mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- 1296–1689 Duchy of Saxony-Wittenberg (Saxe-Wittenberg)
• Flag
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

1296–1689,
Colours of the Duchy of Sachsen-Wittenberg,
notional





The colors of the Saxon duchies were always black and gold. They are derived from the Saxon coat of arms, which goes back to the County of Ballenstedt and the colors of the German Empire. Black and gold have been used for document cords and for many military field signs since the 17th century. However, national colors in the modern sense, they were not yet. The colours of the German states are (called Landesfarben, are often derived from the colours of the coats of arms, and used as cockades, as well as flags), were formed – especially in the German inland countries – rather late, often after the French Revolution and the following wars of liberation. In the period from ca. 1815 to ca. 1830, this process was finally completed in all German states.
Source: Volker Preuß,
Jens Hild


1180–1296,
Coat of arms of the Duchy of Saxony,
Source: Wikipedia (D)

1296–1365,
Coat of arms of the Duchy of Saxony-Wittenberg,
Source: Wikipedia (D)

1370–1689,
Coat of arms of the Electorate of Saxony,
Source: Wikipedia (D)

The Duchy of Saxony-Wittenberg retained the coat of arms of the Duchy of Saxony, the nine-fold divided black and gold shield with the green diamond wreath. The coat of arms of the Duchy of Saxony, which is until today the emblem of the Free State of Saxony, was created about 1180, as the Ascanians, Margraves of Brandenburg and Counts of Ballenstedt became to the Dukes of Saxony: over the coat of arms of Ballenstedt was placed a green diamond wreath. From 1370, the Electors of Saxony added to their coats of arms two crossed red swords on a between black and silver divided background. They are called "Electoral Swords" because they should stand for the dignity of the Electorate. In reality is hidden behind the dignity of the Arch Marshal, the military deputy of the emperor.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Volker Preuß

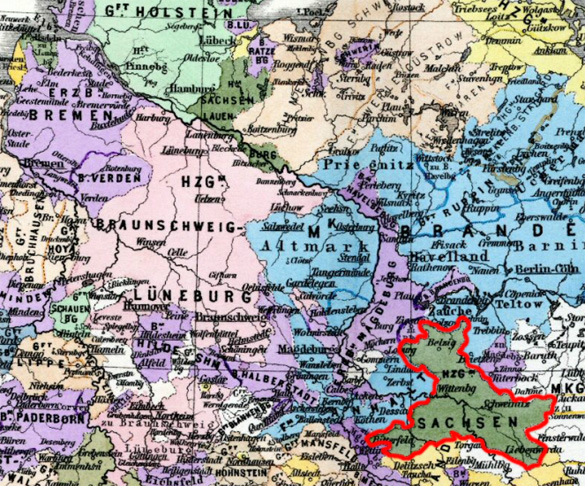
Source: Hand-Atlas für die Geschichte des Mittelalters und die neueren Zeit, 1880, modyfied by: Volker Preuß
The map shows the Duchy of Saxony-Wittenberg in about the year 1400, within a red border.

Area: unknown
Inhabitants: unknown
Capital: Wittenberg (to 1423)
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

The history of Saxony begins with the ancient tribal Duchy of Saxony in today's northwestern Germany in the 5th century. In the Saxon Wars of Charlemagne (772–804), it was conquered and became annexed by the Franks, but it remained, however, as a duchy. Important dukes have been the dukes from the Welf Dynasty (Guelph), known for her opposition to the Hohenstaufen emperors, which ended in 1180 in the desintegration of the duchy by the emperor. The title of the Duke of Saxony remained, but was associated with peripheral regions of the ancient duchy and walked – with the investiture of various noble families – in principle the River Elbe up to the today's Saxony in central Germany. The Duchy of Saxony-Wittenberg came into beeing with the inheritance of the duchy in 1296 and was an historical and geographical bridge between the old and new Saxony. That's why it is sometimes called the "younger Duchy of Saxony", wich ends with the elevation to an electorate in 1356.
400 · the Saxons settle between the Rivers Elbe, Saale, Rhine and Ems, formation of the duchy
804 · end of the Saxon Wars, the region becomes part of the Frankish Empire under Charlemagne
929 · the German King Henry I. conqueres with an army the settlement area of the Hevelli tribe, establish of the Nordmark (North Mark)
983 · Slavs revolt, recapturing of the Nordmark by the Slavs
1134 · Albrecht the Bear from the Ascanian dynasty gets handed over the Nordmark by the German King Lothar von Supplinburg as Margrave of the Nordmark, probably in the hope of its recapturing
1142 · Henry the Lion of the House of Guelph (Welf) receives Brunswick and the Duchy of Saxony as a fiefdom
1157 · Albrecht the Bear conqueres Brandenburg, formation of the Mark Brandenburg, Margraves become the Ascanians, immigration of Germans and Flemings
1180 · in the conflict with the Staufen Emperor, Henry 'the Lion' gets outlawed, in the following struggles Henry 'the Lion' subjects and loses all possessions (even Bavaria), except Brunswick and Lueneburg, and some very small areas, Duke of Saxony becomes the Bernhard I. of Anhalt (Ascanian Dynasty), but only with parts of Eastphalia on the middle of Elbe River, and some areas on the lower Elbe: Lauenburg and Hadeln. Westphalia and Engern had been separated by the emperor. The Ascanians claimed these territories unswervingly and on throughout the ages
1181 · built of the Lauenburg, it is residence to the division of 1296
1187 · first mention of the castle of Wittenberg to protect a crossing point over the River Elbe and near important crossroads
1260 · death of the Duke of Saxony, Albrecht I. of Anhalt (Ascanians), the inheritance goes to his brothers John I. and Albert II.
1296 · Albert II. and the three sons of John I. share the Duchy of Saxony into the Duchies of Saxony-Lauenburg and Saxony-Wittenberg, both duchies keep the Electorate
1356 · Emperor Charles IV. passes the Golden Bull (a kind of constitution), the electoral dignity will be removed from Saxony-Lauenburg and remains with Saxony-Wittenberg (in the future so called Electorate of Saxony), Saxony-Wittenberg also receives the titels of the Imperial Vicar and the Arch Marshal
1356–1370 · reign of the Elector Rudolf II.
1370–1388 · reign of the Elector Wenzel, brother of Rudolf II.
1388–1419 · reign of the Elector Rudolf III., son of Wenzel
1419–1422 · reign of the Elector Albert III., brother of Rudolf III., with the death of Albert III. dies out the Wittenberg line of the Ascanians, Saxony-Lauenburg makes inheritance claims
6th of January in 1423 · King Sigismund awards on the basis of merits in the Hussite Wars, the Electorate of Saxony and the Palatinate of Saxony to Friedrich IV., Margrave of Meissen (Wettin Dynasty), Friedrich IV. calles itself Frederick I. as Elector
1st of August in 1425 · solemn investiture of Frederick I. in Ofen in Hungary
In the following years, the term "Saxony" became extended to all the possessions of the Wettin family, especially to the Mark Meissen. To distinguish it from the old Saxony, the ancient Duchy of Welf Dynasty (Guelph), the Wettin Saxony was called "Upper Saxony". This remained so until that point in time, when the name "Hanover" had prevailed for the old Saxony areas, latest by the elevation to the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814. Upper Saxony in 1806 also became a Kingdom, and the title of an elector was no longer necessary with the collapse of the empire in 1806. The Kingdom of Hanover existed until 1866, the Kingdom of Saxony until 1918.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
RetroBib Retrobibliothek

The name "Wittenberg" could be derived from the word "white mountain", but also a Slavic root is possible, using the word "vysoka", what means "high up". The castle is situated in the flat countryside near Elbe River, but there on a hill.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
Volker Preuß







![]()








