Tschad |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Tschad |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Flagge – Flag: |
|
 |
National- und Staatsflagge – national and state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Flags of the World   |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
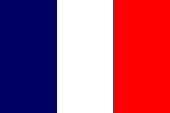 |
1910–1959, Französisch-Äquatorialafrika – French Equatorial Africa, Flagge Frankreichs – flag of France, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Corel Draw 4   |
| Die Flagge des Tschad wurde am 06.11.1959 offiziell eingeführt. Sie ist der französischen Trikolore nachgebildet, und zeigt drei senkrechte Streifen in Blau, Gelb und Rot. Die Farben bzw. Farbtöne scheinen definiert zu sein, jedoch nicht über die Verfassung des Landes und deren Zusatzartikel. Speziell das Blau orientiert sich, so ist zu lesen, am Blau der Flagge Frankreichs, soll also sehr dunkel sein. Angeblich liegt aber eine Quelle für die Definition der Farben vor, die immer wieder zitiert wird. Es handelt sich um den von der französischen Marine herausgegebenen Flaggenkatalog "Album des pavillons nationaux et des marques distinctives". Der sieht vor: Blau = Pantone 281 c (wie in der Flagge von Frankreich), Gelb = 116 c und Rot = Pantone 186 c. Blau steht für den Himmel, das Leben, die Hoffnung, die Landwirtschaft und den südlichen Teil des Landes, Gelb steht für die Sonne und den nördlichen Teil Tschads mit seiner Wüstenlandschaft, Rot steht für den Fortschritt, das Feuer, die Einheit und die Opferbereitschaft des Volkes. Ursprünglich hätten die Farben der Flagge die panafrikanischen Farben Grün, Gelb und Rot sein sollen. Dies wurde jedoch aus innenpolitischen Gründen verworfen, denn die damalige Opposition verwendete Grün in ihren Farben. Die Farben Grün, Gelb und Rot sind die panafrikanischen Farben. Etwa 1900 setzte die Panafrika-Bewegung ein, die Gemeinsamkeiten aller Menschen mit schwarzer Hautfarbe hervorheben wollte. Der Farbendreiklang Grün-Gelb-Rot, den viele afrikanische und auch amerikanische Staaten nach Erlangung ihrer Unabhängigkeit in ihre Flaggen übernahmen, steht für die politische Einheit Afrikas, ja aller Schwarzen. Das erste Land war Ghana im Jahr 1957. Als Ursprung gelten die Landesfarben von Athiopien (Abessinien), dem ältesten unabhängigen Staat Afrikas. |
The flag of Chad was
officially introduced on 6th of November in 1959. It is modeled on the
French tricolor and shows three vertical stripes in blue, yellow and red.
The colours or colour-shades seem to be defined, but not by the country's constitution and its additional articles. The blue in particular is based on the blue of the French flag, so it should be very dark. Apparently there is a source for the definition of the colours that is cited again and again. This is the flag catalog "Album des pavilions nationaux et des marques distinctives" published by the French Navy. This provides: Blue = Pantone 281 c (as in the flag of France), yellow = 116 c and red = Pantone 186 c. Blue represents the sky, life, hope, agriculture and the southern part of the country, yellow represents the sun and the northern part of Chad with its desert landscape, red represents progress, fire, unity and sacrifice people. Originally the colours of the flag should have been the pan-African colours of green, yellow and red. However, this was rejected for domestic political reasons, as the opposition at the time used green in their colours. The colours green, yellow and red are the Pan-African colors. Around 1900, the Pan-African movement began, which wanted to highlight the similarities of all people with black skin. The colour triad green-yellow-red, which many African and American states adopted in their flags after gaining their independence, represents the political unity of Africa, and indeed of all black people. The first country was Ghana in 1957. The national colors are considered to have originated from Ethiopia (Abyssinia), the oldest independent state in Africa. |
|
Quelle/Source: Die Welt der Flaggen, Flags of the World, Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt, Flaggen-Atlas Erde, Volker Preuß |
|
Wappen – Coat of Arms: |
|
 |
Wappen des Tschad – coat of arms of Chad, Quelle/Source: Corel Draw 4 |
| Das Staatswappen wurde am 11.08.1970 eingeführt. Es soll "Friede, Einheit und Gemeinsinn" versinnbildlichen und ist ein französischer Entwurf im europäischen Stil. Es zeigt einen Schild mit blauen und gelben Zickzacklinien. Sie symbolisieren das Wasser des Tschad-Sees und den Sand der Sahara. Oberhalb des Schildes erscheint die rote Sonne der Freiheit. Ein Mufflon und ein Löwe dienen als Schildhalter. Auf dem Band unter dem Wappen steht der der Staatswahlspruch: "Unité, Travail, Progres" → "Einigkeit, Arbeit, Fortschritt". In der Zeit vor der Einführung des heutigen Wappens wurde ein Siegel mit einer Frauengestalt als Staatswappen verwendet. |
The coat of arms of Chad
was introduced on 11 th of August in 1970. It is intended to symbolize
"peace, unity and community spirit" and is a French design in a European
style. It shows a shield with blue and yellow zigzag lines. They symbolize
the water of Lake Chad and the sand of the Sahara. The red sun of freedom
appears above the shield. A mouflon and a lion serve as supporters (shield
holders). On the banner below the shield is written the state motto: "Unité,
Travail, Progres" → "Unity, Work, Progress". In the period before the current coat of arms was introduced, a seal with a female figure was used as the coat of arms. |
| Quelle/Source: Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Flaggen und Wappen der Welt | |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel: |
|
 |
Flugzeugkokarde – aircraft roundel Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
| Landkarte – Map: |
Lage – Position: |
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country: |
Landschaften des Tschad – Landscapes of Chad: |
|
|
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Antike
· Besiedelung durch Berbero-Libysche Stämme, Herausbildung Tschadischer
Sprachen seit 11. Jahrhundert · Einwanderung von Arabern 11.–17. Jahrhundert · Herausbildung der Staaten Kanem und Bornu (seit etwa 1000), Bagirmi (seit 1500) und Wadaï (seit 1600) 1897 · Intervention französischer Truppen in Bagirmi 1898 · Sieg französischer Truppen bei Kusseri in Bagirmi 1903 · Wadaï wird französisches Protektorat 1909 · Tibesti wird französisches Protektorat 1910 · Bildung des Generalgouvernements Französisch-Äquatorialafrika nunmehr bestehend aus den Territorien Gabun, Mittelkongo (heute Kongo-Brazzaville), Ubangi-Schari (heutige Zentralafrika) und Tschad 1913/14 · Borku wird französisches Protektorat 1946 · Französisch-Äquatorialafrika wird Überseeterritorium, in den vier Territorien werden Parlamente gebildet 18.11.1958 · Frankreich gewährt Autonomie als Republik Tschad innnerhalb der Französischen Gemeinschaft 16.05.1960 · Bildung der "Union Zentralafrikanischer Republiken" mit Zentralafrika und Kongo-Brazzaville 11.08.1960 · Frankreich gewährt Unabhängigkeit 1962 · Einführung des Einparteiensystems 1965 · Beginn der Auseinandersetzungen zwischen dem Nord- und dem Südteil des Landes 1974 · Militärputsch unter General Malloum 1979 · Sieg der Truppen von Premierminister Habre über die Truppen von General Malloum 1980 · die Zentralregierung unter Habre wird von Rebellen aus Wadai mit Unterstützung Libyens geschlagen 1982 · Rückkehr der Zentralregierung unter Habre mit Unterstützung der USA und Frankreichs 1987 · Kämpfe zwischen Libyen und Tschad um den Aouzou-Streifen 1990 · Militärputsch unter Deby 1993 · Wahl von Deby zum Präsidenten 1998–1999 · Entsendung von Truppen nach Kongo-Kinshasa 2005 · Schwierigkeiten mit Sudan wegen des Konfliktes in Darfur (200.000 Flüchtlinge im Tschad) 2006–2009 · Bürgerkrieg 2013 · Putschversuch 2013 · Truppen des Tschad operieren in Niger im Azawad-Konflikt |
|
antiquity
· settlement by Berbero-Libyan tribes, evolution of Chadian languages since 11th century · immigration of Arabs 11th–17th century · establishment of the states of Kanem and Bornu (since ca. 1000), Bagirmi (since 1500) and Wadaï (since 1600) 1897 · intervention of French troops in Bagirmi 1898 · victory of French troops near Kusseri in Bagirmi 1903 · Wadaï becomes a French protectorate 1909 · Tibesti becomes a French protectorate 1910 · establishment of the General Gouvernement of French Equatorial Africa, now consisting of the territories Gaboon, Middle Congo (today Congo Brazzaville), Ubangi-Shari (today Central Africa) and Chad 1913/14 · Borku becomes a French protectorate 1946 · French Equatorial Africa becomes an overseas territory, in the four territories they establish parliaments 18.11.1958 · France grants autonomy as Republic of Chad within the French Community 16.05.1960 · formation of the "Union of the Central African Republics" with Central Africa and Congo-Brazzaville 11.08.1960 · France grants independence 1962 · introduction of the single-party-system 1965 · onset of the quarrels between the northern and the southern part of the country 1974 · military coup d’état under General Malloum 1979 · victory of the troops of Prime Minister Habre over the troops of General Malloum 1980 · the central government under Habre becomes hit by rebels from Wadai with support of Libya 1982 · return of the central government under Habre with support by the USA and Frankreichs 1987 · fights between Libya and Chad for the Aouzou Stripe 1990 · military coup d’état under Deby 1993 · Deby becomes elected to the president 1998–1999 · delegation of troops to Congo-Kinshasa 2005 · difficulties with Sudan due to the conflict in Darfur (200.000 refugees in Chad) 2006–2009 · civil war 2013 · coup attempt 2013 · Chad troops operate in Niger in the Azawad conflict |
| Quelle/Source: Wikipedia (DE), Discovery '97, World Statesmen, Volker Preuß |
| Der Name des Tschad geht auf den Tschad-See zurück. Das Wort "Tschad" heißt in der Bornu-Sprache "großes Wasser", Tschad ist also das "Land des großen Wassers". | The name of Chad has its roots in the Chad Sea. The word "Chad" means in the Bornu language "big water", Chad is in this way the "Country of the big Water". |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas der wahren Namen | |