mobile Ansicht, to the English Version tap the flag

- Republik Uganda
- präsidiale Republik
- Eigenbezeichnungen:
– Swahili (Suaheli): Jamhuriya Uganda
– Englisch: Republic of Uganda
• Flaggen
• historische Flaggen
• Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge
• Wappen
• Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens
• Flugzeugkokarde
• Landkarte
• Zahlen und Fakten
• Die Königreiche von Uganda
• Geschichte
• Ursprung des Landesnamens

seit 1962,
National-, Staats-, Handels- und Kriegsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World






Flagge des Präsidenten,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World





1890–1893, British East Africa,
Flagge der Britischen Ostafrika-Kompanie,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

1893–1914, British East Africa,
Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge),
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




1894–1962,
Union Flag → quasi Nationalflagge,
Flagge von Großbritannien,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (EN)






1894–1962,
Handelsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of all Nations






1914–1962,
Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge),
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World



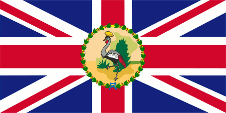
1914–1962,
Flagge des Gouverneurs,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




1962,
National-, Staats- und Handelsflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




1962–1963,
Flagge des Generalgouverneurs,
Seitenverhältnis = 1:2,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World




Nach der Berliner Kongokonferenz (1884/1885) wurde die Britische Ostafrika-Kompanie (IBEA) gegründet um den Osten Afrikas wirtschaftlich und kolonial zu erschließen. Kurze Zeit später wehte die Flagge der Gesellschaft außer über Kenia auch über dem Gebiet heutigen Uganda, das damals aus vielen einheimischen Königreichen bestand. Wegen Missmanagements der IBEA übernahm ab 1893 das britische Außenministerium die Hoheitsrechte der Kompanie, die bis ca. 1903 durchgesetzt waren, so das ab 1893 die Flagge Großbritanniens über dem Land wehte. An Land, bis 1864 auch zur See, repräsentierten der einzelne Bürger und auch die Behörden ihren Status als Bürger oder Organe des United Kingdom durch die Verwendung des Union Jack, "Union Flag" genannt.
Großbritannien hatte in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem eingeführt, in dem:
• Kriegsschiffe einen sogenannten "White Ensign" (Marineflagge), eine weiße Flagge oft mit durchgehendem roten Georgskreuz und mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke,
• Handelsschiffe einen "Red Ensign" (auch "Civil Ensign" → Bürgerflagge genannt, die eigentl. Handelsflagge), eine rote Flagge mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke, und
• Dienstschiffe einen "Blue Ensign" (Regierungsflagge → die eigentliche Staatsflagge), eine blaue Flagge mit dem Union Jack in der Oberecke führten.
Seit 1865 durften Schiffe von Kolonialregierungen einen Blue Ensign mit einem Badge (Abzeichen) im fliegenden Ende verwenden. Die jeweiligen Regierungen sollten entsprechende Bagdes zur Verfügung stellen. Für alle anderen Zwecke war ab diesem Zeitpunkt an Land ausschließlich der britische Union Jack zu verwenden und zur See die übliche rote britische Handelsflagge, der "Red Ensign". Wenn die britische Admiralität der Kolonie die entsprechende Erlaubnis erteilt hatte, durften Handelsschiffe und private Seeleute dieser Kolonien einen Red Ensign mit dem Bagde führen. Dies war für Ostafrika bzw. Kenia und auch Uganda nicht der Fall. Die jeweiligen Regierungen sollten entsprechene Bagdes zur Verfügung stellen.
Ein solches Badge war oft eine auf einer Scheibe platzierte regionale landschaftliche Darstellung, zeigte oft Schiffe, historische Begebenheiten oder konnte auch nur eine Art Logo sein. Sehr oft zeigte ein Badge zusätzlich den Namen des Landes oder auch einen Wahlspruch. Einige Besitzungen hatten aber auch schon von Anfang an ein Wappen, bzw. erhielten über die Jahre eine eigenes Wappen und das Badge wurde abgeschafft. Um ein weitgehend einheitliches Erscheinungsbild im fliegenden Ende der Flaggen zu gewährleisten, wurden Wappen und auch andere Symbole auf einer weißen Scheibe in der Größe der früheren Badges dargestellt. Es gab hier aber auch Ausnahmen, denn einige Kolonien verwendeten diese weiße Scheibe nicht, und platzierten ihr Wappen oder auch nur das Wappenschild - manchmal auch vergrößert - direkt auf das Flaggentuch. Schon in den 40-er Jahren wurde dazu übergegangen die weißen Scheiben zu entfernen und das Wappen direkt zu platzieren oder vergrößert dazustellen. Dieser Umstellungsprozess erfolgte allmählich, nirgendwo gleichzeitig und vollständig. In einigen britischen Besitzungen sind bis heute Flaggen mit der weißen Scheibe in Gebrauch, in anderen nicht mehr und in einigen Gebieten gibt es beide Varianten nebeneinander.
Ab 1893 verwendete die Regierung von Britisch-Ostafrika (auch in Uganda), als britische Kolonie, eine eigene blaue Dienstflagge (Blue Ensign) mit einem Badge im wehenden Teil der Flagge. Das Badge war das beibehaltene Logo der Britischen Ostafrika-Kompanie. Es zeigte eine Sonne mit 24 Strahlen unterhalb der britischen Krone. Das Badge erschien direkt auf dem Flaggentuch und war nicht auf einer weißen Scheibe platziert. Ab 1910 hatte Uganda auch einen Gouverneur. Die blaue Dienstflagge wurde in Uganda 1914 mit einem neuen Badge ausgestattet, in Kenia 1921. Das Badge von Uganda war eine Scheibe und zeigte eine Landschaftsdarstellung mit einem Kronenkranich. Diese Dienstflagge wurde bis zum 01.03.1962 beibehalten. Zu jenem Datum wurde eine neue Flagge eingeführt, sie zeigte drei senkrechte Streifen in Grün, Blau und Grün mit goldenen Trennstreifen und in der Mitte des blauen Feldes einen goldenen Kronenkranich. Großbritannien gewährte Uganda am 09.10.1962 die Unabhängigkeit im Rahmen des Commonwealth, der britische Monarch blieb so Staatsoberhaupt, der vor Ort durch den Generalgouverneur vertreten wird, allerdings nur bis zum 09.10.1963, als Uganda eine Republik wurde. Das Land verblieb jedoch im Commonwealth.
Anlässlich der Unabhängigkeit wurde die heutige Flagge eingeführt. Sie zeigt sechs waagerechte Streifen in Schwarz, Gelb, Rot, Schwarz, Gelb und Rot mit einer weißen Scheibe im Zentrum mit einem Kronenkranich in der Mitte. Schwarz, Gelb und Rot sind die ehemaligen Farben des Uganda People's Congress, der Partei, die das Land in die Unabhängigkeit geführt hat. Rot steht für die Brüderlichkeit aller Menschen, Gelb für die Sonne, Schwarz für die Menschen und für Afrika. Der Kronenkranich wurde vom Badge von Britisch-Uganda übernommen. Die Farben der Flagge orientieren sich vermutlich am britischen Farbsystem, so dass das Farbsystem des Britischen Verteidigungsministeriums gültig sein könnte. Das sieht vor, für Rot = Pantone 186 c und für Tiefgelb = Pantone 116 c.
Quelle:
Flaggen-Atlas Erde,
Flags of the World,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


seit 1962,
Wappen von Uganda,
Quelle, nach: Corel Draw 4

1890–1893, British East Africa,
Badge der Britischen Ostafrika-Kompanie,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

1893–1914, British East Africa,
Badge von Britisch-Ostafrika/Uganda,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World
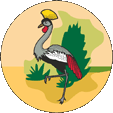
1914–1962,
Badge von Uganda,
Quelle, nach: Flags of the World

Das Staatswappen wurde am 21.09.1962 kurz vor Erlangung der Unabhängigkeit angenommen. Es zeigt einen Bantu-Schild vor zwei gekreuzten Speeren, in seinem oberen Teil mehrere blaue Wellenlinien (sie stehen für die vielen Seen und Flüsse des Landes), in der Mitte des Schildes eine goldene Sonne (Hinweis auf die Lage des Landes unter dem Äquator), und im unteren Teil eine Trommel (Symbol für die königliche Macht). Als Schildhalter dienen eine Gazelle und ein Kronenkranich. Das Schild steht auf einem grünen Hügel mit Kaffee- und Baumwollpflanzen, über den ein Gewässer herabfließt (Quelle des Nil). Darunter in einem Banner das Motto des Landes: "For God and my Country" → "Für Gott und mein Vaterland". Das Badge der Britischen Ostafrika-Kompanie zeigte eine Sonne mit 24 Strahlen unterhalb der britischen Krone. Es wurde bis 1914 beibehalten, danach war es bis 1962 eine Scheibe mit einer Landschaftsdarstellung mit einem Kronenkranich.
Quelle:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


Flugzeugkokarde #1,
Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)

Flugzeugkokarde #2,
Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN)

Lage:
Quelle: CIA World Factbook
Landkarte des Landes:
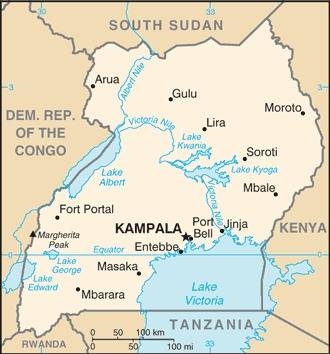
Quelle/Source: CIA World Factbook

Fläche: 241.037 km²
Einwohner: 47.200.000 (2022), davon 18 % Baganda (Bantu), 8 % Banyankole (Bantu), 8 % Bakiga (Bantu), 6 % Lango (Niloten), 4 % Acholi (Niloten), 4 % Lugbara (Niloten), 3 % Banyoro (Bantu), 3 % Batoro (Bantu), 2 % Bahima (Bantu), 6 % Banyarwanda (Bantu), 2 % Karamojong (Niloten)
Religionen: 42 % Katholiken, 32 % Anglikaner, 12 % Moslems, 10 % Protestanten, 1% Animisten
Bevölkerungsdichte: 196 Ew./km²
Hauptstadt: Kampala, 1.500.080 Ew. (2014)
Amtssprachen: Swahili, Englisch
sonstige Sprachen: div. Bantu-, Niloten- und Sudansprachen
Währung: 1 Uganda-Schilling (USh, UGX) = 100 Cent
Zeitzone: MEZ + 2 h
Quelle:
Wikipedia (DE)

Am 08.09.1967 wurden die historischen Königreiche abgeschafft. Das Land war lediglich in 4 Verwaltungsregionen, 15 Unterregionen und 121 Distrikte aufgeteilt. Am 24.07.1993 wurden die Möglichkeit geschaffen, die alten Königreiche wieder einzuführen, um ein gewisses Maß an vor allem kultureller Autonomie zu gewährleisten. In einem bis heute anhaltenden Prozess sind einige Königreiche nach und nach wiedererstanden, so existierten bis 2024 folgende größere Königreiche: Toro, Busoga, Bunyoro, Buganda und Rwenzururu. Das Königreich Ankole, früher ein bedeutendes Königreich, hat bis heute noch keine Anerkennung erhalten. Jedoch sind mehrere andere Königreiche (Padhola) und Häuptlingstümer (Alur, Iteso, Lango) von der Regierung offiziell anerkannt worden. Die Grenzen der größeren Königreiche verlaufen zum allergrößten Teil entlang der Grenzen von Unterregionen.
Quelle: Wikipedia (DE)
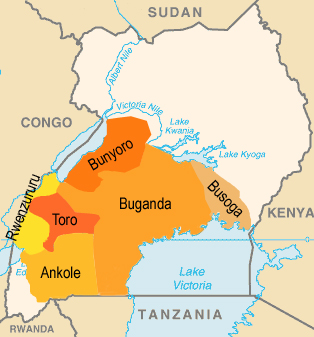
Map/Landkarte: CIA World Factbook, modyfied by: Volker Preuß

seit 1993,
Flagge von Buganda,
Quelle, nach: Mysid, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

seit 1993,
Flagge von Bunyoro,
Quelle, nach: World Statesmen

seit 1993,
Flagge von Toro,
Quelle, nach: World Statesmen

seit 1993,
Flagge von Ankole,
Quelle, nach: World Statesmen
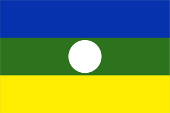
seit 2007,
Flagge von Rwenzururu,
Quelle, nach: World Statesmen

seit 1995,
Flagge von Busoga,
Quelle, nach: Jolle, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons

9. Jahrhundert · Entstehung von Bantu-Stammesstaten im Süden des Landes
17. Jahrhundert · das Königreich Kitwara dominiert die Region
18. Jahrhundert · das Königreich Bunyoro dominiert die Region
19. Jahrhundert · das Königreich Buganda dominiert die Region
1858 · der britische Forscher John Hanning Speke entdeckt den Victoriasee und erkennt ihn als Quellsee des Nils
1871 · Einfall ägyptischer Truppen, der von Niloten bewohnte Norden des Landes kommt als Äquatorprovinz an Ägypten
1877 · Beginn der christlichen Missionierung
1882 · britische Truppen erobern Ägypten
1884/1885 · Kongokonferenz, die britischen Ansprüche auf Buganda werden anerkannt
1885 · der deutsche Kolonialpolitiker Carl Peters besucht Buganda, Abschluss von Verträgen
1882–1898 · Mahdi-Aufstand im Sudan, der Gouverneur der ägyptischen Äquatorprovinz Emin Pascha zieht sich von 1885 bis 1889 nach Wadelai im Norden des Landes zurück
1890 · Ugandavertrag, die Imperial British East Africa Company (IBEA) erwirbt alle deutschen Rechte in Buganda und beginnt mit der Kolonisierung der Region
1893 · das Außenministerium von Großbritannien übernimmt die Verwaltung der Gebiete in Uganda, ab 1895 auch in Kenia, wegen Missmanagements der IBEA
1893 · das Königreich Buganda wird Britisches Protektorat
1894 · Gründung des Protektorats Uganda
1896 · die Königreiche Toro und Bunyoro werden Britisches Protektorat, Buganda, Toro und Bunyoro werden an Uganda angeschlossen
1900 · das Königreich Ankole wird Britisches Protektorat
1900 · Einwanderung von Indern (heute 0,5% der Bevölkerung)
01.04.1905 · Uganda wird aus Britisch-Ostafrika herausgelöst und wird eigenständige Kolonie
bis 1910 · die Stammesgebiete im Südwesten (Chiga, Mpororo), Norden (Lango, Madi, Lugbara, Alur) und Osten (Kumam, Teso, Basoga, Bagischu) werden Britisches Protektorat
bis 1920 · die Stammesgebiete im Nordosten (Acholi, Karamojong) werden Britisches Protektorat
1946 · antibritische Unruhen
1949 · antibritische Unruhen
1953 · der König von Buganda fordert mehr Freiheiten, antibritische Unruhen
1958 · erste Wahlen, Boykott im Königreich Buganda
1960 · anti-monarchistische Unruhen in Buganda
30.12.1960 · Buganda erklärt einseitig seine Unabhängigkeit und den Austritt aus dem britischen Protektorat Uganda, Widerstände der Stammesregionen
1961 · Wahlen, neue Verfassung
01.03.1962 · Großbritannien gewährt Selbstverwaltung (innere Autonomie)
Juni 1962 · Ugandakonferenz, Abkommen über eine föderative Struktur des Landes
09.10.1962 · Großbritannien gewährt die Unabhängigkeit im Rahmen des Commonwealth of Nations
09.10.1963 · Uganda wird Republik, Präsident wird der König von Buganda
1966 · Milton Obote wird Präsident
08.09.1967 · die Königreiche werden abgeschafft
25.01.1971 · Militärputsch durch Idi Amin, Absetzung von Obote
1979 · Vertreibung Amins durch Truppen aus Tansania, das Land bleibt bis 1981 von Truppen Tansanias besetzt
1980 · Wahlen, Milton Obote wird erneut Präsident
1985 · Bürgerkrieg, Obote geht ins Exil, neue Regierung unter Tito Okello
1987 · Bürgerkrieg
24.07.1993 · die Königreiche werden wieder eingeführt
1995 · neue Verfassung
1996 · erste freie Präsidentschaftswahlen, Yoweri Museveni wird Präsident
1997 · Truppen aus Kongo-Kinshasa operieren in Uganda
12.03.2001 · Präsidentschaftswahlen, Yoweri Museveni wird erneut Präsident
2010 · regionale und teilweise Beruhigung des Bürgerkriegs
2011 · Unruhen
Quelle:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97,
Volker Preuß

Der Name "Uganda" leitet sich vom Königreich Buganda ab, dem größten und mächtigsten der vier Königreiche im Land. "Buganda" heißt "Land der Ganda", wobei Ganda "Leute" heißt. Die Baganda sind der größte Bantu-Stamm im Lande, mit 17% Anteil an der Bevölkerung.
Quelle:
Wikipedia (EN), Atlas der wahren Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()


































