Grenada |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Grenada |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flaggen – Flags: |
|
 |
Nationalflagge – national flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 3:5, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4 |
 |
Handels- und Seedienstflagge – merchant flag and official flag at sea, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
 |
Marineflagge – naval flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (D) |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
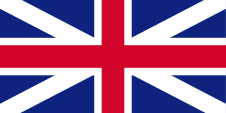 |
1762–1801, Flagge Großbritanniens – flag of United Kingdom, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen |
 |
1801–1875, Flagge Großbritanniens – flag of United Kingdom, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Die Welt der Flaggen |
 |
1875–1903, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
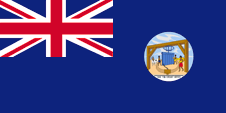
1903–1958, Windward-Inseln Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
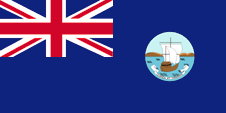 |
1903–1967, Flagge der Regierung (Staatsflagge) – flag of the government (state flag), Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
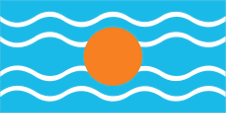 |
1958–1962, Flagge der Westindischen Föderation – flag of the Federation of the West Indies, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 1:2, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
 |
1967–1974, Nationalflagge – national flag, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World |
Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge – Meaning/Origin of the Flag: |
|
| Die heutige Flagge Grenadas wurde am 07.02.1974 eingeführt. Sie zeigt vier Dreiecke in Grün und Gelb, von einem roten Rand umgeben. In der Mitte ein gelber Stern auf einer roten Scheibe, und sechs weitere in dem roten Rand. Die sieben Sterne symbolisieren die sieben Verwaltungsbezirke der Insel. Im grünen Dreieck auf der Lieckseite befindet sich eine Muskatnuss, der wichtigste Exportartikel der Insel. | The today's flag of Grenada was introduced on 7th of February in 1974. It shows four triangles in green and yellow surrounded by a red border. In the middle a yellow star on a red disk and further six in the red border. The seven stars are symbolize the seven administrative districts of the island. In the green triangle near the pole is a nutmeg, the most important export of the island. |
| Die Farbkombination von Grün, Gelb und Rot in der heutigen Flagge sind die Panafrikanischen Farben: Etwa 1900 setzte die Panafrika-Bewegung ein, die Gemeinsamkeiten aller Menschen mit schwarzer Hautfarbe hervorheben wollte. Für die politische Einheit Afrikas steht der Farbendreiklang Grün-Gelb-Rot, den viele afrikanische Staaten nach Erlangung ihrer Unabhängigkeit in ihre Flaggen übernahmen. Das erste Land war Ghana im Jahr 1957. Als Ursprung gelten die Landesfarben von Athiopien (Abessinien, dem ältesten unabhängigen Staat Afrikas. | The
combination of the colours green, yellow and red in the today's flag are the
pan-african colours: Perhaps in 1900 was the beginning of the
Panafrica-Movement, wich wants to emphasize the commons of all people with
black skin. For the political unity of Africa stands the colour-triad green-yellow-red, wich used many african countries in their flags after the independence. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the origin apply the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent state in Africa. |
| Bis 1960 gehörte Grenada zur britischen Kolonie der Windward-Inseln und wurde dann eine eigenständige Kolonie. Die Nationalflagge war in dieser Zeit ein sogenannter "Blue Ensign", ein dunkelblaues Flaggentuch mit einer Flaggendarstellung – dem britischen Union Jack – in der Oberecke. Der Union Jack wies auf die Verbindungen zu Großbritannien hin. | Until
1960 Grenada belonged to the British Windward Islands Colony and became then
a self-contained colony. The national flag was in that times a so called
"Blue Ensign", a dark blue flag with a flag depiction – the British Union
Jack – in the upper left staff quadrant. The Union Jack pointed out to the
connections to United Kingdom. |
Großbritannien hatte in Jahr 1864 ein Flaggensystem eingeführt, in dem:
Seit 1865 durften Schiffe von Kolonialregierungen einen Blue Ensign mit einem Badge (Abzeichen) im fliegenden Ende führen. Die jeweiligen Regierungen sollten entsprechene Bagdes zur Verfügung stellen. Handelsschiffe und seefahrende Privatpersonen aus Kolonien dürfen nur dann einen Red Ensign mit Badge führen, wenn von der britischen Admiralität eine entsprechende Erlaubnis für die Kolonie erteilt wurde. |
United Kingdom introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
Since 1865 ships of colonial governments were permitted to fly the Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end of the flag. The respective governments were asked to design appropriate badges. Merchant ships and seafaring persons from colonies were only permitted to use the Red Ensign with a badge, then also named Civil Ensign, if permission has been given to the respective colony by the British admiralty. |
| Ein solches Badge war oft eine auf einer Scheibe platzierte regionale landschaftliche Darstellung, zeigte oft Schiffe, historische Begebenheiten oder konnte auch nur eine Art Logo sein. Sehr oft zeigte ein Badge zusätzlich den Namen des Landes oder auch einen Wahlspruch. Einige Besitzungen hatten aber auch schon von Anfang an ein Wappen, bzw. erhielten über die Jahre eine eigenes Wappen und das Badge wurde abgeschafft. Um ein weitgehend einheitliches Erscheinungsbild im fliegenden Ende der Flaggen zu gewährleisten, wurden Wappen und auch andere Symbole auf einer weißen Scheibe in der Größe der früheren Badges dargestellt. Es gab hier aber auch Ausnahmen, denn einige Kolonien verwendeten diese weiße Scheibe nicht, und platzierten ihr Wappen oder auch nur das Wappenschild - manchmal auch vergrößert - direkt auf das Flaggentuch. Schon in den 40-er Jahre wurde dazu übergegangen die weiße Scheibe zu entfernen und das Wappen direkt zu platzieren oder vergrößert dazustellen. Dieser Umstellungsprozess erfolgte allmählich, nirgendwo gleichzeitig und vollständig. In einigen britischen Besitzungen sind bis heute Flaggen mit der weißen Scheibe in Gebrauch, in anderen nicht mehr und in einigen Gebieten gibt es beide Varianten nebeneinander. | Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showing ships, historical events or even a kind of a logo. Very often, a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto.
Some British possessions, however, already had a coat of arms from the beginning, or their badge was replaced by a coat of arms over the years. To ensure a uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk in the size of the earlier badges. There were also exceptions, because some colonies did not use the white disk and placed their escutcheon or even coat of arms directly on the bunting, sometimes enlarged. Already in the '40s they started to remove the white disk and placed the coat of arms directly or enlarged. This conversion process was done gradually, nowhere at the same time and completely. In some British possessions, flags with the white disc are still in use, in others no more and in some areas are both variants in use, next to each other. |
| Die Flagge der Windward-Inseln trug ein anderes Badge. Es zeigte einen vierfach geteilten Schild mit den Farben Rot, Gelb, Grün und Weiß, umgeben von einem weißen Gurt mit der Inschrift "Governor in Chief, Windward Islands", oberhalb die britische Krone. Unterhalb ein weißes Spruchband mit dem Motto der Inseln: "i pede fausto" → "Gehe mit gesegnetem Fuß". | The flag of the Windward Islands carryed an other badge. It showed a fourfold divided shield with the colours red, yellow, green and white, surrounded by a white belt with the inscription "Governor in Chief, Windward Islands", above the British crown. Below a white banner with the motto of the islands: "i pede fausto" → "go with blessed foot". |
| Die einzelnen Kolonien der Windward-Inseln führten jedoch meist ihre eigenen "Blue Ensigns" mit einem eigenen Badge. Die Flagge der Windward-Inseln wurde ebenfalls nur von der Regierung der Kolonie verwendet. | The separate colonies of the Windward Islands had however mostly used their own "Blue Ensigns" with an own badge. The flag of the Windward Islands was was also used only by the government of the colony. |
| 1875 bis 1903 verwendete Grenada, als britische Kolonie, die blaue britische Dienstflagge (Blue Ensign) mit einem Badge im wehenden Teil der Flagge. Das Badge zeigte auf einer Scheibe eine von einem Ochsen-Göpel angetriebene Zuckermühle und einige Landarbeiter. Unterhalb das damalige Motto der Insel: "Hae tibi erunt artes" → "Diese Künste werden dir gehören". | Grenada
used the official blue British flag, the Blue Ensign, with a Badge in the
flying end of the flag between 1875 and 1903. The Badge showed on a disk a by an ox-capstan driven sugar-mill and some farmhands. Below the then motto of the island: "Hae tibi erunt artes" → "This arts will be yours". |
| Zwischen 1903 und 1967 zeigte das Badge ein in Richtung Küste fahrendes Schiff. Unten, auf einen Spruchband, das damalige Motto der Insel: "Clarior e tanebris". | The badge showed a in direction of the coast sailing ship between 1903 and 1967. Below – on a banner – the then motto of the island: "Clarior e tanebris" |
| Am 27.02.1967 wurde durch Großbritannien innere Selbstverwaltung gewährt, und Grenada wurde ein autonomer, mit Großbritannien assoziierter Staat. In diesem Zusammenhang wurde eine Flagge eingeführt, welche die Tradition der "Blue Ensigns" beendete. | United Kingdom granted interior self administration on 27th of February in 1967, and Grenada became an autonomous with United Kingdom associated state. On the occasion of that fact was a flag which finished the tradition of the "Blue Ensigns". |
| Sie war waagerecht blau-gelb-grün gestreift mit einer Muskatnuss auf einem großen Oval in der Mitte. Diese Flagge wurde am 19.01.1967 angenommen. Diese drei Farben wurden auch von anderen Mitgliedern der Westindische Föderation benutzt, wenn auch in anderen Zusammenstellungen. | It was
horizontally striped in blue-yellow-green with a nutmeg on a large oval in
the middle. That flag was adoped on 19th of january in 1967. Those three colours were even in use by other members of the Westindian Federation, but in other combinations. |
| Angeblich gibt es auch eine Marineflagge. deren tatsächliche Existenz gilt als nicht sicher. Die Flagge orientiert sich wieder am britischen Ensign-System und zeigt ein durchgehendes weißes Georgskreuz auf weißem Tuch und die Nationflagge in der Oberecke. Die Farben sind wie folgt definiert: Rot = Pantone 032, Gelb = Pantone 109, Grün = Pantone 355. | Supposedly there is also a naval flag.
Its actual existence is unsafe. The flag is oriented on the British Ensign system again and shows a continuous white Georgian cross on a white bunting and the nation flag in the upper corner. The colors are defined as follows: red = Pantone 032, yellow = Pantone 109, green = Pantone 355. |
| Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Wikipedia (D), Flags of the World | |
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen – coat of arms, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens – Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms: |
|
| Das Staatswappen wurde – wie die Flagge – am 07.02.1974 eingeführt. Das Wappenschild wird durch ein gelbes Kreuz geviert. Davon sind zwei Gevierte rot mit einem goldenen Leoparden (→ England), und die anderen beiden sind grün mit einer weißen Marienlilie auf einem goldenem Halbmond. Auf dem Schild ein goldener Helm, ein rot-weißer Wulst sowie rote Rosen. Schildhalter sind rechts ein Gürteltier und links eine blaue Taube. Das Podest des Wappens ist grün mit einem Teich, einer Bananenpalme, einer Maispflanze und gelbe Blüten. | The coat
of arms of the state was like the flag introduced on 7th of February in
1974. The blazon is squared by a yellow cross. From them are two red
coloured with a golden leopard (→ England), and the other both are green
with a white Mary-lily on a golden crescent. On the shield a golden helmet,
a red-white torus as soon as red roses. Shield-holders are an armadillo on
the right and a blue pigeon to the left. The pedestal of the coat of arms is
green with a pond, a banana-palm-tree, a corn-plant and yellow blossoms. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Wikipedia (D) | |
Landkarten – Maps: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
|
|
Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geschichte: |
| 1498 · entdeckt 1650 · Frankreich erwibt Grenada aus Privatbesitz 1762 · britische Eroberung 1779–1783 · französische Besetzung 1833 · Ende der Sklaverei 1834–1960 · Teil der Britischen Kolonie der Windward-Inseln 1958–1962 · Teil der Britischen Kolonie "Westindische Föderation" 1967 · Gewährung innerer Selbstverwaltung 1974 · Großbritannien gewährt Unabhängigkeit 1979 · Maurice Bishop wird Premierminister und baut die Beziehungen zu Kuba aus 1983 · Staatsstreich, Ermordung von Maurice Bishop, militärische Intervention der USA mit Hilfe Karibischer Hilfstruppen, dauerhafte Besetzung der Insel 1984 · Wahlen |
History: |
| 1498 · discovered 1650 · France purchases Grenada from private ownership 1762 · British capture 1779–1783 · French occupation 1833 · end of the slavery 1834–1960 · part of the British Colony of the Windward Islands 1958–1962 · part of the British Colony of the "Federation of the West Indies" 1967 · granting of internal self government 1974 · United Kingdom grants independence 1979 · Maurice Bishop becomes prime minister and extends the dealings to Cuba 1983 · coup d'état, murder of Maurice Bishop, military intervention of the USA under help of Caribbean auxiliary troops, enduring occupation of the island 1984 · elections |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (D), Discovery '97 |
Ursprung des Landesnamens – Origin of the Country's Name: |
|
| Als Kolumbus die Insel in Jahre 1498 entdeckte, nannte er die Insel "Concepción", was "Empfängnis" heißt. Irgendwann kam der Name "Grenada" in Gebrauch, wobei der Ursprung des Namens unbekannt ist. Es wird vermutet dass die Insel von spanischen Seefahrern des 16. Jahrhunderts ihren Namen bekam, um an die Stadt Granada zu erinnern. | When Columbus discovered the island in 1498, he
named the island "Concepción". At some point in time the name "Grenada" came into use, but the origin of the name is unknown. It is believed that the island got its name from Spanish sailors of the 16th century to recall the city of Granada. |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (D) | |