mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- democratic presidial republic
- own name: República Dominicana
- US-American zone of influence
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
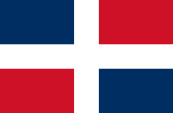
National and merchant flag,
ratio = 15:23,
Source, by:
Flaggen und Wappen,
Corel Draw 4




State and naval flag
ratio = 15:23,
Source, by:
Flaggen und Wappen,
Corel Draw 4






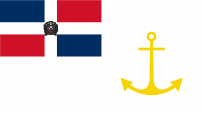
Naval jack
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by: Wikipedia (DE)




since 2000,
Flag of the Army
ratio = 15:23,
Source, by: Ejército Nacional




Flag of the Police
ratio = 15:23,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



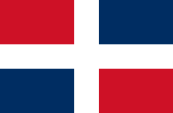
Flag of the President,
ratio = 5:9
Source, by: Flaggen und Wappen



National and merchant flag in war times,
ratio = 15:23,




16th/17th century, to 1801,
to the Spanish sphere of influence,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)



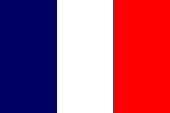
1801–1805,
Flag of France,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4






1805–1808,
Flag of Haiti,
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen




1808–1821,
to the Spanish sphere of influence,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




1821–1822,
National flag,
Source, by: World Statesmen




1822–1844,
Flag of Haiti,
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen



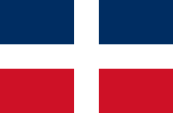
February 1844 to November 1844,
National flag,
Source, by: Flags of the World



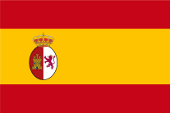
1861–1863,
Flag of Spain,
Source, by: Die Welt der Flaggen



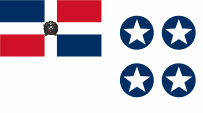
1930–1961,
Flag of the Generalissimo,
Source, by: Flaggenbuch 1939




to ca. 2000,
Flag of the Army,
Source, by: Flags of the World




As the Dominican Republic get independent for the first time in the year 1821, was in use, a yellow-blue-red striped flag flag after the example of Great Colombia, or the flag of Great Colombia itself, because it was aimed a annexation to that state. It disappears with the Haitian annexation in the year 1822. In the anti-haitian liberation fight created the leader of the secret society of the Trintarians, Juan Pablo Duarte, a flag which set a white cross on the initially blue-red flag of Haiti. After the victory over Haiti in the year 1844 this flag became to the flag of the Dominican Republic at the proclamation of the independence on 27th of February in 1844. Because of aesthetical reasons the flag was changed on 6th of November in 1844 (by other sources on 8th of November in 1844) into the today's form. The blue stands for the freedom, the red for the in the fight for freedom sheded blood, the white cross represents the religious believe of the nation. The colors given for the flags today are: red = pt 295, blue = pt 186, green = pt 355, yellow pt 109.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Wikipedia (EN)


Coat of arms of the Dominican Republic,
Source, by:
Flaggen und Wappen,
Corel Draw 4

The in 1844 introduced (and until today only in some details changed) coat of arms of the Dominican Republic shows a blazon after the example of the flag. Median thereupon four crossed Dominican flags, two crossed lances, a opened bible and a golden cross. The scutcheon is surrounded by a garland from ever one palm twig and one laurel twig. Above a blue saying ribbon with the motto of the state in golden letters: "Dios, Patria, Libertad" → "God, Fatherland, Freedom". Below a red banner with the name of the state, likewise in golden letters.
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wappen und Flaggen aller Nationen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
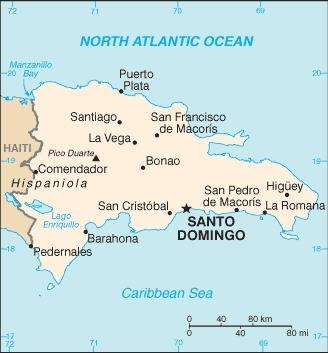
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 18.815 square miles
Inhabitants: 10.700.000 (2019), thereof 70.4% Mestizo/Mulatto, 15.8% Black, 13.5% White
Religions: 75% Roman Catholic, 4% Protestant, 16% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 569 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Santo Domingo, (1936–1961 Ciudad Trujillo), 2.987.013 inh. (2006)
official Language: Spanish
other Languages: Creole French, English
Currency: 1 Dominican Peso (PD, DOP) = 100 Centavos
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

5th of December 1492 · the Spanish seafarer Christoph Columbus discovers that island on which Haiti and the Dominican Republic are today situated, and names it "La Isla Española", and appropriates it for Spain
1494 · start of the Spanish colonization
1496 · foundation of Santo Domingo (today capital of the Dominican Republic), the name of that town gets later taken over for the whole island
1500 · crown colony "Santo Domingo" under a by the Spanish King installed gouverneur
1505 · import of the first black slaves as substitute for the vanishing native Indians
17th cent. · pirates (Buccaneer and Flibusteer) settle down on the coast of the island, especially on the near Tortuga Island (Île de la Tortue), the pirates in the western part of the island stand thereby under French protection
1697 · Peace of Rijswijk, Spain has to cede the western part of the island (Saint Domingue) to France, therewith partition of the island
1794 · abolition of the slavery
1801 · Toussaint l'Ouverture becomes president of Haiti (former Saint Domingue), capture of the Spanish eastern part of the island (Santo Domingo) by the insurgents
1803 · Anti-French riotings, the insurgents strike the French invasors
1st of January in 1804 · Dessalines declares Haiti irrevocably for independent from France and lets proclaim itself as emperor Jacob I. of Haiti, once more intervention by France (in the east of the island)
1805 · Haiti conquers again Santo Domingo (the east of the island), the today's Dominican Republic
1806 · emperor Jakob I. gets assassinated, Blacks and Mulattos turn against each other, civil war, anarchy
1808 · Santo Domingo, the today's Dominican Republic, comes under Spanish rule again
1821 · the Spanish part of the island (Santo Domingo) declares its independence from Spain (Independent State of Spanish Haiti)
1822 · Santo Domingo joins the state Haiti
1843 · overthrow of J. P. Boyer by insurgent Blacks
1844 · revolt of the Mulattos in the initially Spanish part of the island, those separates as independent Republic of Santo Domingo from Haiti (=> Dominican Republic)
27th of February 1844 · independence of the Dominican Republic from Haiti
18th of March 1861 · the Dominican Republic is concerned about a possible occupation by Haiti and is subjects therefore to the protection of Spain and becomes again a Spanish colony colony
14th of September 1863 · the Dominican Republic declares itself as sovereign
11th of July 1865 · Spain recognizes the independence of the country
1869–1870 · US-American intervention
1903–1905 · US-American intervention
1905–1941 · the Dominican Republic is a US-American protectorate
1916–1924 · occupied by troops of USA
1930 · Trujillo coup
1961 · assassinantion of Trujillo
1963 · Bosch became democratical elected president
1963 · military revolt
1964 · mass rebellion
1965 · US-American and OAS intervention
1966 · Balaguer nominated for president
1996 · Reyna became democratical elected president
from 2000 · rotating presidencies after democratic elections
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Wikipedia (D),
World Statesmen

The name of the country has its roots in the name of the capital"Santo Domingo", which means "Holy Sunday". When Columbus on the 5th of December 1492 discovered the island – on which today are placed the states Haiti and Dominican Republic – he named it "La Isla Española" (the Spanish Island), in the course of time it became "Hispaniola". The name is in use until today, although locals sometimes use the word "Kiskeya". Another name for the island was "Santo Domingo", by the in 1496 founded city. In the French part of the island it became "Saint Domingue".
Source: Atlas der wahren Namen,
Wikipedia (D)


![]()


























































