mobile View, to the German Version tap the flag


- Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal
- 1768–2007 Kingdom
- own name: Sanghīya Loktāntrik Ganatantra Nepāl
• Flag
• Historical Flags
• Meaning/Origin of the Flag
• Coat of Arms
• Historical Coats of Arms
• Meaning/Origin of the Coat of Arms
• Aircraft Roundel
• Map
• Numbers and Facts
• History
• Origin of the Country's Name

National flag,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN),
Drawn by User:Pumbaa80, User:Achim1999,
Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons







1930—1962,
National flag,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN),
Orange Tuesday, CC BY-SA 3.0,
via Wikimedia Commons




1856—1930,
National flag,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)




18./19th cent./cent.,
Troop flag,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)



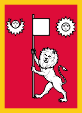
1969,
Standard of the King,
ratio = 11:8,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN),
Sodacan, CC BY-SA 4.0,
via Wikimedia Commons



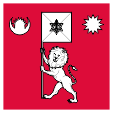
2001,
Standard of the King,
ratio = 1:1,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN),
Sodacan, CC BY-SA 4.0,
via Wikimedia Commons




The today's flag of Nepal was introduced on 16th of december in 1962 – in occasion with the coming into force of the new constitution – by other sources already on 16th of december in 1961. It is the only non-rectangular national flag in the world, it is above beveled and on the flying end performed with a incision. It shows on top of each other a white sun and a white moon on dark-blue framed carmine ground. The flag has its roots in the 19th century. The colours of the flag seem today to be defined as follows: Blue = HEX #003594, which would correspond to Pantone 287, Red = HEX #DD0C39, which would correspond to Pantone 192. About the origin and the meaning of the flag, as soon as of the colours there are differentest theories:
• The shape of the flag as a double-pennant as its roots in early Persian influences.
• The flag is – in difference to beforehand – not more a double-pennant, but unites two fundamental different pennants.
• Sun and moon remember the "eternal cycle of times".
• Sun and moon embody the hope that the nation might exist so long like that celestial bodies.
• Sun and moon embody two rivaling arms of the Rana Family, the Bahadur and the Shamsher.
• Sun and moon embody the historical and locally important families of the Prime Minister (Rana Family = sun) and of the King (Bir Bikram Family = moon).
• The both triangles symbolize the both religions of the country – the Hinduism and the Buddhism – the saw-tooth-form should remember the peaks of the Himalaya.
• A white sun on red cloth with a blue border was the flag of the sub-kingdom of Mastang (also Kingdom of Lo, its existence ended in 2008), so the two-part flag could be interpreted as a combination of the symbolism of the Gurkha State and Mastang.
• Carmine is the national colour of Nepal, officially named "crimson". It is the colour of the here living rhododendron plants.
• Red and blue are the national colours of Nepal.
Before 1962 the depictions of moon and sun in the flag showed faces with caste marks. The flag of the king was single-coloured red with a silvery mounting lion in the middle who carrys a silvery flag. In the upper quadrants – in silver – moon and sun. This could be a contradiction for that, that sun and moon should be symbols of families. Why should both arise together on the banner of the King?
Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (DE), Wikipedia (EN), Volker Preuß


since 2007,
Coat of arms of Nepal,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN),
CAPTAIN MEDUSA, CC BY-SA 4.0,
via Wikimedia Commons


1962–2006,
Coat of arms of Nepal,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)

1946–1962,
Coat of arms of Nepal,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)

1935–1946,
Coat of arms of Nepal,
Source, by:
Wikipedia (EN)

The today's coat of arms was adoped on 18th of May in 2008 and was changed in details in 2020. It shows within a wreath of rhododendron blossoms (national flower) a stylized white map of Nepal in front of the silhouette of Mount Everest and an Himalaya mountains scenery. Underneath a shake hands of man and wife. Below a red banner with the white sanskrit-inscription "Janani Janmabhumisca svargadapi Gariyasi" → "The homeland is expensiver than the heavenly empire". That coat of arms shows in comparison with its predecessor none crown of a king anymore. A sign of the by the new constitution abolished royal power. The between 1962 und 2007 valid coat of arms of the state showed as main-component a Nepalese landscape with the Himalaja mountains in the background, a white cow, a pheasant and rhododendron blossoms. Below was a red banner with the sanskrit-inscription "The homeland is expensiver than the heavenly empire". To the left and on the right stood as supporters ever one gurkha-soldier in modern and historical uniforms. Above two Khukuri daggers, two Nepalese flags, the treads of Gorakhnath (the god of the gurkhas), and the crown of the King as a symbol of the then re-established absolute monarchy. Until the 16th of December in 1962 Nepal used a coat of arms in its shield was to see the Hindu-God Shiva arising from the sea in front of the mountains of the Himalaya. Above the shield two Khukuri daggers, moon and sun and the treads of Gorakhnath – the god of the Gurkha, as well as a red banner. Around the blazon were placed two white banners. In the inner the motto of the state in golden Sanskrit letters "Janani Janmabhumisca svargadapi Gariyasi" → "The homeland is expensiver than the heavenly empire". The outer banner showed in black letters an other motto, so in Latin: "DULCIS ET DECORUM EST PRO PATRIA MORI" → "It is sweet and honorable to die for the Fatherland", an homage to the famous Gurkha-Troops which served in the British army and serve until today. Shield supporters were two Gurkha-Soldiers in British and traditional uniform.
Source:
Flags of the World, Wikipedia (DE), Flaggen Wappen Hymnen, Volker Preuß

 (?)
(?)
Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Flags of the World

Location:

Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:

Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 56.956 square miles
Inhabitants: 29.200.000 (2021), thereof 25% Gurkha and Tibetans, 28% Indians (Chhetri, Bahun)
Religions: 81% Hindu, 9% Buddhist, 4% Muslim, 3% Animist, 1% Christian
Density of Population: 513 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Katmandu (also: Kantipur or Yambu), 985.000 inh. (2020)
official Language: Nepali
other Languages: Maithili, Bhojpuri, Tharu, Tamang, Newari, Tibetan Dialects
Currency: 1 Nepalese Rupee (NPR, NRs) = 100 Paisa, 1 Indian Rupee (INR, iR) = 100 Paise
Time Zone: GMT + 5:45 h
Source:
Wikipedia (DE)

Antiquity · settlement by Tibetan tribes
ca. 250 · the tribe of the Mewari establishes around Katmandu the Principality of Malla
ca. 650 · the Principality of Malla becomes dependent from the Tibetan Turfan Empire
ca. 1150 · Malla becomes independent again
1386–1429 · introduction of the caste system, in the afteryears disintegrates the Principality of Malla in smaller states
ca. 1730 · the Gurkha people starts to conquer the region, establishment of a Gurkha Principality
1756 · the smaller Tibetan Principalities become unifyed under the Gurkha Prince Narayan, as name of the land achieves Nepal
1767 · military attempt of conquer by the British East Indian Company
1787 · Nepal reaches its largest dimension, from Kashmir to Sikkim
1793 · Agreement of trade with United Kingdom
1793 · Nepal has to recognize the supremacy of China, tribute payments to China until 1908
1801 · Nepal associates with United Kingdom by a treaty of protection
1814 · China intensifys its influence in Nepal, the British East Indian Company keeps occupy the country militarily because of that
2nd December 1815 · Peace Treaty of Segauli, Nepal has to cede parts of the country to British India and has to recognize the britische supremacy
1846 · the Rana familiy revolts into the function of the prime minister and makes it dynastic and heritable, the kingship of the family Bir Bikram becomes political insignificant
1854 · military quarrels with Tibet
1856 · Nepal gets trade privileges in Tibet
1920 · first demands to overthrow the Rana Family and for introduction of the constitutional monarchy
1947 · foundation of the Nepalese National Congress
1950 · King Tribhuvan (Tribhavana Bir Bikram Dschung Bahadur, 1911–1955) keeps to convene a liberation army of the Nepalese National Congress in India which invades in Nepal and overthrows the Rana Family
January 1951 · introduction of the constitutional monarchy by Indian pattern, the Rana Family has in the government the position of the premier
November 1951 · King Tribhuvan dissolves the hitherto government and convenes a cabinet of the Nepalese National Congress
1955 · death of von King Tribhuvan, successor is his son Mahendra
1959 · first democratic elections, victory of the Nepalese National Congress
1960 · King Mahendra dissolves the parliament and prohibits the parties, the constitution becomes annuled and the unilateral allegiance with India becomes terminated
1962 · introduction of a new constitution by Pakistani pattern with the so named village-counsel-system (Panchayat-System: no parties, prevalent indirect elections)
1972 · death of von King Mahendra, successor is his son Birendra
1979 · interior roits against the Panchayat-System
1980 · King Birendra keeps to perform a plebiscite about the Panchayat-System which results a majority for that
1989 · India imposes a political motivated trade blockade against Nepal
1990 · bloody roits by so named Democracy and Human Rights Movements, King Birendra introduces a new constitution which reestablishes the constitutional monarchy and substitutes the Panchayat-System by a multi-party-system
1st of June 2001 · King Birendra, Queen Aishwarya and seven further memebers of the royal family perish in the king's palace in Katmandu by the hand of the crown prince Dipendra, committing suicide
4th of June in 2001 · Gyanendra – the younger brother of Birendra – becomes proclaimed to the new King
2002 · dissolution of parliament by the King
2006 · general strike, as a result of which parliament is reinstated, parliament removes executive power from the King, who now only performs representative duties
28th of Dezember 2007 · parliament decides to abolish the monarchy
28th of May 2008 · abolition of the monarchy, proclamation of the republic
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Weltgeschichte,
Discovery '97,
Wikipedia (D)

The name "Nepal" has is roots in the Sanskrit words "nipat → down flying" and "alaya → habitation". That intends the on the mountainsides of the Himalaya gluing villages.
Source:
Handbuch der geographischen Namen


![]()

















 (?)
(?)

