den Artikeln 3, 4 und 5 des Dekrets Nr. 47 der Nationalregierung vom 19. Dezember 1928. Es ist anzunhemen, das damals noch keine Spezifikationen in Richtung der Farbtöne vorgenommen worden sind. Insofern sind sie wahrscheinlich nicht definiert. Jedoch wurden, wie sich auf der Webseite 'Flags of the World' finden lässt, zu den Olympischen Spielen 2012 in London von Seiten Taiwans Farbwerte zur Verfügung gestellt, um die Flaggen zu Olypiade in korrekten Farben dazustellen. Es wurden folgende Farbtöne definiert: Blau = Pantone 2748, Hellblau = Pantone 3005, Rot = Pantone 485, Rosa = Pantone 192, Gelb = Pantone 137, Grün = Pantone 355.
Die meisten Sonderflaggen wurden im Zeitraum 1949 bis 1966 abgeschafft. So zuletzt die Handelsflagge mit den gelben Zickzacklinien. In der zugehörigen Anordnung hieß es, dass während der "Periode der Mobilmachung für die Niederschlagung der kommunistischen Rebellion" die Handelsflagge durch die Nationalflagge ersetzt werden soll. Die Handelsflagge war somit abgeschafft, obwohl die "Periode der Mobilmachung" 1991 für beendet erklärt worden war.
Quelle:
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN),
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Nationalflaggen der Welt,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt

Die Republik China (Taiwan) und die Volksrepublik China versuchen beide immer noch sich selbst als das einzige "China" darzustellen, was dazu geführt hat, das ein Staat nur Beziehungen zu einem China unterhalten kann, entweder zur Volksrepublik oder zur Republik. Es gibt Überlegungen und politische Kräfte auf Taiwan die eine Abkehr von dieser Ein-China-Politik und ein unabhängiges Taiwan fordern. Für diesen Staat wurde 1996 folgende Flagge vorgeschlagen:

1996,
Flagge eines von China unabhängigen Taiwan
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE)



Die Farbe Grün symbolisiert die natürliche Schönheit der Insel und die Notwendigkeit, die Umwelt zu schützen, die weiße Farbe steht für die ursprüngliche Reinheit der Menschen auf der Insel und den Wunsch, diese natürliche Schönheit zu erhalten. Das Symbol in der Mitte stellt vier Herzen in Harmonie dar, die für die vier Bevölkerungsgruppen der Insel stehen: Aborigines, Hakka, Min-nan Taiwanesen und Festlandbewohner.
Quelle: taiwandc.org


Wappen von Taiwan (Republik China),
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (DE)

Das Staatswappen ist das 1895 eingeführte Emblem der Chinesischen Regenerationsgesellschaft, der späteren Guomintang-Partei, eine zwölfstrahlige weiße Sonne auf blauem Grund. Sie symbolisiert die zwölf Doppelstunden des Tages und den Fortschritt.
Quelle: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen


seit 1991,
Flugzeugkokarde,
Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)

1928–1991,
Flugzeugkokarde,
Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)

Lage:
Quelle/Source: CIA World Factbook
Landkarte des Landes:
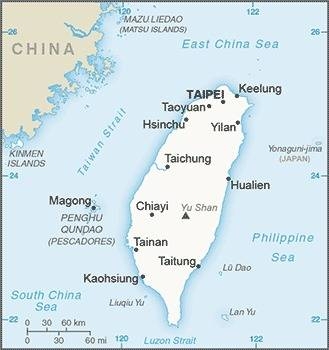
Quelle/Source: CIA World Factbook

Fläche: 36.179 km² (die Insel Taiwan, dazu die Inselgruppen: Dongsha Qundao, Quemoy [Jinmen], Wu Chiu Ju, Matsu Dao, Penghu [Pescadoren], Lan Ju, Peng Chia Ju)
Einwohner: 23.580.712 (2022), davon 98 % Han-Chinesen (70 % Hokkien Min-nan, 14 % Hakka, 14 % Festlandchinesen), 2 % Ureinwohner
Religionen: 43,8 % Shen (Chinesischer Volksglaube), 21,2 % Buddhisten, 15,5 % Daoisten, 3,9 % Christen, 0,3 % Moslems
Bevölkerungsdichte: 652 Ew./km²
Hauptstadt: Taipeh (Japanisch: Taihoku), 2.669.639 Ew. (2018)
Amtssprache: Madarin-Chinesisch
sonstige Sprachen: Taiwan-Chinesisch, Hakka-Chinesisch, Hokkien-Chinesisch, Englisch, Sprachen der Ureinwohner
Währung: Neuer Taiwan-Dollar (TWD, NTD, NT$) = 10 Jiao = 100 Fen (Cents)
Zeitzone: MEZ + 7 h
Quelle:
Wikipedia (D)

Frühzeit · Besiedlung Taiwans aus Südasien, von Taiwan aus Kolonisierung Polynesiens
12. Jahrhundert · erste chinesische Besiedlung
1517 · (nach anderen Quellen 1583 oder auch 1590) Entdeckung durch portugiesische Seefahrer, für einige Jahre Betrieb einer portugiesischen Handelsbasis
17. Jahrhundert · massive chinesische Besiedlung
1620 · Errichtung der niederländischen Handelsbasis Fort Zeelandia im Süden der Insel, Kolonisierung der Insel
1626 · Errichtung der spanischen Handelsbasis San Sebastian im Norden der Insel
1641 · Vertreibung der Spanier durch die Niederländer
1661 · Eroberung durch Chinesische Truppen der Ming-Dynastie
1662 · Vertreibung der Niederländer durch die Chinesen
1683 · Eroberung durch die Mandschuren (spätere Mandschu-Dynastie in China), zur Provinz Fujian
1885 · Taiwan wird eine eigene Provinz Chinas
1894–1895 · Chinesisch-Japanischer Krieg
1895 · China tritt Taiwan an Japan ab, Proklamation der Demokratischen Nation Taiwan (Republik Taiwan), von Japan unterdrückt
1911 · Revolution in China, Sturz der Mandschu-Dynastie
1916–1928 · Bürgerkrieg in China
10.10.1928 · Sieg der Guomindang-Partei, Proklamation der Chinesischen Nationalregierung unter Chiang Kai-Shek (Jiang Jieshi)
1937–1945 · Chinesisch-Japanischer Krieg, Japan besetzt große Teile Chinas bis 1945
1945 · Japan muss Taiwan an China zurückgeben
1945–1949 · Krieg der Kommunisten gegen die Guomindang
1947 · Verhängung des Ausnahmezustands auf der Insel
1949 · die Guomindang gehen nach Taiwan
1950 · Chiang Kai-Shek wird Präsident von Taiwan (Republik China)
1975 · Tod von Chiang Kai-Shek
1987 · Aufhebung des Ausnahmezustands
1992 · Verfassungsänderung, Ende der Vormachtstellung der Guomindang-Partei
1996 · die Volksrepublik China lehnt die Unabhängigkeit Taiwans ab
2001 · erste Handelsbeziehungen mit der Volksrepublik China
2009 · weitere Annäherung an die Volksrepublik China
2016 · starke Verschlechterung der Beziehungen zur Volksrepublik China
Quelle:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (DE)

"Taiwan" ist Chinesisch und heist "Große Bucht", wahrscheinlich eine Anspielung auf die vielen Buchten Insel. Als die Portugiesen die Insel entdeckten nannten sie sie "Ilha Formosa", was "Wunderschöne Insel" heißt. Der Name Formosa hat sich bis in die Neuzeit als Name für die Insel erhalten, wenngleich heute der Name "Taiwan" öfter verwendet wird.
Quelle:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()























![]()
