mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Guinea
- authoritarian presidial republic under rule of the military
- own name: République de Guinée
• Flag
• Historical Flag
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National flag,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (D)






since 1994,
presumed Flag of the President,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World





to 1984,
Flag of the President,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1984–1993,
presumed Flag of the President,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




The flag was officially introduced on 10th of November in 1958. It is divided into three vertical stripes and is with this orientated in the flag of the mother-land France - in the Tricolor - in this way done in many former French colonies. The colour red stands for the in the fight for freedom given blood, yellow stands for the sun and the natural resources of the land, green stands for the vegetation and the agriculture. The colour shades of the flag are probably not defined by law. They seem to be defined by practice as green = Pantone 340, yellow = Pantone 116, red = Pantone 186. The combination of the colours green, yellow and red in the today's flag are the Pan-African colours: Perhaps in 1900 was the beginning of the Panafrica-Movement, wich wants to emphasize the commons of all people with black skin. For the political unity of Africa stands the colour-triad green-yellow-red, wich used many african countries in their flags after the independence. The first country was Ghana in 1957. As the origin apply the colours of Ethiopia (Abessinia), the oldest independent state in Africa.
Source: Wikipedia (D),
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (EN)


since 1997,
Coat of arms of Guinea,
Source, by: Wikipedia (FR)

1984–1993,
Coat of arms of Guinea,
Source, by:
Corel Draw 4,
Wikipedia (FR)

1958–1984,
Coat of arms of Guinea,
Source, by:
Flags of the World,
Wikipedia (FR)

As Guinea get independent in the year 1958, was introduced a coat of arms in the colours red, green and yellow. These are the Pan-African colours, but even the colours of the Parti Democratique de Guinee (PDG), those party which Guinea lead into the independence. The blazon was vertically clefted in red and yellow and thereupon was layed down a green elephant. The elephant was named "Sili" and descends from the emblem of the PDG. Above the blazon a green pigeon with an olive twig in the mouth. The remaining border of the blazon was surrounded by a green ribbon which below the blazon showed the motto of the state: "Travail - Justice - Solidarité" → "Work - Justice - Solidarity". The today's coat of arms was introduced in the year 1985 in result of a change of government in 1984. To do it was changed the hitherto coat of arms like in the following: The elephant was removed, it's place took sword and rifle crossed in front of a tall olive twig, which the now to the left flying white pigeon holds still in her mouth. The blazon carrys now on it's underneath end an elongation in the colours of the country, which reachs now to the simplifyed now white saying-ribbon. The motto of the state remained untouched. Another change was made in 1997. The green and red shield became white, the weapons were removed, the dove and the banner became golden.
Source:
Wikipedia (D),
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Wikipedia (FR)


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
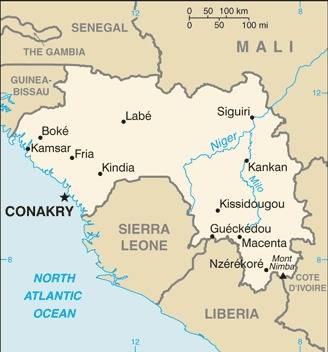
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 94.925 square miles
Inhabitants: 12.530.000 (2020), thereof 33% Fulbe, 30% Mandingo (Malinke), 21% Susu a.m.o.
Religions: 85% Muslim, 8% Christians, 7% Animist
Density of Population: 132 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Conacry, 1.667.864 inh. (2014)
official Language: French
other Languages: Malinke, Pular-Fulbe, Soussou
Currency: 1 Guinean Franc (GNF, F.G.) = 100 Cauris
Time Zone: GMT
Source: Wikipedia (D)

9th–13th cent. · parts of the today's Guinea belong to the Ghana Empire
13th–14th cent. · parts of the today's Guinea belong to the Mali Empire, the Islam gains Guinea
1450–1460 · the coast of Guinea is discovered and explored by the Portugese, Portugal establishes stations upon the Rio Pongo and on Matakong Island and stands there to the 18th century
15th–16th cent. · the area of the today's Guinea belongs to the Fulbe Empire
16th cent. · the Fulbe retire in the region of Fouta Djalon between the river Niger and the coast and convert to the Islam
1725 · establishment of the islamic Fulbe theocracy of Fouta Djalon
1808–1816 · Great Britain establishes missions and merchant bases on the Los Islands an upon Rio Pongo
1820 · French merchants reach the coast of Guinea and came as competitors to the British
1850–1866 · Frenchmen and the British contract "protection and friendship treaties" with the coastal population
1866 · France succeeds in establishing the military outposts of Boké (Rio Nunez), Boffa (Rio Pongo) and Benty (Mellacorée) on the mainland by treaties. The Los Islands however remain under British influence.
1870 · in the outback (eastern the river Niger) establishes the Malinke State of Ouassoulou
1882–1896 · subjection of the whole coast of Guinea (Rivières-du-Sud) by France
1893 · formation of the French Guinea Colony
1896–1897 · subjection of Fouta Djalon by France
1898 · subjection of Ouassoulou by France
1904 · the British cede the Los Islands to the Frenchmen, affiliation of French Guinea to French Western Afrika
1946 · formation of the Overseas Territory
1947 · foundation of the PDG (Parti Democratique de Guinee)
1957 · partial autonomy
2nd of October in 1958 · independence under president Sekou Touré (PDG)
1963 · introduction of the Guinea Franc as new currency
1972 · introduction of the Syli as new currency
1984 · death of Touré, military coup d'état
1991 · new constitution, re-introduction of the Guinea Franc as new currency
1993 · first, however disputed, democratic presidency elections
1995 · elections for a new parliament within a multi-party-system
1999–2000 · conflicts with Liberia
2008 · military coup d'état
2021 · military coup d'état
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
Discovery '97,
Weltgeschichte,
Wikipedia (D)

The name "Guinea" goes back to the Berber word "aguinaou", what means "blacks" and referred originally to all residents of the West African coast from Senegal to Gabon.
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()













