|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
|
Das Land wurde 1964 durch den Zusammenschluss von Sansibar und Tanganjika gegründet. |
The country was founded in 1964 by the merger of Zanzibar and Tanganyika. |
 |
National- und Staatsflagge – national and state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
 |
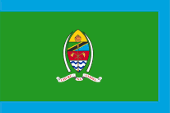
Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Flagge des Präsidenten – flag of the President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
1961–1964, Flagge Tanganjikas – flag of Tanganyika, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, mehr Infos – more Info? hier klicken – click here |
 |
1964–Apr.1964, Flagge Sansibars – flag of Zanzibar, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, mehr Infos – more Info? hier klicken – click here |
| Als sich Sansibar am 27.04.1964 mit Tanganjika zur "Vereinigten Republik von Tanganjika und Sansibar" zusammenschloss wurden die Farben der Flaggen dieser beiden Länder am 30.06.1964 in einer neuen Nationalflagge kombiniert. Diese Flagge zeigt einen von links unten aufsteigenden, golden gesäumten, schwarzen Diagonalstreifen, ein grünes Dreieck links oben, ein blaues Dreieck rechts unten. Die verwendeten Farben wurden von der "Abteilung für Planung und Privatisierung" des Büros des Präsidenten von Tansania festgelegt und folgen dem "British Standard 2660" aus dem Jahre 1955. Grün als BS 0-010, was in etwa Pantone 362 c entsprechen würde, Blau als BS 0-012, was in etwa Pantone 299 c entsprechen würde, und Gelb als BS 0-002, was in etwa Pantone 116 c entsprechen würde. Der schwarze Diagonalstreifen steht für das Volk, Gelb (Gold) für die reichen Bodenschätze des Landes, Grün für die üppige Vegetation und Landwirtschaft und Blau für die vielen Seen, Flüsse und Küsten am Indischen Ozean. |
When Zanzibar merged with
Tanganyika on 27th of April in 1964 to form the "United Republic of
Tanganyika and Zanzibar", the colours of the flags of these two countries
were combined into a new national flag on 30th of June in 1964. This flag
shows a gold-lined, black diagonal stripe rising from the bottom left, a
green triangle at the top left, and a blue triangle at the bottom right. The
used colours were determined by the "Planning and Privatization Department"
of the Office of the President of Tanzania and follow the "British Standard
2660" from 1955. Green as BS 0-010, which would roughly correspond to
Pantone 362 c, blue as BS 0-012, which would roughly correspond to Pantone
299c, and yellow as BS 0-002, which would roughly correspond to Pantone
116c. The black diagonal stripe represents the people, stands for yellow
(gold) for the country's rich natural resources, green for the lush
vegetation and agriculture and blue for the many lakes, rivers and
coastlines on the Indian Ocean. |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (FR), World Statesmen, Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Tansania – Coat of arms of Tanzania, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4 |
| Das Staatswappen von Tansania wurde im Jahre 1964 eingeführt, nach dem Zusammenschluss von Sansibar und Tanganjika zur "Vereinigten Republik von Tanganjika und Sansibar". In seiner Gestaltung basierte es auf dem Wappen Tanganjikas, das 1961 zur Unabhängigkeit jenes Landes eingeführt wurde. Das Wappen Tansanias zeigt einen Massai-Schild mit vier untereinander angeordneten Feldern, darin jeweils eine Fackel (Freiheitsfackel), die Nationalflagge von Tansania, Beil und Hacke, sowie blaue Wellenlinien (Meer) mit einem Speer. Schildhalter sind ein Bantu-Mann und eine Bantu-Frau, die beide einen Elefantenstoßzahn halten. Der Schild ruht auf dem Berg Kilimandscharo, links Kaffee- und rechts Baumwollpflanzen. Das Landesmotto steht in roten Buchstaben auf einem weißen Spruchband. Es ist in Suaheli und lautet: "Uhuru na Umoja" → "Freiheit und Einheit". |
The national coat of arms of Tanzania was introduced in 1964, after the
merger of Zanzibar and Tanganyika to form the "United Republic of Tanganyika
and Zanzibar". Its design was based on the coat of arms of Tanganyika, which
was introduced when that country gained independence in 1961. The coat of arms of Tanzania shows a Maasai shield with four fields arranged one below the other, each containing a torch (torch of freedom), the national flag of Tanzania, hatchet and hoe, as well as blue wavy lines (sea) with a spear. Shield holders are a Bantu man and a Bantu woman, both holding an elephant tusk. The shield rests on Mount Kilimanjaro, with coffee plants on the left and cotton plants on the right. The state motto is written in red letters on a white banner. It is in Swahili and reads: "Uhuru na Umoja" → "Freedom and Unity". |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Volker Preuß | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
seit/since 2010, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: FOX 52, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
1965–2010, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: D. V. Wiebe, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Antike
· Siedlungsgebiet der Bantu-Stämme 8.–15. Jhd. · Sansibar ist häufiges Ziel arabischer und persischer Händler, Gründung von Handelsposten, Islamisierung, arabische Besiedlung 975 · Gründung von Sansibar und Kilwa als arabische Handelsstützpunkte 1499 · der portugiesische Seefahrer Vasco da Gama segelt auf dem Weg nach Indien entlang der Küste 28.01.1499 · Vasco da Gama besucht Sansibar 1505 · Eroberung von Kilwa durch die Portugiesen, Inbesitznahme der gesamten Ostküste Afrikas 1698–1730 · die Küste Tanganjikas fällt an Oman, ebenso Sansibar 1856 · Tod des Sultans von Oman, in Folge britischem Drucks Teilung des Landes (Teilung der Dynastie in zwei Linien) in das Sultanat Oman und das Sultanat Sansibar, die Küste Tanganjikas kommt an Sansibar 17.02.1885 · Carl Peters erwibt im Namen der Deutsch-Ostafrikanischen Gesellschaft (DOAG) Territorien im Landesinneren vom Sultan von Sansibar 27.05.1885 · Errichtung des Protektorats Deutsch-Ostafrika einschließlich Deutsch-Witu (im heutigen Kenia gelegen) 28.04.1888 · die DOAG pachtet die Küste des Festlands vom Sultan von Sansibar 01.07.1890 · Helgoland-Sansibar-Vertrag, das Deutsche Reich verzichtet auf sein Protektorat über Sansibar, im Gegenzug Erwerb der Insel Helgoland von Großbritannien und die Abtretung von Deutsch-Witu an Großbritannien 07.11.1890 · Großbritannien errichtet sein Protektorat über das Sultanat Sansibar, die Sultane von Sansibar regieren künftig im Auftrag der britischen Krone, die durch einen Residenten in Sansibar vertreten ist 20.11.1890 · die Verwaltung des Protektorats Deutsch-Ostafrika wird der DOAG nach Aufständen und Unruhen entzogen, Bildung der Kolonie Deutsch-Ostafrika 1896/1890 · Grenzverträge mit Großbritannien und Portugal 1914–1918 · Erster Weltkrieg (1916 · britische, indische, südafrikanische, belgische und portugiesische Truppen erobern Deutsch-Ostafrika, Widerstand der deutschen Schutztruppe bis zum 14.11.1918, 1918 · portugiesische Truppen besetzen das Ruvuma-Dreieck) 1919 · Ruanda und Urundi kommen unter belgische Verwaltung 1920 · das Ruvuma-Dreieck wird an Portugal abgetreten (zu Portugiesisch-Ostafrika [Moçambique]) 20.07.1922 · Deutsch-Ostafrika wird unter dem Namen Tanganjika britisches Mandatsgebiet des Völkerbundes 11.12.1946 · Tanganjika wird britisches Treuhandgebiet der UNO 1954 · Gründung der TANU-Partei (Tanganyika African National Union), sie fordert die Unabhängigkeit des Landes 1957 · Großbritannien gewährt Sansibar eingeschränkte Autonomie 01.05.1961 · Großbritannien gewährt Tanganjika Selbstverwaltung 09.12.1961 · Großbritannien gewährt Tanganjika die Unabhängigkeit im Rahmen des Commonwealth of Nations 09.06.1962 · Gründung der "Republik Tanganjika" 24.06.1963 · Großbritannien gewährt Sansibar Selbstverwaltung 10.12.1963 · das Sultanat Sansibar wird unabhängig und Mitglied des Commonwealth 12.01.1964 · Revolution, Sturz des Sultans, Sansibar wird Volksrepublik, Massaker an der arabischen Bevölkerung, noch im Januar kommt es zu einem Staatsstreich, die Afro-Shirazi-Partei ergreift die Macht 27.04.1964 · die Volksrepublik Sansibar vereinigt sich mit der Republik Tanganjika zur "Vereinigten Republik von Tanganjika und Sansibar" 29.10.1964 · Umbenennung in "Vereinigte Republik Tansania" 1965 · Etablierung eines Einparteiensystems (TANU in Tanganjika, ASP in Sansibar) 1977 · TANU und ASP schließen sich zur CCM-Einheitspartei zusammen 1978 · Krieg mit Uganda 1992 · Ende des Einparteiensystems Oktober 1995 · erste freie Wahlen in Sansibar nach 30 Jahren ab 2000 · Erstarken der islamistisch geprägten Unabhängigkeitsbewegung auf Sansibar, die für eine Trennung von Tanganjika eintritt, Erstarken der Tanganjika-Nationalbewegung |
|
Antiquity
· settlement area of the Bantu tribes 8th–15th cent. · Zanzibar is a often visited target of Arabian and Persian merchants, establishment of trade stations, islamization, Arabian settlement 975 · foundation of Kilwa and Zanzibar as Arabian trading bases 1499 · the Portugese seafarer Vasco da Gama sails along the coast on his way to India 28th of January 1499 · Vasco da Gama visits Zanzibar 1505 · conquest of Kilwa by the Portugese, appropriation of the whole eastern coast of Africa 1698–1730 · the coast of Tanganyika comes to Oman, as well as Zanzibar 1856 · death of the Sultan of Oman, in result of British pressure division of the country (division of the dynasty in two lines) in the Sultanate of Oman and the Sultanate of Zanzibar, the coast of Tanganyika comes to Zanzibar 17th of February 1885 · Carl Peters acquires places in the innards of the land in the name of the German East African Company (DOAG) from the Sultan of Zanzibar 27th of May 1885 · establishment of the protectorate of German East Africa including German Witu (situated in the today’s Kenya) 28th of April 1888 · the DOAG leases the coast of the mainland from the Sultan of Zanzibar 1st of July 1890 · Heligoland-Sansibar Treaty, the German Empire renounces its protectorate over Zanzibar, in countermove acquisition of the island of Heligoland from United Kingdom and the ceding of German Witu to United Kingdom 7th of November 1890 · United Kingdom establishes its protectorate over the Sultanate of Zanzibar, the Sultans of Zanzibar reign henceforth on behalf of the British crown which is represented by a British Resident in Zanzibar 20th of November 1890 · the administration of the protectorate of German East Africa becomes taken away from the DOAG after riotings and agitations, formation of the colony of German East Africa 1896/1890 · frontier treaties with United Kingdom and Portugal 1914–1918 · First World War (1916 · British, Indian, South African, Belgian and Portuguese troops conquer German East Africa, resistance of the German protection troops until the 14th of November in 1918, 1918 · Portugese troops occupy the Ruvuma Triangle) 1919 · Ruanda and Urundi come under Belgian administration 1920 · the Ruvuma Triangle becomes ceded to Portugal (to Portugese East Africa [Moçambique]) 20th of July 1922 · German East Africa becomes a British mandate of the League of Nations with the name Tanganyikas 11th of December 1946 · Tanganyika becomes a trust territory of the UNO 1954 · foundation of the TANU party (Tanganyika African National Union), it claims the independence of the country 1957 · United Kingdom grants Zanzibar limited autonomy 1st of May 1961 · United Kingdom grants self-administration 9th of December 1961 · United Kingdom grants independence in the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations 9th of June 1962 · formation of the "Republic of Tanganyika" 24th of June 1963 · United Kingdom grants Zanzibar self-rule 10th of December 1963 · the Sultanate of Zanzibar becomes independent and a member of the Commonwealth 12th of January 1964 · Revolution, overthrow of the Sultan, Zanzibar becomes a people’s republic, massacres on the Arabian population, even in January takes place a coup d’état, the Afro-Shirazi Party comes into power 27th of April 1964 · the People’s Republic of Zanzibar unites with the Republic of Tanganyika to the "United Republic of Tanganyika and Zanzibar" 29th of October 1964 · rename in "United Republic of Tanzania" 1965 · establishment of a single-party-system (TANU in Tanganyika, ASP in Zanzibar) 1977 · TANU and ASP unite to the CCM unity party 1978 · war with Uganda 1992 · end of the single-party-system October 1995 · first free elections in Zanzibar since 30 years since 2000 · grow strong of the islamistic shaped independence movement on Zanzibar which advocates a separation from Tanganyika, also growing of the Tanganyika national movement |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97, Volker Preuß |
| Der Name "Tansania" setzt sich zusammen aus "Tanganjika", "Sansibar" und "Azania". "Azania" steht für einen imaginären Bantu-Staat, und einige Länder Afrikas wollten sich nach der Unabhängigkeit diesen Namen geben. Zuletzt auch Südafrika nach dem Ende der Apartheid. | The name "Tanzania" is assembled by "Tanganyika", "Zanzibar" and "Azania". "Azania" stands for an imaginary Bantu state. Some countries in Africa would give themselves that name after the independence. Last even South Africa after the end of the apartheid. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE) | |