mobile Ansicht, to the English Version tap the flag

- Königreich Kambodscha
- konstitutionelle Monarchie
- Eigenbezeichnung:
Preah Reach Ana Pak Kampuchea
- früherer Name: Khmer
• Flaggen
• historische Flaggen
• Bedeutung/Ursprung der Flagge
• Wappen
• Bedeutung/Ursprung des Wappens
• historische Wappen
• Flugzeugkokarde
• Landkarte
• Zahlen und Fakten
• Geschichte
• Ursprung des Landesnamens

Nationalflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 16:25, auch 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Flags of the World






Flagge des Königs,
Seitenverhältnis = 16:25,
Quelle, nach: Sodacan
This W3C-unspecified vector image was created with Inkscape.
[CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons





1893–1942,
Nationalflagge,
Quelle, nach:
Flaggenbuch 1939



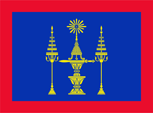
1893–1945(?),
Flagge des Königs,
Quelle, nach:
Flaggenbuch 1939



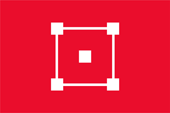
1942–1945 (Japanische Okkupation),
Nationalflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Flags of the World




1945–1948,
Nationalflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
World Statesmen




1948–1970,
Nationalflagge,
Quelle, nach:
Wikipedia (EN)



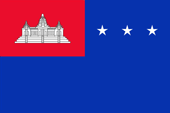
1970–1975,
Nationalflagge,
Quelle, nach:
Wikipedia (EN)




1975–1976,
Nationalflagge,
Quelle, nach:
Wikipedia (EN)



1975–1979,
Nationalflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Wikipedia (EN)
→ Hier klicken für mehr Informationen!




1979–1989,
Nationalflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Wikipedia (EN)




1989–1991,
Nationalflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 2:3,
Quelle, nach:
Wikipedia (EN)




1991–1993,
Nationalflagge,
Seitenverhältnis = 3:5,
Quelle, nach:
World Statesmen




Die Flagge von Kambodscha zeigt drei waagerechte Streifen in den Farben Blau, Rot und Blau, im Verhältnis 1:2:1, und trägt im mittleren roten Streifen eine Abbildung des Tempels von Angkor Wat. Die Farben Blau und Rot fanden schon sehr lange Verwendung in den Flaggen des Landes. Zur Bedeutung der Farben gibt es zwei verschiedene Erklärungen:
1.) Rot steht für das Blut, das im Kampf um Freiheit und Unabhängigkeit vergossen wurde, Blau für den Reichtum des Landes
2.) Rot ist die Nationalfarbe des Khmer-Volkes, und soll Opferbereitschaft ausdrücken, Blau ist die Farbe des Khmer-Königtums und verkörpert die Macht und die Wünsche des Herrschers.
Der weiße Tempel symbolisiert die glorreiche Vergangenheit des Landes. Weiß steht auch für das Vertrauen des Volkes auf seinen Herrscher. Die Flagge existierte in dieser Form bereits bis 1970 und wurde am 29.06.1993 durch einen Erlass von Prinz Sihanouk erneut angenommen. Unter den sozialistischen Regierungen wurden zwischen 1975 und 1989 rote, den Kommunismus symbolisierende Flaggen mit einer gelben Darstellung des Tempels von Ankor Wat verwendet. Die Farben der Flagge von Kambodscha werden neben Schwarz und Weiß folgendermaßen angegeben: Blau = RGB 3|46|161, was Pantone 286 entsprechen würde, Rot = RGB 224|0|37, was Pantone 185 entsprechen würde, Gelb = RGB 252|221|9, was Pantone Yellow C entsprechen würde, Hellblau = RGB 91|146|229, was Pantone 279 entsprechen würde. Das kommunistische Rot wird angegeben mit RGB 218|18|26, was Pantone 1788 entsprechen würde.
Quelle:
Wikipedia (EN)


seit 1993,
Wappen vom Kambodscha,
Quelle:
Sodacan, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

Das Wappen von Kambodscha ist die Heraldik der kambodschanischen Monarchie. Es wurde in ähnlicher Form bereits 1953 angenommen. Es zeigt einen hellblauen Schild mit einem Unaome-Zeichen (Aum-Symbol), ein Schwert, zwei zeremonielle Podestplatten (Phan), einen Lorbeerkranz und den dem Königlichen Orden von Kambodscha, darüber die königliche Krone. Der Schild wird von den zwei königlichen Tieren gehalten, dem Gajasingha (Löwen mit Elefantenrüssel) auf der linken Seite und dem Rajasingha (königlicher Löwen) auf der rechten Seite. Jeder Löwe hält zwei königliche fünfstufige Regenschirme. Das blaue Spruchband zeigt in Khmer die Worte: "Herrscher des Königreichs Kambodscha".
Quelle:
Wikipedia (EN)


1970–1975,
Wappen der Republik Khmer,
Quelle:
Vektorisiert von FOX 52, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons

1975–1982,
Wappen des Demokratischen Kampuchea,
Quelle:
vectorized by Elena in General, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

1979–1981,
Wappen der Volksrepublik Kampuchea,
Quelle:
Ericmetro, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons

1981–1989,
Wappen der Volksrepublik Kampuchea,
Quelle:
Vektorisiert von FOX 52, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons

1989–1992,
Wappen des Staats Kambodscha,
Quelle:
Sarumo74, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons


1989–1993,
Flugzeugkokarde,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (EN)
seit 1993,
Flugzeugkokarde,
Quelle, nach: Wikipedia (EN)

Lage:
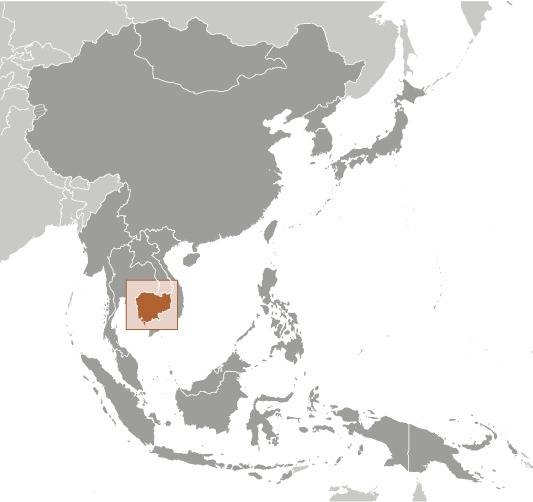
Quelle/Source: CIA World Factbook
Landkarte des Landes:
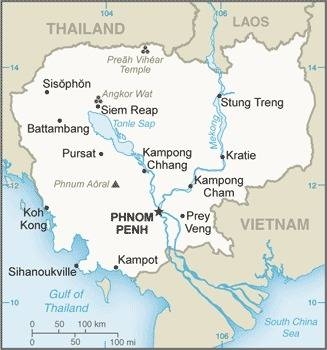
Quelle/Source: CIA World Factbook

Fläche: 181.035 km²
Einwohner: 17.300.000 (2021), davon 95% Khmer, 2% Cham, 2% Chinesen, 0,2% Vietnamesen
Religionen: 97% Buddhisten, 2% Moslems, 0,3% Christen
Bevölkerungsdichte: 96 Ew./km²
Hauptstadt: Phnom Penh, 2.281.951 Ew. (2019)
Amtssprache: Khmer
sonstige Sprachen: Französisch, Englisch
Währung: 1 Riel (KHR) = 100 Sen
Zeitzone: MEZ + 6 h
Quelle:
Wikipedia (EN)

200–600 · Reich Funan
7. Jhd. · Eroberung durch die Khmer, Etablierung des Khmer-Reiches
802 · Gründung des Königreiches Kambuja
13. Jhd. · Einfälle der Thai, Schan und Mongolen
1353 · die Thai erobern die Hauptstadt Angkor, kurzzeitige Etablierung einer Thai-Dynastie
1431 · Verlegung der Hauptstadt von Angkor nach Phnom Penh
1623 · vietnamesische Invasion
1660 · der König der Khmer wird von den Thai gefangen genommen, Kambodscha gerät in siamesische Abhängigkeit
1863 · Frankreich schließt einen Schutzvertrag mit Kambodscha, um es vor der Annexion durch Siam (Thailand) zu bewahren
1867 · Siam erkennt das französische Protektorat über Kambodscha an
1884 · die französische Kolonialverwaltung übernimmt alle hoheitlichen Rechte des Landes
1887 · Bildung von Französisch-Indochina, eigentlich Union von Indochina/Union Indochinoise (Zusammenschluss der französischen Gebiete: Tongking, Annam, Cochinchina, Laos und Kambodscha
1893 · Laos wird an Französisch-Indochina angeschlossen
1941 · Japanische Truppen besetzen Französisch-Indochina, Kambodscha muss Gebiete im Norden und Westen an Thailand (Siam) abtreten
August 1945 · Verkündung der Unabhängigkeit durch Prinz Sihanouk
Oktober 1945 · Einmarsch französischer Kolonialtruppen
1946 · Wiedererrichtung des französischen Protektorats, Beginn des bewaffneten Widerstands gegen die Kolonialmacht (vor allem in Vietnam), bis 1954 Eskalation zum Indochinakrieg
1947 · Frankreich gewährt den Status einer konstitutionellen Monarchie
1949 · Frankreich gewährt Unabhängigkeit im Rahmen der Französischen Gemeinschaft
09.11.1953 · die französische Kolonialverwaltung wird aufgelöst, Tag der Unabhängigkeit
21.07.1954 · Waffenstillstandsverhandlungen auf der Genfer Indochina-Konferenz, der Erste Indochinakrieg endet, Frankreich zieht seine Truppen aus ganz Indochina ab, die Unabhängigkeit Kambodschas wird bestätigt
1955 · Prinz Sihanouk dankt als König ab, erlässt eine neue Verfassung und wird Ministerpräsident von Kambodscha, Politik strikter Neutralität
1960 · Prinz Sihanouk übernimmt das Amt des Staatschefs (Staatspräsident)
1969 · General Lon Nol wird Ministerpräsident
1970 · General Lon Nol putscht gegen Prinz Sihanouk und wird Staatschef, Umbenennung Kambodschas in République Khmer, pro-US-amerikanische Politik, Einmischung in den Vietnamkrieg
1970–1975 · Bürgerkrieg in Kambodscha, kommunistische Rebellen unter Pol Pot (Rote Khmer) und Anhänger von Prinz Sihanouk kämpfen mit Unterstützung von Nord-Vietnam gegen Truppen und Anhänger von General Lon Nol
1972 · General Lon Nol wird Staatspräsident
17.04.1975 · Niederlage der Truppen Lon Nols gegen die Roten Khmer und die Anhänger von Prinz Sihanouk, General Lon Nol geht in die USA ins Exil, Prinz Sihanouk wird Staatschef
1976 · Prinz Sihanouk wird von den kommunistischen Roten Khmer gestürzt und unter Hausarrest gestellt, die République Khmer wird in Demokratisches Kambodscha umbenannt, die Roten Khmer schließen die Grenzen des Landes und beginnen mit "Säuberungsaktionen" größeren Ausmaßes und Beginnen ein Umerziehungsprogramm für das gesamte Volk dem bis 1978 ein Viertel der Bevölkerung des Landes zum Opfer fällt
1977 · Grenzkonflikte mit Vietnam
1978 · Vietnam interveniert in Kambodscha und beendet am 07.01.1979 die Herrschaft der Roten Khmer, Machtübernahme durch den vietnamhörigen Heng Samrin, Prinz Sihanouk geht ins Exil
10.01.1979 · Proklamation der Volksrepublik Kambodscha
1979–1990 · Bürgerkrieg in Kambodscha, Rote Khmer, Royalisten und bürgerliche Gruppen bekämpfen die vietnamesischen Besatzungstruppen und Staatschef Heng Samrin
1982 · Prinz Sihanouk bildet eine Exilregierung unter Einbindung aller Widerstandsgruppen
1985 · Pol Pot tritt als Oberkommandierender der Roten Khmer zurück
1988 · Verhandlungen der Exilregierung mit der Regierung Heng Samrin
1989 · Abzug der vietnamesischen Truppen
1990 · Bildung des Obersten Nationalrates, als gemeinsame Regierung aller Konfliktparteien (Rote Khmer, Royalisten, Bürgerliche, Anhänger Heng Samrins)
1991 · Friedensvertrag von Paris
1993 · Parlamentswahlen (von den Roten Khmer boykottiert), Sieg der FUNCINPEC-Partei von Prinz Ranariddh (Sohn von Prinz Sihanouk), Niederlage der Volkspartei von Hun Sen, neue Verfassung, Kambodscha wird Königreich, Prinz Sihanouk wird König, Prinz Ranariddh wird Premierminister
1994 · die Roten Khmer nehmen den Kampf wieder auf
1997 · bewaffneter Widerstand gegen Prinz Ranariddh, Hun Sen übernimmt die Macht
15.04.1998 · Tod von Pol Pot
26.07.1998 · Parlamentswahlen, Sieg der Volkspartei von Hun Sen, die FUNCINPEC-Partei von Prinz Ranariddh koaliert mit der Volkspartei, Hun Sen wird Ministerpräsident, Prinz Ranariddh wird Parlamentspräsident, Wiedereingliederung der Roten Khmer in das öffentliche Leben und die Armee
1999 · der letzte Führer der Roten Khmer wird gefangen genommen
2004 · König Sihanouk dankt ab, König wird sein Sohn Norodom Sihamoni
Quelle:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (D)

Der Name von Kambodscha geht auf das Reich Kambuja zurück, eine Staatsgründung des Khmer-Volkes, die hier vom 9. bis zum 15. Jahrhundert bestand. Das Reich geriet danach in Abhängigkeit seiner Nachbarn. Dennoch wurde der Name beibehalten, und zwar als "Kampuchea", im Westen als "Kambodscha" bekannt. Nur kurze Zeit, zwischen 1970 und 1975, hieß das Land "Republik Khmer". Heute scheint sich die Praxis durchgesetzt zu haben das Land als sozialistisches Land als "Kampuchea" zu bezeichnen und für den bürgerlich-monarchistischen Staat "Kambodscha", kurios, es ist ein und das selbe Wort.
Quelle:
Wikipedia (D)

mit freundlicher Unterstützung von: Siegfried Ehrmann

![]()


















































