Botswana |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Botswana |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
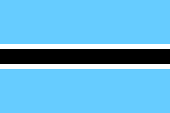 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
Flagge der Armee – flag of the army, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
Präsidentenflagge – flag of the President, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source nach/by: Wikipedia (NL) |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
1884–1966, Flagge von Großbritannien – flag of the United Kingdom, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source: World Statesmen |
 |
1907–1931, |
 |
1931–1966, |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die heutige Flagge ist seit dem 25.01.1966 (nach anderen Quellen seit dem 30.09.1966) eingeführt, von George Winstanley geschaffen, und geht auf die Flagge der Botswana Democratic Party (drei horizontale Streifen in Weiß, Rot und Schwarz) zurück. Sie zeigt insgesamt fünf waagerechte Streifen, drei Streifen in Hellblau, Schwarz und Hellblau, jeweils durch einen schmalen weißen Streifen getrennt, im Verhältnis 9:1:4:1:9. Das Hellblau steht für die Sehnsucht des Landes nach Wasser und symbolisiert auch den blauen Himmel über dem Land. Schwarz steht für die Mehrheit der Bevölkerung, Weiß für die weiße Minderheit. Die Flagge drückt somit den Wunsch eines friedlichen Zusammenlebens der schwarzen Bevölkerung mit der weißen Minderheit aus. | Today's flag was
introduced on the 25th of January, 1966 (other sources mention the 30th of September,
1966), It was created by George Winstanley, and goes back to the flag of the Botswana
Democratic Party (three horizontal stripes in white, red and black). Altogether it shows five horizontal stripes, three stripes in pale blue, black and pale blue, each separated by a narrow white stripe, in the ratio 9:1:4:1:9. The pale blue stands for the yearning of the land for water and symbolizes even the blue skies above the land. Black stands for the majority of the people, white for the white minority. This way the flag expresses the wish for a peaceful coexistence between the black majority and the white minority. |
| Quelle/Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt Translator of the above English text: Joachim Nuthack |
|
| Zur Zeit des britischen Protektorats hatte Betschuanaland keine eigene Flagge. Es wurde durch einen britischen Hohen Kommissar von Südafrika aus verwaltet, und es wurde der britische Union Jack verwendet. | In the times of the
British protectorate Bechuanaland had no own flag. It was administrated by a British High Commissioner in South Africa, and it was used the British Union Jack. |
| Der britische Hohe Kommissar hatte seit 1907 seine eigene Flagge. Es handelte sich um die für Hohe Kommissare übliche Flagge, den Britischen Union Jack mit dem Abzeichen des Hohen Kommissars in der Mitte, eine von einem Kranz umgebene Abkürzung mit der britischen Krone darüber. Bis 1931 war der Britische Hohe Kommissar für Südafrika (Abkürzung: S.A.H.C.) für Betschuanaland zuständig, das von Mafeking in Südafrika aus verwaltet wurde. Nach dem Westminsterstatut wurde Südafrika 1931 unabhängig, und der Hohe Kommissar war nur noch für Betschuanaland, Basutoland und Swasiland zuständig (Abkürzung: H.C.). | The British High Commissioner had his own flag since 1907. It was the for the High Commissioners usual flag, the British Union Jack with the badge of the High Commissioner in the middle, an abbreviation with the British Crown above, surrounded by a garland. Until 1931 the British High Commissioner in and for South Africa (abbreviation: S.A.H.C.) was responsible for Bechuanaland, which was administered from Mafeking in South Africa. After the Statute of Westminster South Africa in 1931 became independent, and the High Commissioner was responsible only for Bechuanaland, Basutoland and Swaziland (abbreviation H.C). |
| Quelle/Source nach/by: Flags of the World | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen von Botswana – coat of arms of Botswana, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Staatswappen von Botswana ist seit dem 25.01.1966 (30.09.1966) eingeführt. Es zeigt auf einem weißen afrikanischen Schild drei blaue Wellenlinien, darüber die Industrie symbolisierende Zahnräder, und darunter ein die Landwirtschaft symbolisierender Stierkopf. Die Wellenlinien stehen für das Wasser, und verweisen, wie die Inschrift "Pula" (Regen), auf die große Bedeutung des Wassers. Schildhalter sind Zebras. Die Farben Schwarz und Weiß symbolisieren auch hier die beiden Rassen, die im Lande leben. Links und rechts des Wappens ist noch ein Elefantenstoßzahn und eine Sorghum-Pflanze zu sehen. | The coat of arms of
Botswana was also introduced on the 25th of January, 1966 (30th of September, 1966). It
shows on a white African shield three blue wave lines in the centre, with sprockets above,
symbolizing industry, and a bull head below, symbolizing agriculture. The wave lines
represent water, and refer, as the inscription "Pula" (rain), to the great
importance of water. Shield holders are zebras. The colors black and white symbolize even with this both races, which live in the land. To the left and right of the scutcheon also stand one elephant tusk and a sorghum plant respectively. |
| Quelle/Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Wappen der Welt Translator of the above English text: Joachim Nuthack |
|
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage
– Position: |
Landkarte
des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
|
16./17. Jhd. · Tswana beginnen zu siedeln 1820 · beginnende britische Kolonisierung 1889 · britische Verwaltung 1895 · britisches Protektorat 30.09.1966 · Unabhängigkeit von Großbritannien 1985–1986 · Streitigkeiten mit Südafrika |
History: |
|
16th/17th cent. · Tswana begin to settle 1820 · beginning British colonization 1889 · British administration 1895 · British protectorate 30th of September 1966 · independence from United Kingdom 1985–1986 · quarrels with South Africa |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D) |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Der Name des Landes leitet sich vom Namen des Volkes der Tswana ab, die 75% der Bevölkerung stellen. | The name of the country comes from the name of the Tswana people, which is 75% of the population. |
| Quelle/Source: nach/by Wikipedia (D) | |