mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Kingdom of Bhutan
- Monarchy with an initial stage of a parlamentary System, without parties
- own names: "Druk Yul Khab" or "Druk Gaykhab"
• Flag
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name
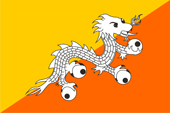
National flag,
ratio – ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4,
Wikipedia (D)







1949 - 1956,
National flag,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: World Statesmen,
Flags of the World



1956 - 1969,
National flag,
ratio = 4:5,
Source, by: World Statesmen,
Flags of the World




The flag of Bhutan is divided diagonally yellow (actually saffron yellow) over orange, and shows in the middle – above all – a white dragon looking to the waving end of the flag. The Tibetan word for Bhutan is "Druk Yul", what means "Dragon Empire". The flag goes back to an initiative of the king in 1949. The first version was square, diagonally divided yellow over red and the dragon was green. In the 50s of the 20th century, the dragon was oriented towards the flagpole so that it faces the wind and the aspect ratio of the flag was adjusted to 3:4. In 1969 changes were made to the flag. The dragon is now looking away from the flagpole again, and the red in the flag has been replaced by orange and the aspect ratio of the flag has been adjusted to 2:3. The dragon holds a sphere in each of its fangs and represents the universe. That sphere, which the dragon holds up a little, is supposed to be the globe, and on some representations even flames burst out of it. Saffron yellow stands for the secular power of the king, and orange red for the spiritual power of Buddhism. The white color embodies cleanliness and honesty.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
World Statesmen,
Flags of the World


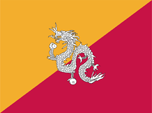
since 1980,
Coat of arms of Bhutan,
Source:
Wikipedia (DE), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

The national coat of arms of Bhutan was redesigned in 1980. It shows a vajra-wheel, a symbol that stands for impenetrability, indissolubility, indivisibility, indestructibility and enlightenment. The wheel is protected by two dragons. They each stand for the secular and spiritual authority. Below the wheel, between the dragons, is placed a lotus flower, a Buddhist emblem. The gemstone "Umbrella" is shown above the wheel. According to other sources, this figure is a parasol, even a Buddhist symbol, but this interpretation is probably a somewhat unfortunate literal translation of the word "umbrella".
Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
1.) Wikipedia (DE)
2.) Wikipedia (DE)

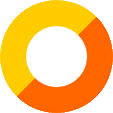
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
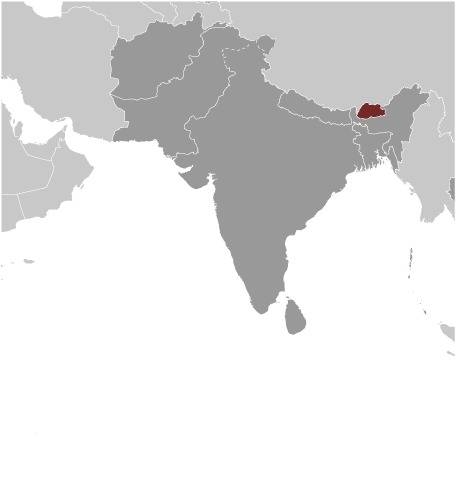
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
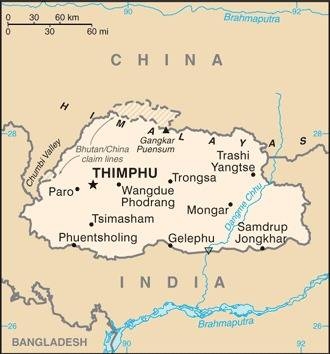
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 99.440 square miles
Inhabitants: 741.700 (2019), thereof 50% Bhutanese (also called: Ngalop, Bhote, Bhutias, Drupka), 35% Nepali
Religions: 75% Lamaistic Buddhism, 22% Hinduism
Density of Population: 50 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Thimphu, 114.551 inh. (2017)
official Language: Dzongkha
other Languages: Nepalese, Hindi
Currency: 1 Ngultrum (Nu) = 100 Chhetrum, 1 Indian Rupie (iR) = 100 Paise
Time Zone: GMT + 6 h
Source: Wikipedia (D),
CIA World Factbook

Early Middle Ages · The region is inhabited by the people of Thepu, formation of a Hindu principality which comes under the rule of Tibet. By mixing of Thepu and Tibetans formes the people of the Bhutia
8th century · penetration of Buddhism
12th century · Buddhism is the state religion
1189 · foundation of the monastery Druk Seva Yangchoobling
1557 · The chieftain of the Bhutia, Shabdung Rimpoche Nawang Namgyal, takes over the power and founds the State of Bhutan, which is defended fiercely against Tibet
1592 · death of Shabdung Rimpoche Nawang Namgyal, laizistic separation of the power under a secular and a spiritual ruler
1767 · Bhutan comes under the suzerainty of China
1772 · beginning British influencing
1864 · partial British occupation
1895 · pro-British Wang-Chuk-revolt
1907 · introduction of hereditary monarchy (Kingdom of Bhutan under the Wang-Chuk Maharajas)
1910–1947 · Bhutan is under the protectorate of the United Kingdom
1935 · British India accepts the autonomy of Bhutan
1949 · India assumes the British protectorate
1954 · formation a first Parliament
1968 · formation a first government
1971 · the Indian protectorate ends
since 1990 · the government pursues a restrictive policy against foreign infiltration by Nepalese immigrants
Source:
Weltgeschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (D)

The name "Bhutan" is derived from the Sanskrit words "Bhota" and "Anta". "Bhota" is the ancient Indian name for Tibet, "Anta" is the End (in the sense of Boundary). Bhutan is: "The Boundary of Tibet." The Bhutia call their country "Druk Jul", which means "Dragon's Empire". The country's name derives from the name of the monastery "Druk Seva Yangchoobling", that was at the time of the creation of the state the administrative center of the country.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
World Statesmen,
Volker Preuss


![]()















