Tschechoslowakei |
|
|
|
| Verweise: | Links: |
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Tschechoslowakei |
|
|
|
| Verweise: | Links: |
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
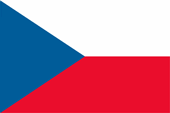
1918–1920, Nationalflagge der Tschechoslowakei – national flag of Czechoslovakia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
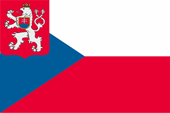
1920–1992, Nationalflagge der Tschechoslowakei – national flag of Czechoslovakia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1935–1939, 1945–1955, Flagge der Patrouillenboote – flag of the patrol boats, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1990–1992, |
 |
19. Jahrhundert/19th century, Böhmische Farben der Tschechen – Bohemian colours of the Czechs, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flaggen und Wappen der Welt |
 |
19. Jahrhundert/19th century, |
 |
seit/from 1868, |
 |
1990–1992, Flagge der tschechischen Teilrepublik innerhalb der Tschechoslowakei – flag of the Czech Republic within Czechoslovakia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1990–1992, |
|
|
|
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die Flagge der Tschechoslowakei wurde am 30.03.1920 eingeführt, und am 17.12.1992 in Vorbereitung der Abspaltung der Slowakei für Tschechien übernommen. Sie zeigt zwei waagerechte Streifen in Weiß und Rot und am Mast ein blaues, bis zu Mitte der Flagge reichendes, gleichschenkliges Dreieck. Die Farben Weiß und Rot sind die seit dem 12. Jahrhundert bekannten böhmischen Wappenfarben (weißer Löwe auf Rot), während das blaue Dreieck die Slowakei repräsentieren sollte. | The flag
of Czechoslovakia was introduced on 30th of March in 1920, and was taken
over as flag of Czechia in preparation for the separation of Slovakia on
17th of December in 1992. It shows two horizontal stripes in white and red
and on the pole a blue until the middle of the flag reaching isosceles
triangle. The colours white and red are the since the 12th century known Bohemian colours (white lion on red), the blue triangle should represent Slovakia. |
| Viele slawische Völker schufen sich in der Zeit nach 1848 (dem Jahr der Revolutionen) – im Zusammenhang mit einem erstarkenden slawischen Nationalismus – eigene Flaggen. Dabei spielte der Panslawismus eine bedeutende Rolle, eine politische Bewegung des 18./19. Jahrhunderts, die alle Slawen in einer Nation einen wollte. Die meisten slawischen Völker lebten jedoch in dieser Zeit unter österreichischer, türkischer oder auch deutscher Herrschaft. Der Panslawismus sah in Russland ein Vorbild, denn die Russen waren, neben Montenegro, die einzige freie slawische Nation. Und so wurden die Farben der russischen Flagge zum Idol der Panslawisten, und letztlich farbliches Vorbild bei der Gestaltung der Flaggen vieler slawischer Nationen. Diese Flaggen trugen und tragen bis auf wenige Ausnahmen die russischen Farben Weiß, Blau und Rot als gemeinsames Merkmal. Daher wird diese Farbkombination "Panslawische Farben" genannt. | Many
Slavic nations create on the 19th century own flags – in context with a
growing Slavic nationalism. Thereby played the Panslavism an important roll,
a political movement of the 18th/19th century, which would unite all Slavs
in one nation. The most Slavic nations however lived in this times under Austrian, Turkish or even German rule. The Panslavism saw in Russia a model, because the Russians were, apart from Montenegro, the only free Slavic nation. In this way the colours of the Russian flag became to an idol of the Panslavists, and in the end to a colour's pattern in the designing of the flags of many Slavic nations. Those flags carried and carry except few exceptions the Russian colours white, blue and red as mutual attribute. From there this colour's combination is named "Panslavic Colours". |
| Erstmals wurden die drei Farben im Jahre 1848 auf dem Slawenkongress in Prag in einer längsgestreiften Trikolore gezeigt. Sie stand für die Tschechen und die Slowaken. | The three colours had been shown for the first time in the year 1848 on the Slavic Congress in Prague, but in a lengthwise striped tricolour. They represented the Czech and the Slovaks. |
| Die Slawen in Mähren bevorzugten letztlich die horizontale Farbkombination von Weiß, Rot und Blau, die sich auch auf das alte (und heute wieder verwendete Wappen Mährens) von vor 1462 zurückführen lassen. | The Slavs in Moravia finally preferred the horizontal colour combination of white, red and blue, which can also be traced back to the old (and nowadays reused coat of arms of Moravia) from before 1462. |
| Dennoch wurde als erste Flagge der Tschechoslowakei am 28.10.1918, den Tag der Gründung des Staates, auf Empfehlung des Nationalrates der Tschechoslowakei eine horizontal gestreifte Bikolore in den böhmischen Farben Weiß und Rot eingeführt. Aber, die neuen Nachbarstaaten der Tschechoslowakei, Österreich und auch Polen, verwendeten die gleichen Farben, so dass eine Unterscheidung notwendig wurde. Außerdem war die Slowakei in der bestehenden Flagge nicht repräsentiert. So wurde am 30.03.1920 – nach vielen Diskussionen – die bekannte Flagge der Tschechoslowakei offiziell eingeführt. | Anyhow
was introduced as the first flag of Czechoslovakia, in recomendation of the
national council of Czechoslovakia, a horizontally striped bicolour in the
bohemian colours white and red on 28th of October in 1918, the day of
founding of the state. But the new neighbouring states of Czechoslovakia, Austria and also Poland, used the same colours, so that it was necessary to bring about a better differentiation. Moreover Slovakia was not represented in the existing flag. Because of that was – after many debates – officially introduced the well known flag of Czechoslovakia on 30th of March in 1920. |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Die Welt der Flaggen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
1920–1938, 1945–1960, kleines Wappen der Tschechoslowakei – lesser coat of arms of Czechoslovakia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: See page for author / CC BY-SA |
 |
1918–1938, 1945–1960, großes Wappen der Tschechoslowakei – greater coat of arms of Czechoslovakia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Shazz / CC BY-SA |
 |
1918–1938, 1945–1960, Schild des großen Wappens der Tschechoslowakei – escutcheon of the greater coat of arms of Czechoslovakia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Shazz / CC BY-SA |
 |
1920–1939, 1945–1960, mittleres Wappen der Tschechoslowakei – middle coat of arms of Czechoslovakia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: See page for author / CC BY-SA |
 |
1939–1945, großes Wappen des Reichsprotektorats Böhmen und Mähren – greater coat of arms of the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Fornax / Public domain |
 |
1960–1990, kleines Wappen der Tschechoslowakei – lesser coat of arms of Czechoslovakia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1960–1990, großes Wappen der Tschechoslowakei – greater coat of arms of Czechoslovakia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1990–1992, Wappen der Tschechoslowakei – coat of arms of Czechoslovakia, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
1990–1992, Wappen der Tschechoslowakei auf der Präsidentenstandarte – coat of arms of Czechoslovakia on the standard of the president, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das große und und teilweise auch das mittlere Wappen der Tschechoslowakei zeigten (außer zwischen den Jahren 1960 und 1990) immer die Heraldik der vielen historischen Regionen, die 1918 zur Tschechoslowakei zusammengefasst worden waren: Böhmen, Mähren, Schlesien, Slowakei, Karpatenukraine, Teschen, Troppau und Ratibor. Das kleine Wappen kombinierte meist den zweischwänzigen böhmischen Löwen mit einem Brustschild, der das historische Wappen der Slowakei enthielt, außer zwischen 1960 und 1990. Der Wappenspruch lautete: "Pravda vitezi", ab 1990 auch in Latein: "Veritas vincit" → "Die Wahrheit siegt". |
The greater and partially
the lesser coat of arms of Czechoslovakia showed (except between the years
1960 and 1990) always the heraldry of the many historic regions which had
been merged to Czechoslovakia in 1918: Bohemia, Moravia, Silesia, Slovakia,
Carpatho-Ukraine, Teschen, Troppau and Ratibor. The lesser coat of arms combined mostly the double-tailed bohemian lion with a chest shield which contained the historic coat of arms of Slovakia, except between the years 1960 and 1990. The Motto in the banner was: "Pravda vitezi", since 1990 even in Latin: "Veritas vincit" → "The truth will win". |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (EN), Volker Preuß | |
|
Lesen Sie hier: Hintergründe, Geschichte und Fakten zum Thema "Der Löwe in der Heraldik". Ausführungen, Varianten, Entwicklung sowie Panther und Leoparden. |
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
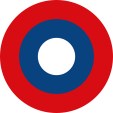 |
1918–1920, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1920–1938, 1945–1992, Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| Geschichte Böhmens bis 1918 (→ hier
klicken) Geschichte Mährens bis 1918 (→ hier klicken) Geschichte Österreichisch-Schlesiens bis 1918 (→ hier klicken) Geschichte der Slowakei (→ hier klicken) Geschichte der Karpatenukraine (→ hier klicken) 28.10.1918 ·
Gründung der Tschechoslowakei durch
den Zusammenschluss von Böhmen,
Mähren,
Österreichisch-Schlesien, der
Slowakei und der Karpatenukraine |
History: |
| History of Bohemia to 1918 (→ click
here) History of Moravia to 1918 (→ click here) History of Austrian Silesia to 1918 (→ click here) History of Slovakia (→ click here) History of Carpatho-Ukraine (→ click here) 28th of October 1918
· formation of Czechoslovakia by
merger of Bohemia, Moravia,
Austrian Silesia, Slovakia and the
Carpatho-Ukraine |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D), World Statesmen, Discovery '97, Weltgeschichte |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name "Tschechoslowakei" verbindet die beiden geographischen Begriffe "Tschechien/Tschechei" und "Slowakei" zu einem Wort. | The name
"Czechoslovakia" merges the two geographic terms "Czechia" and "Slovakia" to
one word. |
| Quelle/Source: Volker Preuß | |