Togo |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Togo |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
 |
National-, Staats- und Handelsflagge – national, state and merchant flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:1,618, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
| Deutsch-Togo – German Togo: | |
 |
1893–1914, Deutsches Reich – German Empire, Dienstflagge Kolonialamt / Auswärtiges Amt – Official flag colonial office / foreign office, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1914, geplante Flagge für Deutsch-Togo – planned flag for German Togo, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, Flag Reconstruction following Mark Sensen (Feb 98) based on traditional interpretation from Afrika-Nachrichten article 1933 |
| Französisch-Togo – French Togo: | |
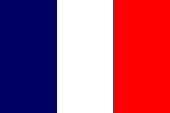 |
1922–1956, Nationalflagge Frankreichs – national flag of France, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4   |
 |
1956–1958, Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:8, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
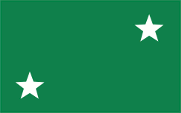 |
1958–1960 Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 5:8, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
| Britisch-Togo – British Togo: | |
| ab 1956 Bestandteil der Goldküste – since 1956 a part of Gold Coast | |
 |
1922–1957, Union Flag → quasi Nationalflagge, Flagge Großbritanniens – flag of United Kingdom, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
 |
1956–1957, Goldküste – Gold Coast, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
seit/since 1957, Flagge von Ghana – flag of Ghana, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D)   |
| Die heutige Flagge Togos wurde am 23.04.1960 eingeführt und am 27.04.1960 – am Tag der Unabhängigkeit – offiziell gehisst. Die Seitenverhältnisse entsprechen, weltweit einmalig, dem "Goldenen Schnitt", also 1:1,618. In der Praxis wird jedoch häufig 2:3 oder 3:5 verwendet. Die Flagge zeigt fünf waagerechte Streifen in Grün, Gelb, Grün, Gelb und Grün mit einem weißen, fünfzackigen Stern in einer roten Oberecke. Rot steht für Nächstenliebe, Treue und Patriotismus, Grün steht für die Hoffnung, die Landwirtschaft und den fruchtbaren Boden, Gelb steht für Arbeit und die Bodenschätze des Landes. Der weiße Stern repräsentiert Freiheit, Fortschritt, Reinheit und Aufgeschlossenheit. Die Farbtöne der Flagge scheinen definiert zu sein, jedenfalls lassen sich folgende unverbindliche hexadezimalen Farbwerte finden: Rot #EE0000, Gelb #FFD700 und Grün #2E8B57. Daraus lassen sich folgende Pantone-Farbtöne ableiten: Rot = Pantone 1788 c, Gelb = Pantone 109 C und Grün = Pantone 348 c. Grün, Gelb und Rot sind auch als die "Panafrikanischen Farben" bekannt: Etwa 1900 setzte die Panafrika-Bewegung ein, die Gemeinsamkeiten aller Menschen mit schwarzer Hautfarbe hervorheben wollte. Der Farbendreiklang Grün-Gelb-Rot, den viele afrikanische und auch amerikanische Staaten nach Erlangung ihrer Unabhängigkeit in ihre Flaggen übernahmen, steht für die politische Einheit Afrikas, ja aller Schwarzen. Das erste Land war Ghana im Jahr 1957. Als Ursprung gelten die Landesfarben von Athiopien (Abessinien), dem ältesten unabhängigen Staat Afrikas. Als deutsche Kolonie verwendete das Land keine besondere Nationalflagge. Es galten die Farben des Deutschen Reiches: Schwarz, Weiß und Rot. Behörden verwendeten die Flagge des Kolonialamtes sowie Abarten davon. Diese war zwar schwarz, weiß und rot waagerecht gestreift und zeigte in der Mitte eine weiße Scheibe mit dem Reichsadler. Ab 1913 wurde überlegt, für die Kolonien eigene Hoheitszeichen zu schaffen. Erste Entwürfe lagen 1914 vor, jedoch wurde das Projekt wegen des Ausbruchs des Ersten Weltkriegs und wegen des Verlusts der Kolonien nicht mehr realisiert. Die Flagge der autonomen Republik zeigte zwischen 1956 und 1960 ein grünes Grundtuch mit zwei weißen fünfzackigen Sternen in den Ecken (manchmal werden sie auch gelb dargestellt) und zwischen 1956 und 1958 zusätzlich die französische Trikolore in der Oberecke. Die Bedeutung der beiden Sterne ist nicht bekannt, vielleicht standen sie für den französischen und den britischen Landesteil, oder für Togo diesseits und jenseits der Fazao-Berge (Nord- und Südtogo). |
The current flag of Togo
was introduced on 23rd of April in 1960 and was officially hoisted on 27th
of April in 1960 – the Independence Day. The aspect ratios correspond to the
"Golden Ratio", which is unique in the world, they are 1:1,618. However, in
practice 2:3 or 3:5 is often used. The flag shoes five horizontal stripes of
green, yellow, green, yellow and green with a white five-pointed star in a
red top corner. Red stands for charity, loyalty and patriotism, green stands
for hope, agriculture and the fertile soil, yellow stands for work and the
country's natural resources. The white star represents freedom, progress,
purity and open-mindedness. The colours of the flag seem to be defined, in
any case the following non-binding hexadecimal colour values can be found:
red #EE0000, yellow #FFD700 and green #2E8B57. The following Pantone colours
can be derived from this: Red = Pantone 1788 c, Yellow = Pantone 109 C and
Green = Pantone 348 c. Green, yellow and red are also known as the "Pan-African colours": The Pan-African movement began around 1900, which wanted to highlight the similarities of all people with black skin. The color triad green-yellow-red, which many African and American states adopted in their flags after gaining their independence, represents the political unity of Africa, and indeed of all black people. The first country was Ghana in 1957. The national colors are considered to have originated from Ethiopia (Abyssinia), the oldest independent state in Africa. As a German colony, the country did not use a specific national flag. The colors of the German Empire were used: black, white and red. Authorities used the flag of the Colonial Office as well as variations of it. This was horizontally striped in black, white and red and showed a white disc with the imperial eagle in the middle. From 1913 onwards, consideration was given to creating their own national emblems for the colonies. The first drafts were available in 1914, but the project was no longer implemented due to the outbreak of the First World War and the loss of the colonies. Between 1956 and 1960, the flag of the autonomous republic showed a green base bunting with two white five-pointed stars in the corners (sometimes they are also shown in yellow) and between 1956 and 1958 it also had the French tricolor in the upper corner. The meaning of the two stars is not known, perhaps they stood for the French and British parts of the country, or for Togo on either side of the Fazao Mountains (northern and southern Togo). |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (D), Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen-Atlas Erde, Volker Preuß | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
seit/since 1962, Emblem von Togo – Emblem of Togo, Quelle/Source: Edem Fiadjoe, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons |
 |
80-er/90-er – 80s/90s, falsche Variante des Emblems von Togo – incorrect variant of the emblem of Togo, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
80-er/90-er – 80s/90s, falsche Variante des Emblems von Togo – incorrect variant of the emblem of Togo, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen |
 |
1914, geplantes Wappen von Deutsch-Togo – planned coat of arms of German Togo, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World, Flag Reconstruction following Mark Sensen (Feb 98) based on traditional interpretation from Afrika-Nachrichten article 1933 |
|
Das erste Wappen für das
unabhängige Togo zwischen 1960 und 1962 war ein Wappenschild, darauf das
Bild der Flagge. Das heutige Staatswappen von Togo wurde am 14.03.1962
eingeführt. Es zeigt in der Mitte ein sonnenförmiges goldenes Schild mit den
Buchstaben "RT" (= Republique Togolaise), darunter nach links und nach
rechts blickend, je ein roter Löwe mit Pfeil und Bogen. Oberhalb des
Sonnenschildes sind zwei zwei Nationalflaggen platziert und ganz oben ein
Spruchband mit dem Motto "Travail, Liberté, Patrie" → "Arbeit, Freiheit,
Vaterland". Um das Aussehen des Wappens kam es in den 80-er und 90-er Jahren des 20. Jahrhunderts zu Verwirrungen, weil auch durch Behörden des Landes falsche Versionen in Umlauf gebracht wurden. So wurde ein anderes Motto in das Spruchband eingesetzt. "Union, Paix, Solidarité" → "Einheit, Frieden, Solidarität", oder der Sonnenschild bekam die Form eines Wappenschilds, oder die Schwänze der Löwen wurden nach innen gebogen. Das Land war einst eine deutsche Kolonie. Die deutschen Kolonien unterstanden – Kiautschou ausgenommen – dem Reichskolonialamt. Entsprechend verwendeten Behörden dessen Siegel, Flaggen und das Reichswappen. Ab 1913 wurde überlegt, für die Kolonien eigene Hoheitszeichen zu schaffen. Erste Entwürfe lagen 1914 vor, jedoch wurde das Projekt wegen des Ausbruchs des Ersten Weltkriegs und wegen des Verlusts der Kolonien nicht mehr realisiert. Das gedachte Aussehen der Wappen und Flaggen konnte in den 20er und 30er Jahren des 20. Jahrhunderts anhand von Fragmenten lediglich rekonstruiert werden. Die meisten Rekonstruktionen beziehen sich auf einen Artikel der Zeitung "Afrika-Nachrichten" von 1933 und die daraus folgenden Rekonstruktionen des niederländischen Vexillologen Mark Sensen vom Februar 1998, die auch auf diesen Seiten berücksichtigt werden. Die Wappen selbst sollten oberhalb des Wappenschilds noch die Kaiserkrone tragen, jedoch nicht auf den Flaggen, wenn man der Rekonstruktion von Mark Sensen folgt. Die Wappenschilde zeigten immer den gleichen Aufbau: Ein horizontal zweigeteiltes Schild, dessen Schildhaupt auf weiß den Reichsadler mit dem Brustschild des Hauses Hohenzollern zeigte. Im Hauptteil eine stilisierte Darstellung von Pflanzen, Tieren oder Landschaften, die je nach Land unterschiedlich gefärbt waren. Das geplante Wappen von Deutsch-Togo zeigte eine weiße Palme und zwei Schlangen auf schwarzem Grund. |
The first coat of arms
for the independent Togo was between 1960 and 1962 a heraldic shield with
the image of the flag on it. The current coat of arms of Togo was introduced
on 14th of March in 1962. In the middle it shows a sun-shaped golden shield
with the letters "RT" (= Republique Togolaise), underneath, looking to the
left and to the right, each a red lion with a bow and arrow. Two national
flags are placed above the sun-shield and at the top there is a banner with
the motto "Travail, Liberté, Patrie" → "Work, Freedom,
Fatherland". There was confusion about the appearance of the coat of arms in the 80s and 90s of the 20th century because incorrect versions were also circulated by the country's authorities. So a different motto was inserted into the banner. "Union, Paix, Solidarité" → "Unity, Peace, Solidarity", or the sun-shield took the shape of a heraldic shield, or the lions' tails were bent inwards. The country was once a German colony. The German colonies – with the exception of Kiautschou (Kiaochow) – were subordinated to the Colonial Office of the German Empire. Accordingly, authorities used its seals, flags and the imperial coat of arms. From 1913 onwards, consideration was given to creating their own national emblems for the colonies. The first drafts were available in 1914, but the project was no longer implemented due to the outbreak of the First World War and the loss of the colonies. The intended appearance of the coats of arms and flags could only be reconstructed using fragments in the 1920s and 1930s. Most of the reconstructions refer to an article in the newspaper "Afrika-Nachrichten" from 1933 and the resulting reconstructions by the Dutch vexillologist Mark Sensen from February 1998, which are also included on these pages. The coats of arms of the colonies should bear the imperial crown above the escutcheon, but not on the flags, if one follows Mark Sensen's reconstruction. These heraldic shields always had the same structure: a horizontally divided shield, the head of which showed the imperial eagle on white with the breastplate of the House of Hohenzollern. The main part is a stylized representation of plants, animals or landscapes that were colored differently depending on the country. The planned coat of arms of German Togo showed a white palm tree and two snakes on a black background. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, 1.) Wikipedia (D), 2.) Wikipedia (DE), Volker Preuß | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1471/1473
· Entdeckung der Küste des heutigen Togo durch portugiesische Seefahrer 16. Jhd. · Beginn der Erschließung der Küste durch Europäer; afrikanische Stämme wandern aus dem Norden und später auch aus dem Osten ein ca. 1850 · die Norddeutsche Missionsgesellschaft beginnt ihre Arbeit 1856–1865 · Einrichtung französischer Handelsposten in Agu, Anecho und Porto Seguro 1870–1880 · Einrichtung deutscher Handelsposten an der Küste Juli 1884 · Landung des deutschen Kanonenbootes "Möve", Gustav Nachtigal, deutscher Generalkonsul für Westafrika, erklärt nach Verhandlungen die Küste des heutigen Togo am 05.07.1884 zum deutschen Schutzgebiet 24.12.1885 · Frankreich erkennt das deutsche Protektorat an 1897/1899 · Grenzverträge mit Frankreich und Großbritannien ergeben ein deutsches Schutzgebiet Togoland von ca. 87.200 km² 1905 · Umbenennung von Togoland in Deutsch-Togo 1914–1918 · Erster Weltkrieg (August 1914 Eindringen britischer und französischer Truppen, 25.08.1914 Sprengung der Funkstation Kamina durch die Besatzung, 27.08.1914 Kapitulation der deutschen Polizeitruppe, deren Angehörige später nahezu alle in der Kriegsgefangenschaft sterben) 1920 · Versailler Diktat, das Deutsche Reich verliert alle seine Kolonien, Togo wird ein Mandatsgebiet des Völkerbundes unter Mandat Frankreichs und Großbritanniens, Vertreibung der wenigen Deutschen (ca. 300 Personen) 1922 · Togo wird in Französisch-Togoland (2/3 der Landesfläche im Osten und die gesamte Küste) und Britisch-Togoland (1/3 der Landesfläche im Westen) aufgeteilt 1946 · Togo wird Treuhandgebiet der UNO, Französisch-Togoland wird ein mit Frankreich assoziiertes Territorium 1955 · Französisch-Togoland wird als "Togo" eine autonome Republik innerhalb der Französischen Gemeinschaft (Communauté Française) 1956 · nach einer Volksabstimmung wird Britisch-Togoland der Britischen Kolonie Goldküste (Ghana) angeschlossen, Aufhebung der britischen UN-Treuhandschaft 1958 · Wahlen in Togo (ehem. Französisch-Togoland) 27.04.1960 · Unabhängigkeit für Togo 1963 · Militärputsch, Machtübernahme durch Nicolas Grunitzky 1967 · Rücktritt von Nicolas Grunitzky, Machtübernahme durch die Armee unter Oberstleutnant Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma 1969 · Einparteiensystem unter der Einheitspartei RPT, Vorsitzender: Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma 1974 · Verstaatlichung der Phosphatminen 1986 · Putschversuch, Einmischung durch Frankreich 1990 · Unruhen 1991 · zögerliche Demokratisierung 05.02.2005 · Tod von Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma 24.04.2005 · Wahl von Faure Gnassingbé Eyadéma, Sohn von Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma, zum Präsidenten von Togo April/Mai 2005 · Unruhen mit über 500 Toten, tausende Flüchtlinge |
|
1471/1473
· discovery of the coast of Togo by Portugese seafarers 16th century · start of the european exploitation of the coast; African tribes immigrate from the north and later even from the East ca. 1850 · the North German Mission Society starts its work 1856–1865 · establishment of French trade stations in Agu, Anecho and Porto Seguro 1870–1880 · establishment of German trade stations at the coast July 1884 · debarkation of the German gunboat "Möve" (Seagull), Gustav Nachtigal, German consul general for Western Africa, declares the coast of the today's Togo after negotiations for a German protectorate on 5th of July in 1884 24th of December 1885 · France recognizes the German protectorate 1897/1899 · border treaties with France and United Kingdom result a German Togoland territory of ca. 33.670 square miles. 1905 · rename of Togoland in German Togo 1914–1918 · First World War (August 1914 invasion of British and French troops, 25th of August in 1914 blast of the Kamina radio station by the crew, 27th of August 1914 capitulation of the German police unit, its members will nearly all die in the later war imprisonment) 1920 · Versailles Dictate, the German Empire loses all its colonies, Togo becomes a Mandate Territory of the League of Nations under mandate of France and United Kingdom, expulsion of the few Germans (ca. 300 persons) 1922 · Togo becomes separated in French-Togoland (2/3 of the area in the east and the whole coast) and British-Togoland (1/3 of the area in the west) 1946 · Togo becomes a trust territory of the UNO, French-Togoland becomes a with France associated territory 1955 · French-Togoland becomes as "Togo" an autonomous republic within the French Community (Communauté Française) 1956 · after a referendum British-Togoland becomes affiliated to the British Colony of Gold Coast (Ghana) angeschlossen, repeal of the British UN trust-status 1958 · elections in Togo (former French-Togoland) 27th of April in 1960 · independence for Togo 1963 · military coup d’état, take over by Nicolas Grunitzky 1967 · resignation of Nicolas Grunitzky, take over by the armed forces under Lieutenant-Colonel Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma 1969 · single-party-system under the unity-party RPT, chairman: Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma 1974 · dispossession of the phosphate mines 1986 · attempted coup d’état, intervention of France 1990 · riots 1991 · hesitant democratization 5th of February in 2005 · death of Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma 24th of April in 2005 · election of Faure Gnassingbé Eyadéma, son of Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma, to the president of Togo April/May 2005 · agitations with more then 500 dead persons, thousands of refugees |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, World Statesmen, Discovery '97, Wikipedia (D) |
| Zum Ursprung des Landesnames gibt es mindestens zwei Erklärungen: Der Name "Togo" geht auf den ca. 100 km² großen Togo-See zurück, der vier Kilometer hinter der Küste liegt. Das Wort Togo bedeutet in der Sprache des Kabiyé-Volkes (Kabre) "Wasserkante". Der Name wurde wahrscheinlich von der Ortschaft "Togokomé" (Togodorf, Togoville) auf den See übertragen. Eine zweite Erklärung sucht den Ursprung des Namens in der Sprache der Ewe, in der "togo" angeblich "hinter dem Fluss" heißen soll. Der amtliche Name des Landes ist "République togolaise", also "Togolesische Republik". | There are at least two explanations for the origin of the country's name: The name "Togo" goes back to the approximately 100 km² large Lake Togo, which lies four kilometers behind the coast. The word Togo means "water edge" in the language of the Kabiyé people (Kabre). The name was probably transferred to the lake from the village of "Togokomé" (Togodorf, Togoville). A second explanation seeks the origin of the name in the language of the Ewe people, in which "togo" supposedly means "behind the river". The country's official name is "République Togolaise", i.e. "Togolese Republic". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Wikipedia (EN) | |