
The Roman Empire initially has no flag. The legions used as military field sign so named legion's eagles, which were used in principle like a standard, were object of high respect, and had a very great ideal value. Very noted is the Roman seal, the four letters "SPQR" (Senatus Populusque Romanus) → „senate and people of Rome“. This was in the official usage very often applyed, and was to find on buildings or even military field signs. As Constantin in the year 312 triumphed over Maxentius near the Milvian bridge, he used an older Roman cloth flag, which received in consequence of his victory the character of an empire's banner. About the designing of this flag is nothing known, but one assumes, even because of temporal later made depictions, that it obviously was a red, by the coat of arms of the town Rome inspired flag. This banner was added before the battle near the Milvian bridge by christian symbolism because of a vision of Constantin. How, and exact wherewith, is not known. A cross was it indeed not, because Constantin's instruction of construction told from a combination of two letters, from them one arises by crossing of two lines. Probably was it the monogram of Christus. This flag will also not have been attached to the pole as we know it today. The flag cloth was certainly square and hung on a crossbar.
Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Volker Preuß

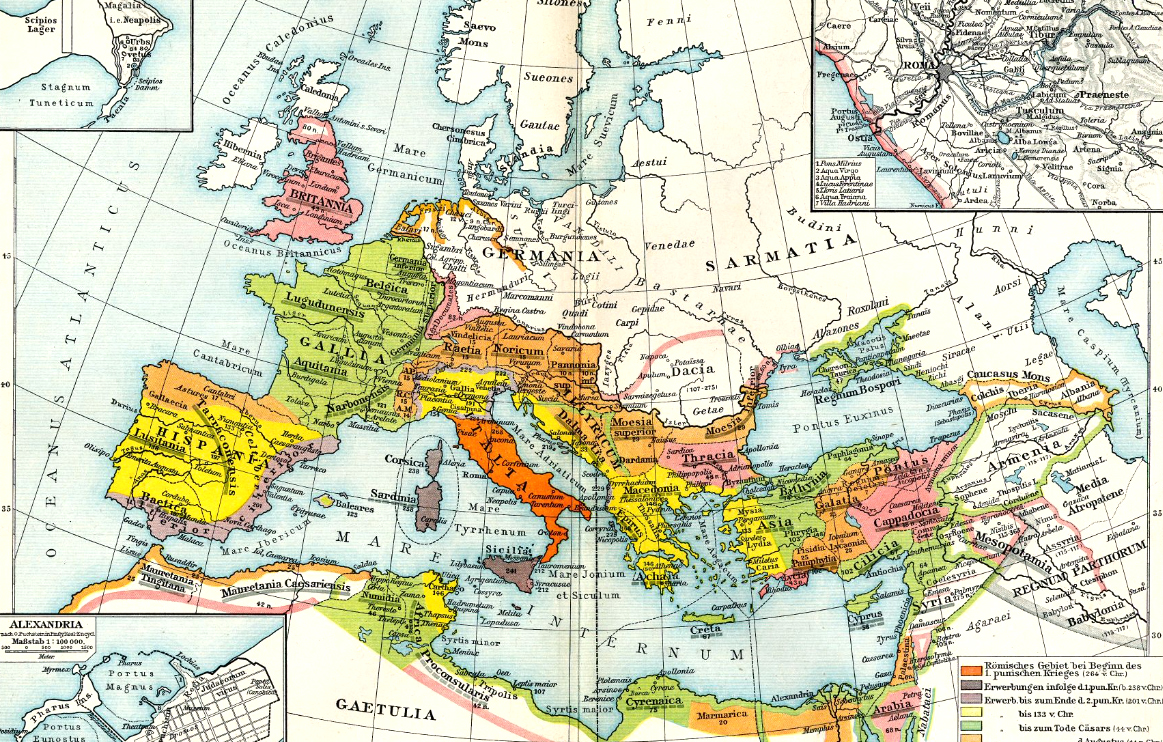
Source: F. W. Putzgers Historischer Schul-Atlas

Area: ca. 9.117.000 square miles (5 A.D.)
Inhabitants: 50 to 90 Mio. (5 A.D.)
Capital: Rome
official Language: Latin
Currency: Denarius system, ca.: 1 aureus = 25 denarii = 100 sesterces = 200 dupondies = 400 aces = 800 semis = 1600 quadrants
Source:
Wikipedia (DE),
Wikipedia (EN)

753 B.C. · foundation of Rome Town
bis 218 B.C. · conquest of nearly the whole Italian peninsula
201 B.C. · conquest of the Iberian peninsula
228 B.C. · conquest of Illyria (Dalmatia)
148–146 B.C. · conquest of Greece (Macedonia)
146 B.C. · conquest of Carthago
74–64 B.C. · conquest of Cyrenaica and Little Asia
58–51 B.C. · conquest of Gallia
41–42 B.C. · conquest of North Africa
30–10 B.C.. · conquest of european territories up to the Danube River (Donau)
30 B.C. · conquest of Egypt
20 B.C. · conquest of Libya
12 B.C. to 9 · failed subjection of Germania (Teutons)
43 · conquest of Britain
63 · conquest of Cappadocia
105–107 · conquest of Dakia, Arabia, Mesopotamia, Assysria and Armenia
117 · loss of Mesopotamia, Armenia and Assysria
162–180 · first Teuton invades
270 · loss of Dakia
378–395 · further Teuton invades
395 · partition of the empire in West Roman Empire and East Roman Empire
409–420 · loss of Spain and Gallia to the Teutons
429 · loss of North Africa to the Teutons
476 · dismissal of the last Roman emperor Romulus Augustulus, end of the (West)Roman Empire
486 · collapse of the Realm of Syagrius
Source: Atlas zur Geschichte,
Weltgeschichte,
Wikipedia (EN)

The name of the country as "Roman Empire" goes back to the city of Rome and is a literal translation of the own name "Imperium Romanum". Occasionally one reads "Imperium Romanorum", which would be the "Empire of the Romans".
Source: Volker Preuß


![]()



![]()
