mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


• Flag
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

Flag of the province,
ratio = 1:2,
Source: Corel Draw 4







1870–1905,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
World Statesmen,
Flags of the World




1905–1966,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
World Statesmen




The flag of Manitoba was adoped on 12th of May in 1966. It ist orientated in the British Ensign System. This cause and the use of the Union Jack point to the connexions to United Kingdom. United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• war ships fly the "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with an uninterrupted red St. George's-Cross and with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag,
• merchant ships fly a "Red Ensign" (also named "Civil Ensign" → civil flag, the real merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag, and
• governmental ships fly the "Blue Ensign" (flag for the use by the gouvernment → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper staff quadrant of the flag.
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. Very often, a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. Some British possessions, however, already had a coat of arms from the beginning, or their badge was replaced by a coat of arms over the years. To ensure a uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk in the size of the earlier badges. There were also exceptions, because some colonies did not use the white disk and placed their escutcheon or even coat of arms directly on the bunting, sometimes enlarged. Already in the '40s they started to remove the white disk and placed the coat of arms directly or enlarged. This conversion process was done gradually, nowhere at the same time and completely. In some British possessions, flags with the white disc are still in use, in others no more and in some areas are both variants in use, next to each other. Until the year 1922 there had officially been used, the British Union Jack, the so-called Royal Union Flag, by the departments of the provinces, or (from 1922 nearly only) the Canadian blue official flag, the typical British Blue Ensign, with the coat of arms of Canada in the flying end. Nevertheless, the provincial authorities had their own seals and later also coats of arms, which were unauthorized placed in the flying end of the blue official flag. A permit should have been approved by the British authorities for this procedure, this was not the case, but was tolerated. Private individuals had to use the Union Jack and from 1892 the so-called Red Ensign, the red version of the Canadian flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner and the coat of arms of Canada in the flying end. In the course of Canada's gradual separation from United Kingdom, the new maple leaf flag was introduced for Canada in 1965 and the Blue and Red Ensigns – belonging to the British flag system – were abolished as national symbols. This trend was also adopted by some provinces and territories, where new flags were also introduced. In some provinces and territories this process had started earlier. However, not in Ontario and not in Manitoba. Here, people did not agree with the abolition of the British symbolism on the flags. Both provinces created their own Red Ensigns: Ontario in 1965, Manitoba in 1966. This type of flag did not exist there before, because the Canadian Red Ensign was used as the civil flag in these provinces. Only Manitoba had its own Blue Ensign, which was used by government agencies and departments. A Red Ensign is normally a type of flag that may be used by all citizens (actually only at sea), but the Red Ensigns of Ontario and Manitoba (differing from the Ensign system) are also used as provincial flags by authorities and departments. The flags of these provinces follow in this way British specifications due to history. They are: Blue = Pantone 280, Red = Pantone 186, Yellow = Pantone 116, Green = Pantone 364.
Source:
Volker Preuß,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Enzyklopädie,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (EN)


Escutcheon of Manitoba,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4

There is a regular coat of arms for Manitoba, with a console, shield holders (supporters), withe a crest and the motto. Here is only shown the central part of the coat of arms, the escutcheon. The escutcheon of Manitoba shows in the shield's head the English Cross of St. George, beneath a bison in the prairie, a hint for Manitoba as a prairie province.
Source:
Volker Preuß

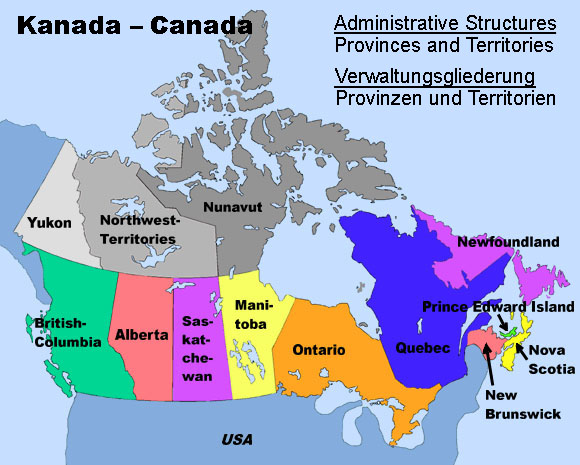
Map: Volker Preuß

Area: 250.115 square miles
Inhabitants: 1.387.000 (2016), thereof 14 % native Indians
Density of Population: 6 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Winnipeg, 778.500 inh. (2016)
official Languages: English, French
other Languages: German, Ukrainian
Currency: Canadian currency
Time Zone: GMT – 6 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

1613 · Thomas Button discovers the area of the today's Manitoba
1670 · Charles II., King of England, gives large parts of the today's north of Manitoba to the Hudson's Bay Company, in the following years pelt rade with the natives, the south of Manitoba is ranged by French
1738 · foundation of Fort Rouge
1822 · the Hudson's Bay Company builds in place of Fort Rouge the Upper Fort Gary, the arising estate is named Winnipeg
1869 · the Hudson's Bay Company cedes all their prerogatives to the British Dominion of Canada
1870 · foundation of the Province of Manitoba, named after the Manitoba Lake. The word "Manitoba" is from native Indian origin and means "path of the great spirit", Winnipeg becomes capital
1912 · territorial enlargement in the north by annexion of great parts of the Territory of Keewatin
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (D),
Discovery '97

The name of the province goes back to the Manitoba Lake an the Cree Indians. They called it
manitou-bou, which is to translate as "Path of the Great Spirit".
Source:
Wikipedia (D), Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()












