
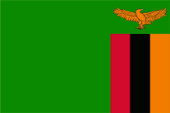
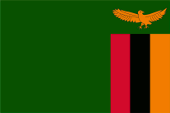
The flag of Zambia was hoisted for the first time on the occasion of the independence on 24th of October in 1964. The design and also the colours of the national flag of Zambia are described in the National Flag and Armorial Ensigns Act of 4th of June in 1965: The flag is green with an orange eagle in flight over a rectangular block of three vertical stripes coloured red, black and orange from left to right; with overall dimensions of 3:2; and according to the following colour specifications: "Spectrum Green" British Colour Council shade reference 100, "Union Jack Red" British Colour Council shade reference 210, "Jet Black" British Colour Council shade reference 220, "Spectrum Orange" British Colour Council shade reference 57. These shades are no longer applicable today. These shades that are used today suggest that, in addition to black, the following colours could be involved: Green = Pantone 363, Red = Pantone = 186, Orange = Pantone 716. In 1996, the flag of Zambia was slightly modified. The dark shade of green originally used in the flag was replaced by a lighter green and the eagle was adapted to the shape of the eagle in the country's coat of arms. The flag has its roots in the colours of the United National Independence Party (UNIP), which led the country into freedom, but yellow was substituted by orange. Green stands for forests and fields, red for the struggle for freedom and progress, black for the people of Zambia, orange for the wealth in copper. Until 1924 Northern Rhodesia was a possession of the British South Africa Company (BSAC) and not a British sovereign territory. The flag of the BSAC showed the British Union Jack with the emblem of the BSAC in the middle of the flag on a white disk. The emblem showed a golden lion which held an elephant tusk in its right paw. It stood on a red-golden torus. Below the shortcut of the company: B.S.A.C. In the year 1924 Northern Rhodesia became a British protectorate. A special official flag there was not introduced. There was only in use the British Union Jack. In the year 1939 was now introduced a Blue Ensign. It showed in the flying end the in 1927 awarded coat of arms. In the year 1953 Northern Rodesia became united with Southern Rhodesia and Nyasaland to the Central African Federation. The federation got an own flag, a Blue Ensign with the coat of arms of the federation in the flying end. The federation was dissolved in 1963 and Northern Rodesia became independent in 1964.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß


1927–1953,
Blazon of Northern Rhodesia,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1953–1963,
Blazon of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland,
Source, by: Flags of the World

since 1965,
Coat of arms of Zambia,
Source: Corel Draw 4

The today’s coat of arms was introduced on 19th of February in 1965. It shows a black shield with white wave-lines, which is supported by two inhabitants of the country, to the left a man and on the right a woman. Above the coat of arms two pickaxes and a orange coloured eagle. The pedestal of the shield shows abundant green vegetation and a cob of corn. Below – within a banner – the motto of the country: "One Zambia, one Nation". The wave-lines and the eagle have their roots in the in 1927 awarded coat of arms of the protectorate of Northern Rhodesia. But on the colonial coat of arms he held even a fish in its claws. The wave lines within the shield symbolize the Victoria Falls. The tools above the shield point out to the richness in mineral resources. The eagle counts for a symbol of freedom and independence, but it also symbolizes the ability to elevate itself above the problems of the country. In the times of the Central African Federation – between the years 1953 and 1963 Northern Rhodesia was united with Southern Rhodesia and Nyasaland – was in use the coat of arms of the federation. This consisted of a twice divided shield and its three parts were dovetailed separated from each other. In the head of the shield a sun (Nyasaland), in the middle part a red lion (Southern Rhodesien) and in the lower part of the shield silvery wave-lines on black ground (Northern Rhodesia). The dovetailed division – a kind of gearing – should express the close connexion of the three parts of the country.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Flaggen und Coat of arms of the Welt,
Volker Preuß


Aircraft Roundel,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)

Location:
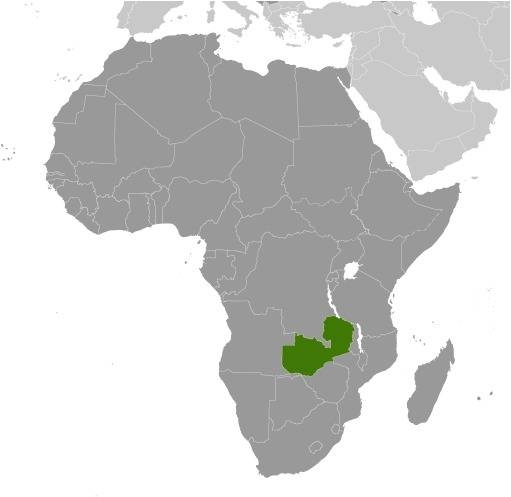
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
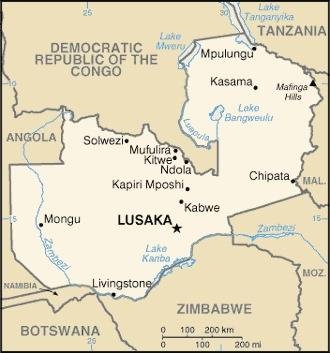
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 290.585 square miles
Inhabitants: 19.610.769 (2022), thereof 21% Bemba (Bantu), 14% Tonga (Bantu), 8% Tumbuka (Bantu), 7% Nyanja-Chewa (Bantu), 6% Rotse/Lozi (Bantu), and another up to 60 peoples and tribes of the Bantu, and furthermore 100.000 Chinese, 20.000 Europeans (mostly British)
Religions: 75% Protestant, 20% Roman Catholic, 2% Animist, 2% Non-Religious
Density of Population: 67 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Lusaka, 2.204.059 inh. (2022)
official Language: English
other Languages: Bantu languages
Currency: 1 Kwacha (K, Kw, ZMW) = 100 Ngwee
Time Zone: GMT + 2 h
Source:
Wikipedia (DE),
Wikipedia (EN)

17th–18th century · settlement by tribes of the Bantu
ca. 1750 · the north of the today’s Zambia (Northern Rhodesia) becomes submited by the Lunda Empire, at the upper Zambesi River establishes the Barotse Empire
1798 · the Portugese discoverer Lacerda goes from Moçambique through the region of the today’s Zambia (Northern Rhodesia)
1831–1832 · the Portugese discoverer Monteiro goes from Moçambique through the region of the today’s North Eastern Zambia (North Eastern Rhodesia) and reaches the Meru Sea
1840 · the Barotse Empire gets conquered and taken over by the from South Africa coming Makololo tribes
1852–1853 · the Portugese trader Silva Porto goes from Angola through the region of the today’s Zambia (Northern Rhodesia) and reaches Moçambique, first traversing of Central Africa
1853 · the British discoverer David Livingstone visits Nariele, the capital of the Barotse Empire
1854–1856 · the British discoverer David Livingstone visits the Zambesi River and discoveres the Victoria Falls
1860–1861 · the British discoverer David Livingstone visits once again the Zambesi River
1866–1873 · the British discoverer David Livingstone visits the today’s North East Zambia (North East Rhodesia) and discoveres the sources of Congo River and the Bangwelo Sea
1884–1885 · the Portugese discoverers Capello and Ivens go from Angola through Central Africa and reach the Meru Sea, target was to investigate the creation of a feasible land-connection between Portugese Angola and Portugese Moçambique
1889 · foundation of the British South Africa Company (BSAC) on initiative of the British politician Cecil Rhodes with the target to acquire and colonize the northward from the Transvaal River situated territories
1890 · Cecil Rhodes forestalls the Portugese and acquires in orders of the BSAC large territories northern and southern of Zambesi River
1891 · Queen Victoria of United Kingdom grants the BSAC the concessions to develop the country
23rd of January 1894 · formation of the BSAC private colony "Northern Zambesia" (including the Barotseland Protectorate)
3rd of May 1895 · the BSAC unites "Northern Zambesia" with "Southern Zambesia" (today’s Southern Rhodesia / Zimbabwe) to the "Protectorate of Rhodesia"
29th of January 1900 · the BSAC administration of the country becomes separated once more between Northern Rhodesia (former Northern Zambesia) and Southern Rhodesia (former Southern Zambesia), Northern Rhodesia becomes separated in North Western Rhodesia and North Eastern Rhodesia
1902 · opening of the lead and zinc mines of Broken Hill (Kabwe)
1905–1910 · the Cape Congo Railroad is in construction and traverses Rhodesia in north-south direction
17th of August 1911 · North Western Rhodesia and North Eastern Rhodesia become re-united to Northern Rhodesia by the BSAC
25th of November 1918 · General Lettow-Vorbeck – the Commander of the German colonial army – capitulates with his troops under orders of the German government in Abercorn
1st of October 1923 · Southern Rhodesia becomes a British crown colony with limited self-rule
26th of April 1924 · Northern Rhodesia becomes a British Protectorate
1931 · commencement of the copper mining
1st of August 1953 · Northern Rhodesia, Southern Rhodesia and Nyasaland become united to the "Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland" (also Central African Federation), in the afteryears the by Europeans ruled Southern Rhodesia dominates the federation, against that fact formed up increasing resistance in Northern Rhodesia
1955 · big miner's strikes
March 1959 · infliction of the state of emergency
1961 · constitutional conference of London
1962 · elections for parliament, new constitution, formation of a government
31st of December 1963 · Northern Rhodesia leaves the Central African Federation, dissolution of the federation
22nd of January 1964 · Northern Rhodesia gets granted interior autonomy (self-rule)
May 1964 · negotiations about compensations for the BSAC in the upcoming nationalization of the mines
24th of October 1964 · Northern Rhodesia gets independent as "Republic of Zambia"
1968 · first elections after the independence
1969 · partial nationalization of the copper mining industry
1972 · Zambia becomes a presidial one-party-state, the state party is the UNIP
1973 · new constitution, nationalization of the copper mining industry
1975 · expropriation of all private soil possessions
1988 · commencement of an economic crisis, reform's pressure
1990 · permission of opposition parties
1991 · free elections, new constitution (multi-party-system)
October 1997 · attempted military coup d’état
1998 · prohibition of the most opposition parties
2020 · Zambia is temporarily insolvent
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (DE)

The name "Zambia" has its roots in the "Zambesi" River. Already in 1894 the land was given the name "Zambesia" by the British, but it achieves already in 1895 the name "Rhodesia", which has its roots in Cecil Rhodes the great patron of the country.
Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Volker Preuß


![]()



















![]()
