Source, by: Flags of the World






German Togo:

1893–1914,
German Empire,
Official flag colonial office / foreign office,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1914,
planned flag for German Togo,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Flag Reconstruction following Mark Sensen (Feb 98)
based on traditional interpretation
from Afrika-Nachrichten article 1933



French Togo:
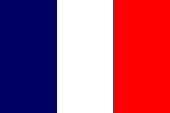
1922–1956,
National flag of France,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4






1956–1958,
National flag,
ratio = 5:8,
Source: Flags of the World



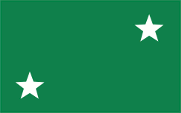
1958–1960,
National flag,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flags of the World



British Togo:
since 1956 a part of Gold Coast

1922–1957,
Union Flag → quasi National flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World






1956–1957, Gold Coast,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




since 1957,
Flag of Ghana,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)






The current flag of Togo was introduced on 23rd of April in 1960 and was officially hoisted on 27th of April in 1960 – the Independence Day. The aspect ratios correspond to the "Golden Ratio", which is unique in the world, they are 1:1,618. However, in practice 2:3 or 3:5 is often used. The flag shoes five horizontal stripes of green, yellow, green, yellow and green with a white five-pointed star in a red top corner. Red stands for charity, loyalty and patriotism, green stands for hope, agriculture and the fertile soil, yellow stands for work and the country's natural resources. The white star represents freedom, progress, purity and open-mindedness. The colours of the flag seem to be defined, in any case the following non-binding hexadecimal colour values can be found: red #EE0000, yellow #FFD700 and green #2E8B57. The following Pantone colours can be derived from this: Red = Pantone 1788 c, Yellow = Pantone 109 C and Green = Pantone 348 c. Green, yellow and red are also known as the "Pan-African colours": The Pan-African movement began around 1900, which wanted to highlight the similarities of all people with black skin. The color triad green-yellow-red, which many African and American states adopted in their flags after gaining their independence, represents the political unity of Africa, and indeed of all black people. The first country was Ghana in 1957. The national colors are considered to have originated from Ethiopia (Abyssinia), the oldest independent state in Africa. As a German colony, the country did not use a specific national flag. The colors of the German Empire were used: black, white and red. Authorities used the flag of the Colonial Office as well as variations of it. This was horizontally striped in black, white and red and showed a white disc with the imperial eagle in the middle. From 1913 onwards, consideration was given to creating their own national emblems for the colonies. The first drafts were available in 1914, but the project was no longer implemented due to the outbreak of the First World War and the loss of the colonies. Between 1956 and 1960, the flag of the autonomous republic showed a green base bunting with two white five-pointed stars in the corners (sometimes they are also shown in yellow) and between 1956 and 1958 it also had the French tricolor in the upper corner. The meaning of the two stars is not known, perhaps they stood for the French and British parts of the country, or for Togo on either side of the Fazao Mountains (northern and southern Togo).
Source:
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (D),
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen-Atlas Erde,
Volker Preuß


since 1962,
Emblem of Togo,
Source: Edem Fiadjoe,
CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons

80s/90s,
incorrect variant of the emblem of Togo,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4

80s/90s,
incorrect variant of the emblem of Togo,
Source, by: Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen

1914,
planned coat of arms of German Togo,
Source, by: Flags of the World,
Flag Reconstruction following Mark Sensen (Feb 98)
based on traditional interpretation
from Afrika-Nachrichten article 1933

The first coat of arms for the independent Togo was between 1960 and 1962 a heraldic shield with the image of the flag on it. The current coat of arms of Togo was introduced on 14th of March in 1962. In the middle it shows a sun-shaped golden shield with the letters "RT" (= Republique Togolaise), underneath, looking to the left and to the right, each a red lion with a bow and arrow. Two national flags are placed above the sun-shield and at the top there is a banner with the motto "Travail, Liberté, Patrie" → "Work, Freedom, Fatherland". There was confusion about the appearance of the coat of arms in the 80s and 90s of the 20th century because incorrect versions were also circulated by the country's authorities. So a different motto was inserted into the banner. "Union, Paix, Solidarité" → "Unity, Peace, Solidarity", or the sun-shield took the shape of a heraldic shield, or the lions' tails were bent inwards. The country was once a German colony. The German colonies – with the exception of Kiautschou (Kiaochow) – were subordinated to the Colonial Office of the German Empire. Accordingly, authorities used its seals, flags and the imperial coat of arms. From 1913 onwards, consideration was given to creating their own national emblems for the colonies. The first drafts were available in 1914, but the project was no longer implemented due to the outbreak of the First World War and the loss of the colonies. The intended appearance of the coats of arms and flags could only be reconstructed using fragments in the 1920s and 1930s. Most of the reconstructions refer to an article in the newspaper "Afrika-Nachrichten" from 1933 and the resulting reconstructions by the Dutch vexillologist Mark Sensen from February 1998, which are also included on these pages. The coats of arms of the colonies should bear the imperial crown above the escutcheon, but not on the flags, if one follows Mark Sensen's reconstruction. These heraldic shields always had the same structure: a horizontally divided shield, the head of which showed the imperial eagle on white with the breastplate of the House of Hohenzollern. The main part is a stylized representation of plants, animals or landscapes that were colored differently depending on the country. The planned coat of arms of German Togo showed a white palm tree and two snakes on a black background.
Source:
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
1.) Wikipedia (D),
2.) Wikipedia (DE),
Volker Preuß


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
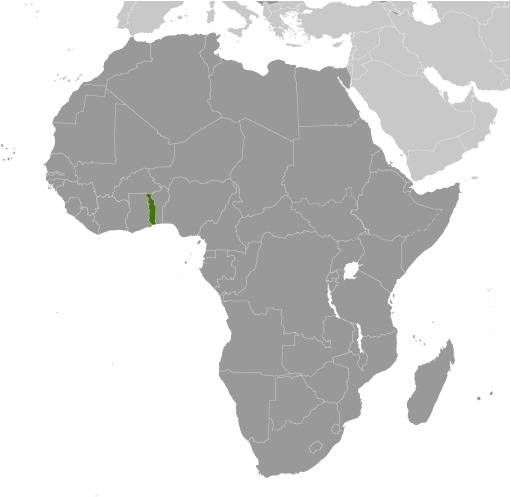
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
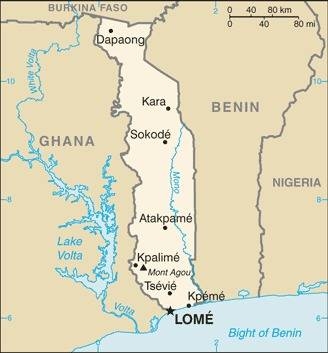
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 21.925 square miles
Inhabitants: 8.500.000 (2021), thereof 40 % Ewe, 16 % Kabiyé (Kabre), 13 % Akebu, 10 % Gurma, 7 % Yoruba
Religions: 33 % Animist, 28 % Roman Catholic, 20 % Muslim, 9 % Protestant, 5 % other Christian
Density of Population: 388 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Lomé, 1.708.000 inh. (2017)
official Language: French
other Languages: Ewe, Kabiyé etc., also German
Currency: CFA-Franc BCEAO (XOF) = 100 Centimes
Time Zone: GMT
Source:
Wikipedia (DE),
Wikipedia (EN)

1471/1473 · discovery of the coast of Togo by Portugese seafarers
16th century · start of the european exploitation of the coast; African tribes immigrate from the north and later even from the East
ca. 1850 · the North German Mission Society starts its work
1856–1865 · establishment of French trade stations in Agu, Anecho and Porto Seguro
1870–1880 · establishment of German trade stations at the coast
July 1884 · debarkation of the German gunboat "Möve" (Seagull), Gustav Nachtigal, German consul general for Western Africa, declares the coast of the today's Togo after negotiations for a German protectorate on 5th of July in 1884
24th of December 1885 · France recognizes the German protectorate
1897/1899 · border treaties with France and United Kingdom result a German Togoland territory of ca. 33.670 square miles.
1905 · rename of Togoland in German Togo
1914–1918 · First World War (August 1914 invasion of British and French troops, 25th of August in 1914 blast of the Kamina radio station by the crew, 27th of August 1914 capitulation of the German police unit, its members will nearly all die in the later war imprisonment)
1920 · Versailles Dictate, the German Empire loses all its colonies, Togo becomes a Mandate Territory of the League of Nations under mandate of France and United Kingdom, expulsion of the few Germans (ca. 300 persons)
1922 · Togo becomes separated in French-Togoland (2/3 of the area in the east and the whole coast) and British-Togoland (1/3 of the area in the west)
1946 · Togo becomes a trust territory of the UNO, French-Togoland becomes a with France associated territory
1955 · French-Togoland becomes as "Togo" an autonomous republic within the French Community (Communauté Française)
1956 · after a referendum British-Togoland becomes affiliated to the British Colony of Gold Coast (Ghana) angeschlossen, repeal of the British UN trust-status
1958 · elections in Togo (former French-Togoland)
27th of April in 1960 · independence for Togo
1963 · military coup d’état, take over by Nicolas Grunitzky
1967 · resignation of Nicolas Grunitzky, take over by the armed forces under Lieutenant-Colonel Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma
1969 · single-party-system under the unity-party RPT, chairman: Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma
1974 · dispossession of the phosphate mines
1986 · attempted coup d’état, intervention of France
1990 · riots
1991 · hesitant democratization
5th of February in 2005 · death of Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma
24th of April in 2005 · election of Faure Gnassingbé Eyadéma, son of Etienne Gnassingbé Eyadéma, to the president of Togo
April/May 2005 · agitations with more then 500 dead persons, thousands of refugees
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Discovery '97,
Wikipedia (D)

There are at least two explanations for the origin of the country's name: The name "Togo" goes back to the approximately 100 km² large Lake Togo, which lies four kilometers behind the coast. The word Togo means "water edge" in the language of the Kabiyé people (Kabre). The name was probably transferred to the lake from the village of "Togokomé" (Togodorf, Togoville). A second explanation seeks the origin of the name in the language of the Ewe people, in which "togo" supposedly means "behind the river". The country's official name is "République Togolaise", i.e. "Togolese Republic".
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Wikipedia (EN)


![]()

























![]()
