mobile Ansicht, to the English Version tap the flag

- Republik Türkei
- ehemaliges Osmanisches Reich
- präsidiale Republik
- Eigenbezeichnung: Türkiye Cumhuriyeti
• Flaggen
• historische Flaggen
• Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge
• Wappen
• Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens
• Flugzeugkokarde
• Landkarte
• Zahlen und Fakten
• Geschichte
• Ursprung des Landesnamens

National-, Staats, Handels- und Marineflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World






Flagge des Präsidenten,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Flagge des Oberbefehlshabers der Marine,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:1,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



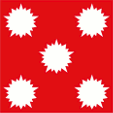
Flagge des Großadmirals,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:1,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



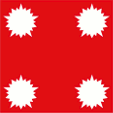
Flagge eines Admirals,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:1,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



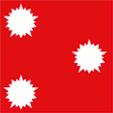
Flagge eines Vizeadmirals,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:1,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Flagge eines Konteradmirals,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:1,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Flagge eines Flottillenadmirals,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:1,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




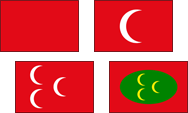
15.–18. Jahrhundert,
mögliche Varianten der Flagge des Osmanischen Reiches,
Quelle, nach: Die Welt der Flaggen, Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild

1793–1844,
Flagge des Osmanischen Reiches,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (EN)




1844–1923,
Flagge des Osmanischen Reiches,
Quelle, nach: commons.wikimedia.org, histor. Abb./Pic.




ca. 1844–1919,
Handelsflagge des Osmanischen Reiches,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




ca. 1844–1912,
Handelsflagge für Albaner,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




ca. 1844–1919,
Handelsflagge für Griechen,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




ca. 1844–1919,
Handelsflagge für Moslems auf dem Weg nach Mekka,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




1890–1923,
Flagge des Osmanischen Reiches,
Quelle, nach: histor. Abb./Pic.




bis 1922,
Flagge des Sultans,
Quelle, nach: histor. Abb./Pic.




bis 1922,
Flagge des Sultans zur See,
Quelle, nach: histor. Abb./Pic.




bis 1924,
Flagge des Kalifen,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (EN)




1919–1937,
Zollflagge,
Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild




ab 1937,
Zollflagge,
Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild




ab 1936,
Flagge der Zollschiffe,
Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild



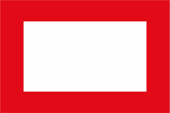
Lotsen(ruf)flagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World
Diese Art Flaggen wurde im 20. Jahrhundert abgeschafft, heute gilt:
 Lotse an Bord
Lotse an Bord
 Erbitte Lotse
Erbitte Lotse




Unterscheidungsflagge für Lotsenfahrzeuge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World
Diese Art Flaggen wurde im 20. Jahrhundert abgeschafft, heute gilt:
 Lotse an Bord
Lotse an Bord
 Erbitte Lotse
Erbitte Lotse




ab 1937 (?),
Flagge der Hafenaufsicht,
Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild




ab 1937 (?),
Quarantäneflagge,
Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild



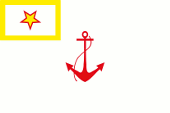
ab 1937 (?),
Flagge der Hafenkommandanten,
Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild




Die Flagge der Türkei zeigt auf einem einfarbig roten Tuch einen weißen Halbmond und einen fünfstrahligen weißen Stern. In ihrer heutigen Form wurde die Flagge um 1844 eingeführt, und am 05.06.1936 – nach anderen Quellen am 29.05.1936 – offiziell und per Gesetz bestätigt. Rot und Weiß gelten heute als die Nationalfarben. Die Türkei ist der Erbe des Osmanischen Reiches. Dessen Flaggengeschichte beginnt am Anfang des 14. Jahrhunderts mit einem weißen Banner, das Osman Bey durch den anatolischen Seldschukenherrscher Mesud II. überreicht wurde. Ab dem 15. Jahrhundert kommt die Farbe Rot in Gebrauch, die Farbe des Kalifen Omar I., die auf den Flaggen und Bannern erschien. Diese konnten einfarbig rot sein, oder auch einen oder mehrere weiße Halbmonde zeigen. Eine Standardisierung gab es noch nicht. Um 1793 – unter der Herrschaft von Sultan Selim III. – wurde erstmals ein neben dem Halbmond platzierter weißer Stern auf der Flagge erwähnt. Er soll mit dem 1801 gestifteten Halbmondorden im Zusammenhang stehen und demzufolge – wie auf dem Orden – acht Strahlen haben. Er gilt als Siegeszeichen. In Jahre 1844, in der Zeit der Tanzimat-Reformen, soll dann vom achtstrahligen zum fünfstrahligen Stern gewechselt worden sein, der den Menschen symbolisiert. Damit wäre im Prinzip in jenem Jahr das heutige Design der Flagge eingeführt worden. Standardisierungen gab es aber immer noch nicht, so dass das Erscheinungsbild von Halbmond und Stern immer wieder variierte und keineswegs einheitlich war. Das führte, gerade im Bereich der privaten Beflaggung, z.B. Handelsflagge, zu zahlreichen Varianten, die als Handelsflagge in Flaggenkataloge aufgenommen worden sind. So gibt es z.B. auch Abbildungen von roten Flaggen mit einem Stern in der Oberecke, die die Handelsflagge darstellen sollen. Generell war die Handelsflagge eigentlich einfarbig rot, jedoch gab es Varianten für bestimmte Nationalitäten oder Bevölkerungsgruppen, die innerhalb des Osmanischen Reiches eine privilegierte Stellung einnahmen.
Erst 1936 und 1937, unter der Herrschaft von Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, hat man Regularien geschaffen, die das Erscheinungsbild der Flagge definierten. Am 25.01.1985 wurden per Beschluss Nummer 85/9034 Artikel 4 des Ministerrats die Abmessungen der Flagge festgelegt. Der Farbton des Rot scheint definiert, es lässt sich eine Angabe finden: Hexadezimal #E30A17. Daraus lässt sich ein Pantone-Farbton ableiten: Pantone 1788 c.
Der Stern ist eigentlich das Symbol der Stadt Konstantinopel und er steht für die Jungfrau Maria. Als die Türken diese Stadt im Jahre 1453 nach ihren jahrelangen Wanderungen und über 100 Jahren Krieg gegen das Oströmische Reich eroberten, übernahmen sie den Stern in ihre Symbolik, so wurde er zum Siegeszeichen. Auf den roten Halbmond-Flaggen des Osmanischen Reiches tauchte der Stern erst recht spät am Beginn des 18. Jahrhunderts als Ergänzung auf. Der Halbmond ist ein uraltes und weit verbreitetes heidnisches Symbol der Menschheit. Er steht für Fruchtbarkeit und Gesundheit. Er wurde von den Türken wahrscheinlich schon aus den Steppen Mittelasiens mitgebracht. Natürlich gibt es auch eine Legende. Sie lässt den Halbmond dem Herrscher Osman I. (1259–1326), dem Gründer der osmanischen Dynastie und des Osmanischen Reiches in einem Traum von fruchtbaren und durch den Islam zu unterwerfenden Ländern erscheinen. Ein weitere Legende geaht auf Sultan Murad II. (1404–1451) zurück, der nach der Schlacht auf dem Amselfeld (Kosovo) im Jahre 1448 das Spiegelbild des Mondes in einem See aus dem Blut der getöteten Christen gesehen hat. Letztlich geht der gesamte islamische Symbolismus, in Form von Halbmond und Stern, auf das Osmanische Reich zurück. Der letzte Kalif (aus dem Haus der Abbasiden) war 1258 hingerichtet worden. Der Kalif, Nachfolger Mohammeds, war religiöses und weltliches Oberhaupt des "Islamischen Reichs". Um 1460 wurde das Kalifat vom Herrscher des Osmanischen Reichs wiederbelebt. Diese Funktion wurde besonders wichtig als die Türken im Jahre 1517 die Stadt Mekka eroberten, und die Funktion der obersten Hüter und Bewahrer der heiligen Stätten übernahmen. Die Kontrolle über die heiligen Stätten ging während des Ersten Weltkriegs verloren (Mekka 1916, Medina 1918). Das Kalifat wurde 1924 von der türkischen Nationalversammlung abgeschafft. Als es in Teilen des Osmanischen Reiches im 19. Jahrhundert zu Unabhängigkeitsbewegungen kam, setzte Abdul Hamid II. diesen Bewegungen erfolgreich das einigende Band des Panislamismus entgegen. Zum Symbol des Panislamismus machte er eine grüne Flagge (Farbe des Mantels des Propheten Mohammed), und setzte die türkischen Symbole darauf. Die Flagge des Islam war erschaffen. Das türkische Kalifat und das Osmanische Reich haben so über die Jahrhunderte die Symbolik von Halbmond und Stern in Welt des Islam eingebracht.
Aus historischen Flaggenkatalogen sind viele Abbildungen von Sonderflaggen bekannt, z.B. aus dem Bereich Schifffahrtsbehörden, Lotsenwesen oder Zoll, die meist 1937 eingeführt worden waren. Diese sind heute abgeschafft, einerseits durch die internationalen Standardisierungen im Lotsenwesen, andererseits wurden sie durch die allgemeine Flagge ersetzt und auch der Zoll verlor seine Sonderstellung. Er ist mittlerweile dem Handelsministerium unterstellt, dass kein eigenes Hoheitszeichen verwendet. Alle Ministerien haben eigene Flaggen, meist weiß mit einem runden Logo und Inschrift in Rot in der Mitte, die jedoch keine Hoheitszeichen sind. Ebenso gibt es eigene Flaggen für die Truppenteile der türkischen Armee (Heer, Marine, Luftwaffe) die ebenfalls keine Hoheitszeichen sind und nicht auf Fahrzeugen oder Schiffen verwendet werden.
Quelle:
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (TR),
World Statesmen,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen und Wappen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
Flaggen-Atlas Erde,
Die Welt im bunten Flaggenbild,
Volker Preuß


Hoheitszeichen der Türkei,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (DE)

Emblem der Türkei für den nichtstaatlichen Gebrauch,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (DE)

Emblem der Türkei im Diplomatischen Dienst,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (DE)

Emblem der Türkei mit Inschrift,
Quelle, nach: Corel Draw 4

1882–1922,
Wappen des Osmanischen Reiches,
Quelle, nach: Juristiltins,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

Die Türkei hat seit Gründung der Republik (1923) kein Wappen im herkömmlichen Sinne mehr. Stattdessen wird ein Emblem in verschiedenen Ausführungen genutzt, das Halbmond und Stern zeigt, meist in einem roten Oval, so wie es auch schon im Osmanischen Reich seit 1876 verwendet wurde. Nach Einführung der republikanischen Verfassung wurde dieses Hochoval beibehalten und wird gelegentlich durch den Namen des Landes am oberen Rand ergänzt: "Türkiye Cumhuriyeti" → "Republik Türkei". Manchmal erscheint der Name des Landes auch in Gold. Das Wappen des Osmanischen Reiches zeigte im Wesentlichen zentral einen ovalen Schild und links und rechts je eine Fahne, die grüne Fahne stand für Rumelien, den europäischen Landesteil, die rote Fahnen für den asiatischen Landesteil.
Quelle:
1.) Wikipedia (DE),
2.) Wikipedia (DE)


seit 1972
Flugzeugkokarde,
Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)
1918–1972,
Flugzeugkokarde,
Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)

Lage:
Quelle: CIA World Factbook
Landkarte des Landes:
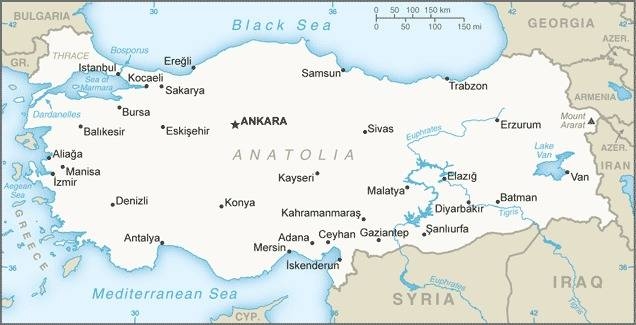
Quelle/Source: CIA World Factbook
Osmanisches Reich:
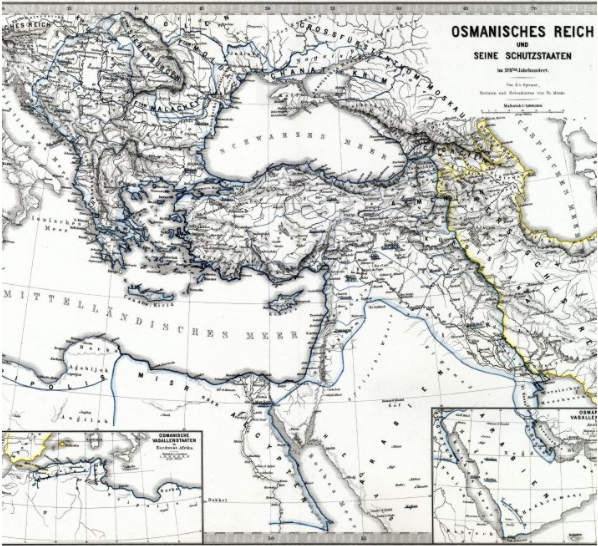
Quelle/Source: Hand-Atlas für die Geschichte des Mittelalters und die neueren Zeit von Spruner und Menke

Fläche: 783.562 km²
Einwohner: 85.279.553 (2022), davon 70% Türken, 19% Kurden, 4% Zaza, 3% Tscherkessen, 2% Bosniaken, 3% Araber, Albaner, Lasen
Religionen: 92% Moslems, 2% andere Religionen (Christen, Juden, Jesiden), 6% Nicht-Religiöse
Bevölkerungsdichte: 109 Ew./km²
Hauptstadt: Ankara, 5.747.325 Ew. (2021)
Amtssprache: Türkisch
sonstige Sprachen: Kurdisch, Zazaki, Arabisch
Währung: 1 Türkische Lira (TRY, TL) = 100 Kuruş
Zeitzone: MEZ + 2 h
Quelle:
Wikipedia (DE)

11. Jahrhundert · türkische Stämme (unter ihnen die Seldschuken) dringen aus Zentralasien über Buchara in verschiedene historische islamische Reiche ein (Karachaniden-Reich, Ghasnawiden-Reich und Bujiden-Reich), nehmen den Islam als Glauben an und dringen bis nach Kleinasien in das Herz des Oströmischen Reiches (Byzantinisches Reich) ein
1097 · Kylydsch-Arslan gründet in Ostanatolien das bis 1307 bestehende Seldschukenreich
1300 · der Türke Osman I. führt die türkischen Stämme im Glaubenskrieg gegen Byzanz und erobert Westanatolien
1326–1375 · Eroberungen der Osmanen (die Nachkommen Osmans) in Westanatolien, Rumelien und Thrakien
1375–1461 · Eroberungen der Osmanen in Ostanatolien, Nordanatolien, Griechenland, Bulgarien, Makedonien und Serbien
1451 · der Osmane Mehmed nimmt den Titel Sultan an, und erneuert wenig später das Kalifat
1453 · Eroberung von Konstantinopel
1461–1517 · Eroberungen der Osmanen in Albanien, Bosnien, Ostanatolien, Krim, Syrien, Palästina, Ägypten und Hedschas
1517–1566 · Eroberungen der Osmanen in Georgien, Cyrenaica, Tripolitanien, Irak, Asir, Jemen, Ungarn, Siebenbürgen, Walachei, Moldau und Transnistrien
1571 · Seeschlacht von Lepanto, Verlust der Vorherrschaft im Mittelmeer, jedoch Eroberung von Zypern
1683 · erfolglose Belagerung von Wien
1699 · Verlust Ungarns, Siebenbürgens und Podoliens
1739–1783 · Verlust der Bukowina, Transnistriens und der Krim
1812 · Verlust von Bessarabien
1829 · Griechenland wird unabhängig
1830 · Serbien wird unabhängig, Algerien geht an Frankreich verloren
1875 · Staatsbankrott
1876 · Verfassung
1878 · Verfassung aufgehoben
1877–1878 · russisch-türkischer Krieg, Niederlage der Türkei
1878 · Berliner Kongress, Unabhängigkeit für Rumänien, Serbien und Montenegro, Autonomie für Bulgarien, Zypern wird an Großbritannien abgetreten
1881 · Frankreich besetzt Tunesien
1882 · Großbritannien besetzt Ägypten
1908 · Österreich-Ungarn besetzt Bosnien-Herzegowina
1909 · Verfassung
1911–1912 · Italienisch-Türkischer Krieg, Italien erobert Tripolitanien und die Cyrenaica
1912-1913 · Balkankriege, das Osmanische Reich verliert alle europäischen Besitzungen außer Istanbul und Adrianopel
1914–1918 · Erster Weltkrieg, Osmanische Reich gehört zu den Mittelmächten und kämpft gegen die Entente, 1915-1916 Völkermord an den Armeniern, ab 1917 Rückzug an allen Fronten, außer im Kaukasus, 1918 nur noch Anatolien und der Kaukasus werden gehalten, Griechische Truppen besetzen Smyrma (Izmir)
1920 · Frieden von Sèvres, Verlust aller Besitzungen außer Anatolien, Abtretung von Smyrna an Griechenland, Unabhängigkeit für Kurdistan
1921–1922 · Rückeroberung von Smyrna und Vertreibung aller Griechen unter Mustafa Kemal
1922 · der Osmane Mehmed VI. wird abgesetzt, Ende des Osmanischen Reiches
1923 · Proklamation der Republik Türkei, Frieden von Lausanne, die Türkei erhält ihr heutiges Staatsgebiet
1924 · Abschaffung des Kalifats
1923–1945 · Modernisierung des Landes, Neutralität
23.02.1945 · Kriegserklärung an das Deutsche Reich im Zweiten Weltkrieg (1939-1945)
1952 · Beitritt zur NATO
1955 · Beitritt zum Bagdad-Pakt (CENTO)
1960 · Militärputsch
1963 · Assoziierungsabkommen mit der EWG (heute EU)
1974 · Besetzung von Nordzypern
1980 · Militärputsch
1982 · neue Verfassung
ab 1991 · militärische Auseinandersetzungen mit den Kurden
ab 1995 · Erstarken islamistischer Kräfte
1996 · türkisch-griechische Auseinandersetzungen im Mittelmeer und auf Zypern
2003–2014 · die islamistisch-nationalistische AKP-Partei stellt den Ministerpräsidenten, das Land erreicht Stabilität, jedoch Islamisierung bei zunehmender Ignorierung der demokratisch-laizistischen Verfassung
2014 · die islamistisch-nationalistische AKP-Partei stellt den Ministerpräsidenten und den Präsidenten, weitere Islamisierung und Wandlung in eine autoritäre Diktatur unter Verletzungen der demokratisch-laizistischen Verfassung, militärische Auseinandersetzungen mit den Kurden
15.07.2016 · Putschversuch des Militärs, Beginn einer Säuberungswelle in Justiz, Militär, Verwaltung und Bildungswesen
Quelle:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen,
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte,
Volker Preuß

Der Name "Türkei" ist schon sehr alt und wurde schon immer für das Land der Türken verwendet, dass sie nach ihrer Ankunft aus Mittelasien besetzt hatten, auch unter der Herrschaft der Osmanen, der Nachfahren Osmans I., als der Begriff "Osmanisches Reich" verwendet wurde.
Quelle: Volker Preuß


![]()











































