mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Kingdom of Thailand
- parliamentary monarchy
- former name: Siam
- own names:
Prathet Thai, Prades Thai, Muang Thai
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National, state and merchant flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World






Naval war flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Naval jack,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Army,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Navy,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Air Force,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Standard of the King,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag for Ambassadors,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag for Consuls,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World





1782–1817,
National and state flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen




1817–1855,
National and state flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen




1855–1916,
National and state flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen




1891–1916,
War flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen




1916–1917,
National and state flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt




1942–1945,
National state and war flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




The current flag of Thailand was introduced on 28th of September in 1917. It shows five horizontal stripes in red, white, blue, white and red in a ratio of 1:1:2:1:1. The colors of the flag were unified in a proclamation from the Prime Minister's Office dated on 30th of September in 2017 to mark the 100th anniversary of the adoption of the today's flag. The colour specifications contain therein also values from the RGB color space, such as 165-25-49 for red and 45-42-74 for blue, which would roughly correspond to the following Pantone colors: Red = Pantone 201 c, Blue = Pantone 5255 c. The flag is called "Tairong" or "Trairanga" (tricolor). It originally only showed the colours red and white. Blue was added in 1917, ostensibly to indicate that Thailand was an ally of the Entente in World War I. Many flags of the Entente states (France, Great Britain, USA) also showed the colours red, white and blue.
There are the following theories about the interpretation of colours:
• Red and white symbolize the blood sacrifices and purity of the people, while blue is associated with royalty
• Red represents the nation, white represents religion and blue represents the monarchy
• The colour combination of blue, white and red as national colors dates back to the time of the First World War, when the country was an ally of the Entente, and this was intended to be expressed by using these colors, as the most important countries of the Entente also used these colours in their flags.
The emblem of the ruling house of the Chakri dynasty is the chakra (Buddhist wheel of teaching, the name of the dynasty comes from it), which in Siam had the shape of a circumferential disk with flame-like blades on the edge. The first flag of Siam, from 1782, was red with a white chakra. In 1817 a white elephant was added to the center of the wheel, and from 1855 only the white elephant was used. The white elephant is a very ancient Siamese symbol, and a three-headed elephant was the national emblem in ancient times (including in neighboring Laos). The image of an elephant in bridle and armor was introduced for the war flag in 1891. In 1916 the flag was greatly simplified: It only showed a red bunting with two horizontal white stripes. Supposedly this shape of the flag was intended to prevent accidental flying upside down. After Siam sided with Japan in World War II, the white elephant flag was revived. The blue, white and red flag that had been in effect until then would have been assigned to the Allies in terms of colour, and so confusion was ruled out, especially in the markings of the air force. Conversely, the central red dot disappeared from the US Air Force star, just as the central red dot disappeared from the British cockade (only in the Pacific war theater).
Source:
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN),
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Corel Draw 4,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Volker Preuß


Coat of arms of Thailand,
Source: Sodacan, Public domain,
via Wikimedia Commons

The coat of arms of Thailand was introduced by King Rama VI. on the occasion of his accession to the throne in 1910. It shows a stylized Garuda – the mythical ride-bird of Vishnu – the god of bravery. The Garuda is the protector from all poisons and other damaging influxes. The royal standard shows the Garuda on yellow ground and was as well introduced in 1910.
Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Flags of the World

Aircraft emblem (fin flash),
Source, by: Flags of the World

1941–1945,
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1941–1945,
Aircraft emblem (fin flash),
Source, by: Flags of the World

Location:

Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
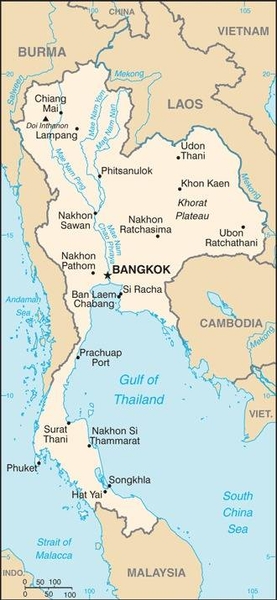
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 198.114 square miles
Inhabitants: 69.648.117 (2022), thereof 80% Thai (Siamese), 10% Chinese, 7% Malays, 3% Khmer
Religions: 90% Buddhist, 4% Muslim, 3% Christian, 1% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 352 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Bangkok (Thai: Krung Thep), 8.305.218 inh. (2010)
official Languages: Thai (Siamese)
other Languages: Khmer, Chinese, Malay, English
Currency: Baht (B, THB) = 100 Satang
Time Zone: GMT + 7 h
Source: Wikipedia (EN)

1st–13th century · immigration of the Siamese from southern China
12th century · the area of the today’s Tahiland comes to the Khmer Kingdom of Angkor
1238 · foundation of the Siamese Kingdom of Sukhothai (Sukhodaja) under King Intarachit
1350 · transfer of the capital from Sukhothai to Ayuthia (also Ayutthaya, 25 miles northern Bangkok)
1555 · conquest of the Siamese Empire of Ayuthia by Burma
1579 · national revolt under Phra Naret
1593 · Ayuthia is independent again
16th century · Europeans debark at the coast, establishment of trading stations
17th/18th century · civil wars, confusions, tributary of China
1767 · Burma conquers Siam, destruction of Ayuthia town
1768 · national revolt under Phaja Tack Sin, expulsion of the Burmese, Phaja Tack Sin proclaimes itself to the king and transfers the capital to Bangkok
1782 · General Phaja Chakri murders Phaja Tack Sin and nominates itself to the king (Rama I.), establishment of the until today ruling Chakri dynasty (since 1916 called Rama dynasty)
18./19. century · expansion of Siam by conquest of Luang Prabang and Champasak (Laos) und Siem-Reap (Cambodia)
1855–1857 · treaties with Great Britain, France and USA
1893–1907 · Siam has to cede Luang Prabang, Siem-Reap and Champasak to France
1896 · Great Britain and France belay zones of influence in the west, south and east, central Siam remains free and independent
1909 · Siam renounces for the benefit of Great Britain for the supremacy over Perlis, Kedah, Kelantan and Terengganu
1914–1918 First World War · Siam participates on the side of the Entente
1932 · new constitution, end of the absolute monarchy
1938 · coup d’état by Marshal Pibul Songgram
23.06.1939 · proclamation of the Kingdom of Thailand
1939–1945 Second World War · March 1941: Thailand occupys Sayaboury, Siem-Reap and Champasak · December 1941: treaty with Japan · January 1942: declaration of war to Great Britain and USA, marching in of Japanese troops · 1943: annexation of parts of Shanland (Burma) and annexation of Perlis, Kedah, Kelantan and Terengganu · 1944: overthrow of the Songgram government · 15th of August 1945: withdrawal of the Japanese troops · September 1945: Thailand cedes Shanland, Perlis, Terengganu, Kedah and Kelantan
7th of December 1946 · Thailand cedes Sayaboury, Siem-Reap and Champasak back to France
1948 · coup d’état by Marshal Pibul Songgram (to 1957)
1954 · Thailand joins the SEATO
1958 · coup d’état by Marshal Sarit Thanarat
1964 · death of Marshal Pibul Songgram
since 1968 · frequently coups d’état and comings into power, agitations and riotings
2011 · border conflict and armed clashes with Cambodia over the Prasat Preah Vihear temple
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (DE),
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte

The country was originally called "Kingdom of Sukhothai" or "Kingdom of Ayuthia" after its capital, but in the 14th century it was also called "Muang Thai", the "Land of the Free". After the capital was moved to Bangkok, the name "Siam" gradually became established. This name was derived from the Siamese people. It was official from 1856. Since Siam was able to successfully prevent colonial appropriation, the old name "Muang Thai" was returned to in 1939 and Siam was again called the "Land of the Free", internationally known as "Thailand".
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Die Völker der Erde


![]()





















































