mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Republic of Trinidad and Tobago
- parliamentary republic
- consisting in the islands Trinidad and Tobago
- own name: Republic of Trinidad and Tobago
• Flags
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

since 1962,
National and state flag,
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by: Flags of the World






Merchant flag and state flag at sea,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



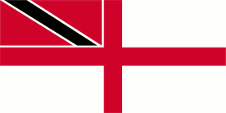
Naval flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag ot the President,
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by: TriniPosseStar,
CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons




Flag of the Prime Minister,
ratio = 3:5,
Source, by: Prez001,
CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons





1889–1962,
Union Flag → quasi National flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source: Wikipedia (EN)






1889–1962,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations






1889–1958,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1958–1962,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1962–1976,
Flag of the Queen,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




1962–1976,
Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World



Flags of Trinidad ← click here
Flags of Tobago ← click here

Federation of the West Indies (1958–1962):
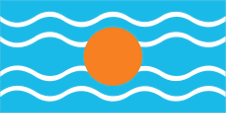
Flag of the Federation of the West Indies,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




The flag of Trinidad and Tobago was adopted and officially hoisted for the first time on 31st of August in 1962, on the occasion of independence. It shows a red base bunting with a white-lined black slanting bar from top left to bottom right. The colour red symbolizes the courage and vitality of the people, but also the power and warmth of the sun. The colour white represents the water of the ocean, but also the purity of national aspirations and emancipation. Black is the symbolic colour for strength, for national unity, for energy, performance and wealth.
The colours shown in most of the careful, multi-coloured reproductions of the flags of Trinidad and Tobago (sometimes also in the coat of arms) suggest that Trinidad and Tobago's colours and colour-shades are traditionally based on the British colour system, so that the British Ministry of Defense colour system would be used. This purports for red = Pantone 186 c, for royal blue = Pantone 280 c and for deep yellow = Pantone 116 c.
The presidential flag is blue and features the national coat of arms in gold in the center, surrounded by a golden wreath. The Prime Minister's flag is white and shows the national flag in the upper corner and the national coat of arms surrounded by a golden wreath in the flying end.
The Queen's former flag between 1962 and 1976 featured the image of the heraldic shield of Trinidad and Tobago with the personal emblem of the Queen in the center. The flag was abolished with the introduction of the Republic.
During the very eventful history of the two islands, their owners changed often, and with them the flags used here. United Kingdom last secured ownership of the both islands in 1803, so that from that year on the flag of United Kingdom flew unchallenged over the island. On land, and until 1864 also at sea, the individual citizen and also the authorities represented their status as citizens or organs of the United Kingdom by the use of the Union Jack, called the "Union Flag".
United Kingdom had introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• War ships use a so-called "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with a red St. George's cross throughout and with the Union Jack in the upper corner,
• Merchant ships use a so-called "Red Ensign" (also called "Civil Ensign" → citizen flag, the actual merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner, and
• Governmental ships use a "Blue Ensign" (flag of the government → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper orner.
Since 1865, colonial government ships were permitted to use a Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end. From this point on, only the British Union Jack was to be used for all other purposes on land and the usual red British merchant flag, the "Red Ensign", at sea. If the British Admiralty had granted the appropriate permission to one colony, merchant ships and private sailors from this colony were allowed to use a Red Ensign with the Bagde. This was not the case for Trinidad and Tobago. The respective governments should provide appropriate bagdes.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showed ships, historical events or could just be a kind of logo. Very often a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. However, some possessions had a coat of arms right from the start, or received their own coat of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. In order to ensure a largely uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk the same size as the earlier badges. But there were exceptions here, as some colonies did not use this white disk and placed their coat of arms or just the shield – sometimes enlarged – directly on the flag cloth. As early as the 1940s, the white discs were removed and the coat of arms was placed directly or enlarged. This transition process occurred gradually, never simultaneously and completely. In some British possessions flags with the white disc are still in use, in others they are no longer used and in some areas both variants exist side by side.
From 1875, the government of Trinidad, as a British colony, used the blue British official flag (Blue Ensign) with a badge in the waving part of the flag. The badge, introduced in 1875, showed a mountainous coastal landscape with a coastal fortification. A flag, a Blue Ensign, flies on the coastal fortifications. A British warship with reefed sails lies in the roadstead in the coastal waters. A rowing boat can be seen in the foreground. The lower part of the disc shows the island's motto on a white surface: "Miscerique probat populus et foedera jungle" → "It has proven successful to mix the peoples and unite them in unity". In 1889 Tobago was placed under the administration of Trinidad and the badge was retained unchanged for Trinidad and Tobago until 1958.
At the same time, the colony was part of the British colony "West Indian Federation" from 1958 to 1962, an attempt to consolidate the administration and also to counteract the independence efforts of the associated islands and colonies. The flag of the "West Indian Federation" was a light blue flag with four horizontal white wavy lines and a golden disc in the middle. It symbolized the sun over the Caribbean Sea. There is some doubt about the color of the blue; it is often assumed to be the usual British heraldry blue. However, a contemporary description calls it an "imperial blue" which would be light blue and many contemporary prints also show this light blue.
In this context, the badge was abolished in 1958 and the image of the badge was transferred to an escutcheon and also used on the "Blue Ensign", the governmental flag. The colony's motto appeared on a golden banner below the escutcheon.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
World Statesmen,
Flags of the World,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen-Atlas Erde,
Volker Preuß


since 1962,
Coat of arms of Trinidad and Tobago,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4

1889–1958,
Badge of Trinidad and Tobago,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1958–1962,
Badge of Trinidad and Tobago,
Source, by: Flags of the World

The national coat of arms was officially awarded by Queen Elizabeth II. on 9th of August in 1963 and, like the flag, was it introduced on 31st of August in 1962 on the occasion of independence. The coat of arms shows black at the top and red at the bottom, divided by a silver chevron. In the black field there are two hummingbirds, they represent the two islands and their natural riches. In the red field there are three caravels, they are Columbus's ships. They represent the sea that separates and connects both islands. Shield holders are a Scarlet Ibis on the left (representing Trinidad) and a Cocorico on the right (representing Tobago). Above the shield is a golden helmet with white and red covers and a white and red bulge. At the top there are gems: a wooden steering wheel and a palm tree. The shield rests on a base depicting an island landscape. At the bottom there is a golden banner with the country's motto: "Toghether we aspire - together we achieve" → "Together we strive - together we are successful". The badge, introduced in 1875, showed a mountainous coastal landscape with a coastal fortification. A flag, a Blue Ensign, flies on the coastal fortifications. A British warship with reefed sails lies in the roadstead in the coastal waters. A rowing boat can be seen in the foreground. The lower part of the disc shows the island's motto on a white surface: "Miscerique probat populus et foedera jungle" → "It has proven successful to mix the peoples and unite them in unity". In 1889 Tobago was placed under the administration of Trinidad and the badge was retained unchanged for Trinidad and Tobago until 1958. The badge was abolished in 1958 and the image of the badge was transferred to an escutcheon. The colony's motto appeared on a golden banner below the escutcheon.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flags of the World,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Volker Preuß


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
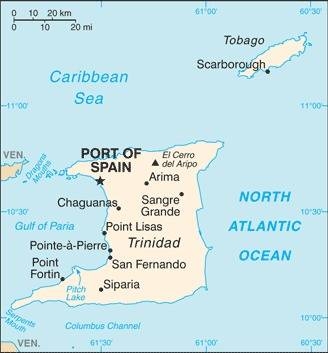
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 1.980 square miles
Inhabitants: 1.500.000 (2021), thereof 35% Indians and other Asians, 34% Afro-Americans, 23% mixed, 1% Chinese and Europeans
Religions: 24% Roman Catholic, 21% Hindu, 13% Protestant, 6% Anglican, 6% Baptist, 6% Muslim, 2% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 758 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Port of Spain, 49.031 inh. (2011)
official Language: English
other Languages: Patois Creole, Spanish
Currency: 1 Trinidad and Tobago Dollar (TTD, TT$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source:
Wikipedia (DE)

History of Trinidad ← click here
History of Tobago ← click here
1st of January 1899 · Trinidad becomes united with Tobago to the colony of Trinidad and Tobago
1939–1945 · Second World War, the islands become build up to the bigest allied military base in the Caribbean Sea
1958–1962 · Trinidad and Tobago is a part of the Federation of the West Indies
1959 · United Kingdom grants inner self administration
31st of August 1962 · United Kingdom grants independence in the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations, the country becomes a constitutional monarchy under the British monarch as chief of state
1970 · agitations
1972 · state of emergency
1st od August 1976 · Trinidad and Tobago becomes a republic, but remains in the Commonwealth of Nations
1980 · Tobago gets partial inner self administration
1987 · Tobago gets autonomy
Source:
Wikipedia (EN),
World Statesmen,
Volker Preuß

As the Spanish seafarer Christoph Columbus discovered the island in 1498 he named it "Trinidad", because of the three characteristic mountain peaks in the silhouette of the island. Trinidad means Trinity.
Tobago was also discovered by the Spanish seafarer Christoph Columbus in the year 1498. He named it "Bella Forma" (the Wellshaped), by other sources "Isla de la Asunción" (Ascension Island). Only some years later it was named "Isla La Magdalena" (Magdalena Island). Later the island had many names, according to its respective owner. So even "Nieuw Walcheren" or "Neukurland". The French and the British called it "Tobago". This name has its roots in the word Tobacco. Otensibly even that island's name has its roots in Columbus, because he watched that the Cariben smoking Tobacco-Leafs in a Tambaku, and he used this name for the island.
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen,
World Statesmen,
etymonline.com,
Volker Preuß


![]()




























