mobile Ansicht, to the English Version tap the flag

- Königreich Thailand
- parlamentarische Monarchie
- früherer Name: Siam
- Eigenbezeichnungen:
Prathet Thai, Prades Thai, Muang Thai
• Flaggen
• historische Flaggen
• Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge
• Wappen
• Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens
• Flugzeugkokarde
• Landkarte
• Zahlen und Fakten
• Geschichte
• Ursprung des Landesnamens

National-, Staats und Handelsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World






Seekriegsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Gösch,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Flagge des Heeres,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Flagge des Marine,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Flagge der Luftwaffe,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Standarte des Königs,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:1,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Flagge für Botschafter,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Flagge für Konsuln,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World





1782–1817,
National- und Staatsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen




1817–1855,
National- und Staatsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen




1855–1916,
National- und Staatsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen




1891–1916,
Kriegsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen




1916–1917,
National- und Staatsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Flags of the World,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt




1942–1945,
National-, Staats und Kriegsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Flags of the World




Die heutige Flagge Thailands wurde am 28.09.1917 eingeführt. Sie zeigt fünf waagerechte Streifen in Rot, Weiß, Blau, Weiß und Rot im Verhältnis 1:1:2:1:1. Die Farben der Flagge wurden in einer Bekanntmachung des Büros des Premierministers vom 30.09.2017 anlässlich des 100. Jahrestages ihrer Einführung vereinheitlicht. Die darin enthaltenen Farbvorgaben enthalten auch Werte aus dem RGB-Farbraum, so für Rot 165-25-49 und für Blau 45-42-74, was in etwa folgenden Pantone-Farbtönen entsprechen würde: Rot = Pantone 201 c, Blau = Pantone 5255 c. Die Flagge wird "Tairong" oder "Trairanga" (Trikolore) genannt. Sie zeigte ursprünglich nur die Farben Rot und Weiß. Blau wurde im Jahre 1917 ergänzt, angeblich um darauf hinzuweisen, dass Thailand im Ersten Weltkrieg ein Verbündeter der Entente war. Viele Flaggen der Entente-Staaten (Frankreich, Großbritannien, USA) zeigten ebenfalls die Farben Rot, Weiß und Blau.
Zur Deutung der Farben gibt es folgende Theorien:
• Rot und Weiß symbolisieren die Blutopfer und die Reinheit des Volkes, während Blau mit dem Königshaus in Verbindung gebracht wird
• Rot steht für die Nation, Weiß für die Religion und Blau für die Monarchie
• Die Farbkombination Blau, Weiß und Rot als Nationalfarben geht auf die Zeit des Ersten Weltkrieges zurück, als das Land ein Verbündeter der Entente gewesen ist, und dies mit der Verwednung dieser Farben zum Ausdruck gedracht werden sollte, da die wichtigsten Länder der Entente diese Farben ebenfalls in ihren Flaggen hatten.
Das Emblem des Herrscherhauses der Chakri-Dynastie ist das Tschakra (buddhistisches Rad der Lehre, der Name der Dynastie stammt davon ab), das in Siam die Gestalt einer umlaufenden Scheibe mit flammenartigen Klingen am Rand hatte. Die erste Flagge Siams aus dem Jahr 1782 war rot mit einem weißen Tschakra. Im Jahre 1817 wurde dem Zentrum des Rades ein weißer Elefant hinzugefügt, und ab 1855 wurde nur noch der weiße Elefant benutzt. Der weiße Elefant ist ein sehr altes siamesisches Symbol, und ein dreiköpfiger Elefant war in alten Zeiten das Nationalemblem (auch im benachbarten Laos). Für die Kriegsflagge wurde im Jahre 1891 das Bild eines Elefanten in Zaumzeug und Rüstung eingeführt. Im Jahre 1916 wurde die Flagge sehr stark vereinfacht: Sie zeigte nur noch ein rotes Tuch mit zwei waagerechten weißen Streifen. Angeblich sollte diese Form der Flagge das versehentliche umgekehrte Hissen verhindern. Nachdem sich Siam im Zweiten Weltkrieg an die Seite Japans stellte, wurde die Flagge mit dem weißen Elefanten wiederbelebt. Die bis dato gültige blau-weiß-rote Flagge wäre farblich den Alliierten zuzuordnen gewesen, und so wurden Verwechslungen ausgeschlossen, gerade auch in der Kennzeichnung der Flugzeuge der Luftwaffe. Umgekehrt verschwand aus dem US-Luftwaffen-Stern der zentrale rote Punkt, genau so wie der zentrale rote Punkt aus der britischen Kokarde (nur auf dem pazifischen Kriegsschauplatz).
Quelle:
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN),
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Corel Draw 4,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Volker Preuß


Wappen von Thailand,
Quelle: Sodacan, Public domain,
via Wikimedia Commons

Das Staatswappen von Thailand wurde von König Rama VI. bei seiner Thronbesteigung 1910 eingeführt. Es zeigt einen stilisierten Garuda, den mythischen Reitvogel Vishnus, des Gottes der Tapferkeit. Der Garuda gilt als Beschützer vor allen Giften und anderen schädlichen Einflüssen. Die königliche Standarte zeigt den Garuda auf gelbem Grund, und wurde ebenfalls 1910 eingeführt.
Quelle: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen


Flugzeugkokarde,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

Kennzeichen für Militärflugzeuge (fin flash),
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

1941–1945,
Flugzeugkokarde,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

1941–1945,
Kennzeichen für Militärflugzeuge (fin flash),
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

Lage:

Quelle: CIA World Factbook
Landkarte des Landes:
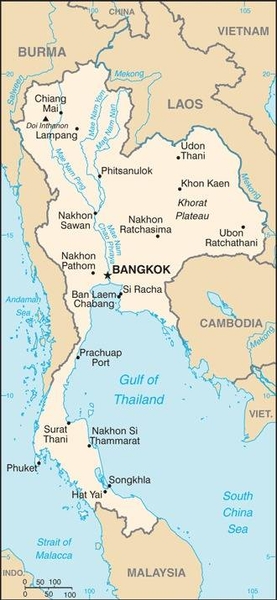
Quelle: CIA World Factbook

Fläche: 513.115 km²
Einwohner: 69.648.117 (2022), davon 80% Thai (Siamesen), 10% Chinesen, 7% Malayen, 3% Khmer
Religionen: 90% Buddhisten, 4% Moslems, 3% Christen, 1% Nicht-Religiöse
Bevölkerungsdichte: 136 Ew./km²
Hauptstadt: Bangkok (Thai: Krung Thep), 8.305.218 Ew. (2010)
Amtssprachen: Thai (Siamesisch)
sonstige Sprachen: Khmer, Chinesisch, Malayisch, Englisch
Währung: Baht (B, THB) = 100 Satang
Zeitzone: MEZ + 6 h
Quelle: Wikipedia (EN)

1.–13. Jahrhundert · Einwanderung der Siamesen aus Südchina
12. Jahrhundert · des Gebiet des heutigen Tahiland kommt an das Khmer-Königreich von Angkor
1238 · Gründung des Siamesischen Königreichs Sukhothai (Sukhodaja) unter König Intarachit
1350 · Verlegung der Hauptstadt von Sukhothai nach Ayuthia (auch Ayutthaya, 40 km nördlich Bangkok)
1555 · Eroberung des Siamesischen Reiches von Ayuthia durch Burma
1579 · Nationalaufstand unter Phra Naret
1593 · Ayuthia ist wieder unabhängig
16. Jahrhundert · Europäer landen an der Küste, Errichtung von Handelsstationen
17./18. Jahrhundert · Bürgerkriege, Wirren, Tributpflicht an China
1767 · Burma erobert Siam, Zerstörung der Stadt Ayuthia
1768 · Nationalaufstand unter Phaja Tack Sin, Vertreibung der Burmesen, Phaja Tack Sin lässt sich zum König ausrufen und verlegt die Hauptstadt nach Bangkok
1782 · General Phaja Chakri ermordet Phaja Tack Sin und ernennt sich selbst zum König (Rama I.), Gründung der bis heute regierenden Chakri-Dynastie (ab 1916 Rama-Dynastie genannt)
18./19. Jahrhundert · Ausdehnung Siams durch Eroberung von (Laos) und Siem-Reap (Kambodscha)
1855–1857 · Verträge mit Großbritannien, Frankreich und den USA
1893–1907 · Siam muss Luang Prabang und Siem-Reap und Champasak an Frankreich abtreten
1896 · Großbritannien und Frankreich sichern sich Einflussgebiete im Westen, Süden und Osten, Zentralsiam bleibt jedoch frei und unabhängig
1909 · Siam verzichtet zugunsten Großbritanniens auf die Oberhoheit über Perlis, Kedah, Kelantan und Terengganu
1914–1918 Erster Weltkrieg · Siam nimmt auf der Seite der Entente teil
1932 · neue Verfassung, Ende der absoluten Monarchie
1938 · Putsch durch Marschall Pibul Songgram
23.06.1939 · Proklamation des Königreichs Thailand
1939–1945 Zweiter Weltkrieg · März 1941: Thailand okkupiert Sayaboury, Siem-Reap und Champasak · Dezember 1941: Vertrag mit Japan · Januar 1942: Kriegserklärung an Großbritannien und die USA, Einmarsch japanischer Truppen · 1943: Annexion von Teilen Shanlands (Burma) und Annexion von Perlis, Kedah, Kelantan and Terengganu · 1944: Sturz der Regierung Songgram · 15.08.1945: Abzug der japanischen Truppen · September 1945: Thailand tritt Shanland, Perlis, Terengganu, Kedah und Kelantan wieder ab
07.12.1946 · Thailand tritt Sayaboury, Siem-Reap und Champasak wieder an Frankreich ab
1948 · Putsch durch Marschall Pibul Songgram (bis 1957)
1954 · Beitritt zur SEATO
1958 · Putsch durch Marschall Sarit Thanarat
1964 · Tod von Marschall Pibul Songgram
seit 1968 · häufige Putsche und Machtübernahmen, Unruhen und Aufstände
2011 · Grenzkonflikt und bewaffnete Auseinandersetzungen mit Kambodscha um den Tempel Prasat Preah Vihear
Quelle:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (DE),
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte

Ursprünglich hieß das Land nach seiner Hauptstadt: "Königreich Sukhothai" oder "Königreich Ayuthia", aber im 14. Jahrhundert auch schon "Muang Thai", das "Land der Freien". Nach der Verlegung der Hauptstadt nach Bangkok setzte sich allmählich der Name "Siam" durch. Dieser Name leitete sich vom Volk der Siamesen ab. Ab 1856 war er offiziell. Da Siam eine koloniale Vereinnahmung erfolgreich verhindern konnte, besann man sich 1939 auf den alten Namen "Muang Thai" und Siam wurde wieder das "Land der Freien", international "Thailand" genannt.
Quelle:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Die Völker der Erde


![]()





















































