mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Ghana
- presidial republic
- own name: Republic of Ghana
- former name: Gold Coast
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
• Map of the historical Regions

National and merchant flag, jack and standard of the president,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)





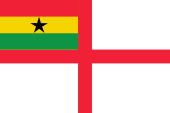
Naval flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flaggen und Wappen



Flag of the air force,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Wikipedia (D)



Civil air ensign,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (D)





to 1957,
flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1964–1966,
National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1963–2003,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 5:8,
Source, by: Flaggen und Wappen




to 2003(?),
Flag of the president,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World

The today's flag of Ghana was introduced on 6th of March in 1957 in occasion to the independence day and reestablished on 28th of February in 1966. It shows three horizontal stripes in red, yellow and green with a black five-jagged star in the yellow middle stripe. The colors of the flag are even known as the "Panafrican colors": Perhaps in 1900 was the beginning of the Panafrica-Movement, wich wants to emphasize the commons of all people with black skin. The colour-triad green-yellow-red, wich used many african and even american countries in their flags after the independence, stands for the political unity of Africa, of all black People. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the origin apply the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent state in Africa. Red stands in the flag of Ghana for the blood, given in the fight for freedom and independence, yellow for the wealth of the land (gold, former name of the country "Gold Coast"), green for forests and agriculture. The star is the "lead-star of the african freedom". Ghana is partially orientated in the British Ensign-System. This points to the connexions to United Kingdom. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" => civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment => the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. Until the independence was used in the Gold Coast the blue, British official flag (Blue Ensign) with the in 1889 introduced emblem (badge). It showed an elephant with threatening gesture in front of a palm tree amid an African scenery. In the lower part of the badge were to see the letters "G.C." in red. In the year 1964 the president Kwane Nkrumah introduced a one-party-system in Ghana. The flag of Ghana was because of that changed in this way, that it equaled the flag of the governing party (Convention People's Party). For it was colored the yellow middle stripe into white. After a military revolt in the year 1966 was re-introduced the old flag again. With the exception of black, the colors are defined as follows: red = Pantone 032, yellow = Pantone 109, green = Pantone 355.
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Die Welt der Flaggen, Flags of the World


Coat of arms of Ghana,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4

The coat of arms of the state Ghana get awarded by queen Elisabeth II. on 4th of march in 1957. The blazon is squared by a golden bordered green cross with a golden leopard: the first field dhowes crossed a baton and a sword, the second field a castle, the third field a cacao tree and the fourth a gold mine. In the middle of the green cross is positioned a golden leopard. He stands for the former colonial power, United Kingdom. Over the shield a torus with a black star and two golden eagles as shield-holders. On the border the motto "Freedom and Justice".
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen


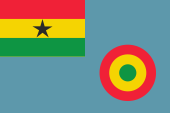
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
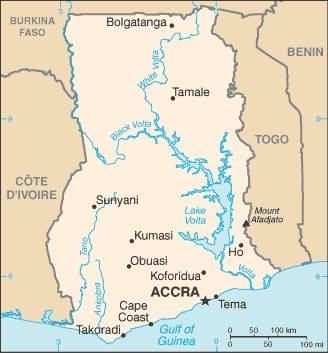
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 92.098 square miles
Inhabitants: 30.790.000 (2021), thereof 47% Akan, 16% Mole-Dagbani, 14% Ewe, 7% Ga-Dangme, 6% Gurma, 2% Grusi and 1,4% European, Arab and Indian
Religions: 71% Pentecostal Christian, 17% Protestant, 10% Catholic, 12% other Christian, 19% Muslim, 3% Animist, 1% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 334 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Accra, 2.388.000 inh. (2017)
official Language: English
other Languages: Asante, Ewe, Fante, Boron (Brong), Dagomba, Dangme, ...
Currency: 1 Cedi (C, GHS) = 100 Pesewas
Time Zone: GMT
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

ca. 1200 · immigration of the Akan tribes
1471 · discovering of the Gold Coast by the Portugese
1482 · foundation of the Portugese Fort Elmina
ca.1500–ca.1870 · foundation and management of many Forts and trade stations by european powers (Netherlands, Brandenburg, France, England, Denmark, Sweden), however since the 18th cent. growing British dominance
1683 · foundation of the Brandenburg-Prussian fort Großfriedrichsburg (until 1720, today called Prince's Town)
1685 · foundation of the Brandenburg-Prussian fort Dorothea (until 1709)
1694 · foundation of the Brandenburg-Prussian fort Takrama (until 1708, today Nsama)
1719 · foundation of the Ashanti Empire of the Akan people (capital = Kumasi)
1750 · only the coast is still controlled by the Netherlands, United Kingdom and Denmark
1807 · the Ashanti Empire achieve his largest expanse
1821 · foundation of the British crown colony Gold Coast
1872 · United Kingdom controles the whole coast
1826–1874 · subjection of the Ashanti Empire by United Kingdom, establishment of the British protectorate over Ashanti-Land
1874–1901 · subjugation of the outback of the Gold Coast (Northern Territory) by United Kingdom, establishment of the British protectorate over the Northern Territory, however triumphs the name Gold Coast for the whole British territory (official since 1874)
1922 · Western Togo (until 1918 German colony) gets incorporated to the Gold Coast as a mandate of the League of Nations
1949 · foundation of the Convention People's Party (CPP) by Kwame Nkrumah
1951 · elections, victory of the CPP, granting of inner self administration for the Gold Coast
1956 · plebiscite in West Togo for the annexion by the Gold Coast
6th of March in 1957 · independence as Dominion of Ghana within the Commonwealth
1st of July in 1960 · Ghana becomes a republic
1964 · establishment of a one-party-system
1966 · military coup d'état, interdiction of the CPP, in consequence military governments, except 1969–1972 and 1979–1981
1981 · party ban
1992 · repeal of the party ban
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Discovery '97,
Wikipedia (D)

The name "Ghana" means translated "king" and goes back to the traditional title of the tribal chiefs.
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen

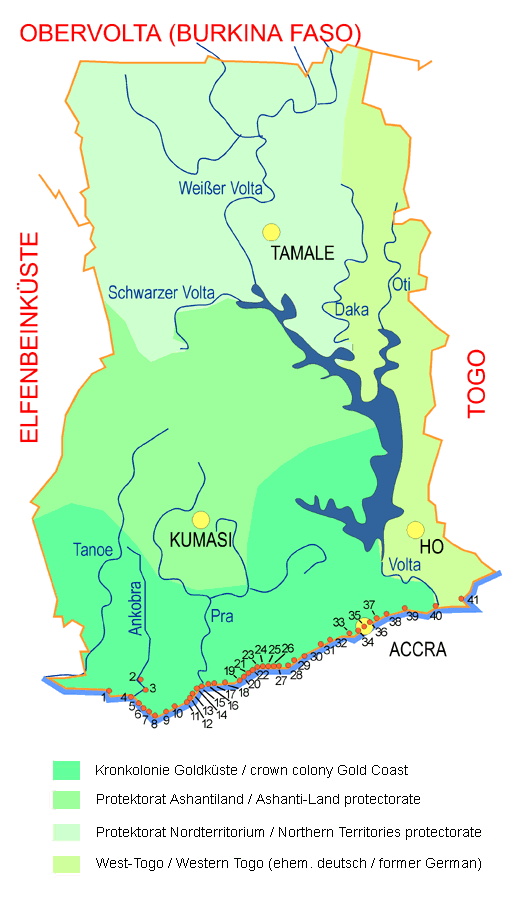
Source: Weltgeschichte
number's cey for the forts and trade stations of the europeans 1482 to 1872:
1 — Apollonia (Beyin) — 1750 brit., 1867 nied., 1872 brit.
2 — Elise Carthago — 1640–1680 nied.
3 — Duma — 1623–1636 port.
4 — Ruyghaver — 1640–1680 nied.
5 — St. Anthony (Axim) — 1515 port., 1642 nied., 1664 brit., 1665 nied., 1872 brit.
6 — Großfriedrichsburg — 1683 brand., 1720–1725 nied.
7 — Takrama — 1694–1708 brand.
8 — Dorothea — 1685–1709 brand.
9 — Metal Cross (Dixcove) — 1691 brit., 1867 nied., 1872 brit.
10 — Batenstein — 1598 nied., 1664 brit., 1665 nied., 1872 brit.
11 — Witzen (Takoradi) — 1652 schwed., 1657 dän., 1659 nied., 1664 brit., 1665-1693 nied.
12 — Sekondi — 1680 brit., 1779 frz., 1867 nied., 1872 brit.
13 — Orange — 1670 nied., 1872 brit.
14 — St. Sebastian (Shama) — 1520 port., 1640 nied., 1664 brit., 1665 nied., 1872 brit.
15 — Fanzösisches Fort — 1680–1688
16 — Commenda — 1670 brit., 1695 nied., 1867 brit.
17 — Vredenburg — 1688 nied., 1782 brit.
18 — São Jorge de Minha (Elmina) — 1482 port., 1637 nied., 1872 brit.
19 — Cape Coast Castle — 1652 schwed., 1659 dän., 1661 nied., 1662 brit., 1663 nied., 1664 brit.
20 — Royal — 1658 dän., 1685 brit.
21 — Portugiesisches Fort — 1650–1662
22 — Nassau — 1598 nied., 1664 brit., 1665 nied., 1782 brit., 1785 nied., 1867 brit.
23 — Britisches Fort — 1660 brit., 1663 nied., 1664 brit.
24 — Anashan (Anamabu) — 1683–1690 port.
25 — William — 1657 schwed., 1659 dän., 1674 brit.
26 — Egya — 1663 brit.
27 — Amsterdam (Saltpond) — 1631 brit., 1665 nied., 1782 brit., 1785 nied., 1867 brit.
28 — Tantamkweri — 1725 brit.
29 — Leydsamheid (Apam) — 1697 nied., 1782 brit., 1785–1811 nied.
30 — Winneba — 1687 brit.
31 — Beraku — 1667 nied., 1782 brit.
32 — Shido — 1690 brit.
33 — Fort James — 1673 brit.
34 — Crèvecoeur — 1650 nied., 1782 brit., 1785 nied., 1867 brit.
35 — Christiansborg (Accra) — 1578 port., 1657 schwed., 1659 dän., 1679 port., 1694 dän., 1850 brit.
36 — Portugiesisches Fort — 1530–1578
37 — Augustenborg — 1787 dän., 1850 brit.
38 — Friedensborg — 1784 dän., 1850 brit.
39 — Vernon (Tema) — 1787 brit.
40 — Konigstein (Ada) — 1784 dän., 1850 brit.
41 — Prinzenstein (Keta) — 1784 dän., 1850 brit.
brand. = brandenburgisch/Brandenburg (← hier klicken)
brit. = britisch/British
dän. = dänisch/Danish
frz. = französisch/French
nied. = niederländisch/Dutch
port. = portugiesisch/Portugese
schwed. = schwedisch/Swedish


![]()




























