Source, by: Flags of the World





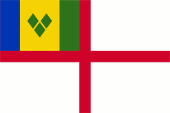
since 1979,
Flag of the Coast Guard,
ratio = 2:3,
Source, by: Flags of the World




since 1979,
Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Saint Vincent
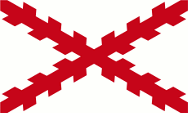
16th century,
The island belongs to the Spanish sphere of influence,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)



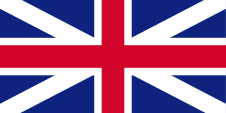
1776–1779, 1783–1801,
Flag of United Kingdom,
Source, by:
Die Welt der Flaggen






1779–1783,
Flag of France,
Source, by: Sodacan [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons




1801–1975,
Union Flag → quasi national flag,
Flag of United Kingdom,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Wikipedia (EN)






1864–1975,
Merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of all Nations





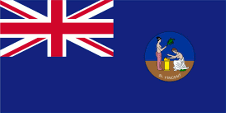
1877–1907,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World



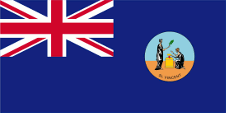
1907–1975,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1975–1979,
National, state and merchant flag,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1979–1985,
National, state and merchant flag,
ratio = 4:7,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1985 (Mar–Oct),
National, state and merchant flag,
ratio = 4:7,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Windward Islands (1833–1958):

1886–1958,
doubtful,
Flag of the government (state flag),
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




1886–1960,
Flag of the Governor,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




Federation of the West Indies (1958–1962):
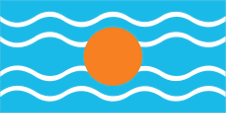
Flag of the Federation of the West Indies,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by: Flags of the World




Flag of the Governor General,
ratio = 1:2,
Source, by:
Flags of the World




The todas's flag of Saint Vincent was introduced on 21st of October in 1985. It shows three vertical stripes in blue, yellow and green, in a ratio of 1:2:1. In the wide yellow central stripe are placed three stylized green diamonds form a "V". The color blue represents the ocean, yellow the natural riches and green the vegetation of the island and its fertility. According to another interpretation, blue represents the sky, yellow represents the sun and green represents the lush vegetation on the island. The three green diamonds in a V-formation stand for "Vincent", and embody the nickname of the island: "Gemstones of the Antilles", but they are also reminiscent of the leaf of the breadfruit tree on the previously valid flag. As the country follows the British ensign and color system, the colors of the flag will correspond to the spectrum specified by the British Ministry of Defense in its regulatory publication "Flags of all Nations" for the following colors: green = pt 364 c, red = pt 186 c, yellow = pt 116 c, blue = pt 286 c.
The island finally belonged to United Kingdom since 1783, so that from that year the flag of United Kingdom flew unchallenged over the islands, which administratively belonged to the British colony of the Windward Islands between 1838 and 1958. The Windward Islands were part of the United Kingdom, had their own administration and their own governor. On land, and until 1864 also at sea, individual citizens and the authorities represented their status as citizens or bodies of the United Kingdom by using the Union Jack, known as the Union Flag.
United Kingdom had introduced a flag system in 1864 in which:
• Warships use a so-called "White Ensign" (naval flag), a white flag often with a red St. George's cross throughout and with the Union Jack in the upper corner,
• Merchant ships use a so-called "Red Ensign" (also called "Civil Ensign" → citizen flag, the actual merchant flag), a red flag with the Union Jack in the upper corner, and
• Governmental ships use a "Blue Ensign" (flag of the government → the actual state flag), a blue flag with the Union Jack in the upper orner.
Since 1865, colonial government ships were permitted to use a Blue Ensign with a badge in the flying end. From this point on, only the British Union Jack was to be used for all other purposes on land and the usual red British merchant flag, the "Red Ensign", at sea. If the British Admiralty had granted the appropriate permission to one colony, merchant ships and private sailors from this colony were allowed to use a Red Ensign with the Bagde. This was not the case for the Saint Vincent or the Windward Islands. The respective governments should provide appropriate bagdes.
Such a badge was often a regional landscape representation placed on a disk, often showed ships, historical events or could just be a kind of logo. Very often a badge also showed the name of the country or a motto. However, some possessions had a coat of arms right from the start, or received their own coat of arms over the years and the badge was abolished. In order to ensure a largely uniform appearance in the flying end of the flags, coats of arms and other symbols were displayed on a white disk the same size as the earlier badges. But there were exceptions here, as some colonies did not use this white disk and placed their coat of arms or just the shield – sometimes enlarged – directly on the flag cloth. As early as the 1940s, the white discs were removed and the coat of arms was placed directly or enlarged. This transition process occurred gradually, never simultaneously and completely. In some British possessions flags with the white disc are still in use, in others they are no longer used and in some areas both variants exist side by side. The Windward Islands were given their own badge in 1886. It showed a shield divided into four parts with the colours red, yellow, green and white, surrounded by a white belt with the inscription "Governor in Chief, Windward Islands", with the British crown above. Below a white banner with the motto of the islands: "i pede fausto" → "Walk with a blessed foot".
However, the individual colonies of the Windward Islands had their own "Blue Ensigns" with their own badge; only the governor used the badge on his flag. A "Blue Ensign" for the Windward Islands may nevertheless have existed. From 1877, the government of St. Vincent, as a British colony, used the blue British official flag (Blue Ensign) with a badge in the waving part of the flag. Introduced in 1877, the badge depicted two classically dressed allegorical female figures (Peace and Justice) sacrificing at an altar. Until 1907, the name of the country could be found at the bottom of the badge: "St. Vincent", and from 1907 the colony's motto was placed there: "Pax et Justitia" → "Peace and Justice". From 1979 the "Blue Ensign" was no longer used because the predecessor of today's flag was introduced.
At the same time, the colony was part of the British colony "West Indian Federation" from 1958 to 1962, an attempt to consolidate the administration and also to counteract the independence efforts of the associated islands and colonies. The flag of the "West Indian Federation" was a light blue flag with four horizontal white wavy lines and a golden disc in the middle. It symbolized the sun over the Caribbean Sea. There is some doubt about the color of the blue; it is often assumed to be the usual British heraldry blue. However, a contemporary description calls it an "imperial blue" which would be light blue and many contemporary prints also show this light blue.
On 27th of October in 1969, United Kingdom granted internal self-government and St. Vincent became an with United Kingdom associated autonomous state. In this context, a new flag should be introduced, which would have ended the tradition of the "Blue Ensigns". This was waived even though the design of that flag had already been completed. In 1975, however, the country received the right to use the "Blue Ensign" with the badge as a national, state and merchant flag.
On 27th of October in 1979, St. Vincent was granted independence by United Kingdom. In this context, the predecessor of the today's flag was introduced. It was designed by a local artist and showed the same colours as the today's flag, also in a vertical arrangement, but the stripes were the same width. The English College of Arms added narrow white dividing stripes. In the center of the yellow stripe was placed the island's coat of arms on a large breadfruit leaf, to commemorate Captain William Bligh, who brought some breadfruit trees to the islands from Tahiti as food for the slaves. Since this flag – which was very beautiful by Caribbean standards – did not meet with popular approval, the white dividing stripes were removed in March 1985. In a further step, the flag was changed into today's version by a Swiss heraldist on 21st of October in 1985, despite legal concerns. The leaf and crest were removed and replaced with three stylized diamonds, and the yellow stripe was widened.
Source:
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen,
Die Welt der Flaggen,
Wikipedia (EN),
Volker Preuß

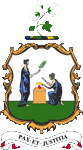
since 1912,
Coat of arms of Saint Vincent,
Source, by: Corel Draw 4

1886–1958,
Windward Islands,
Badge of the Windward Islands,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1877–1907,
Saint Vincent,
Badge of Saint Vincent,
Source, by: Flags of the World

1907–1979,
Saint Vincent,
Badge of Saint Vincent,
Source, by: Flags of the World

The coat of arms was awarded on 29th of November in 1912 and maintained unchanged. It shows a shield with two classical dressed allegorical wife figures (Peace and Justice), who sacrify on an altar. Above the shield appears a blooming cotton plant, below the shield the motto of the country: "Pax et Justitia" → "Peace and Justice".
Source:
Flaggen Wappen Hymnen

Location:
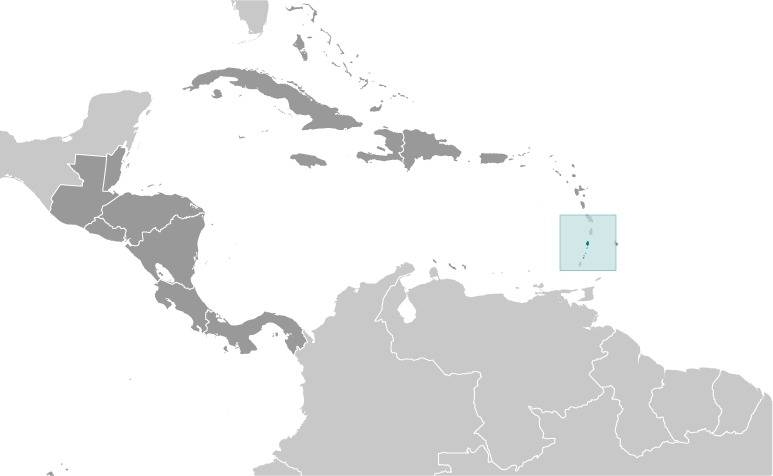
Source: CIA World Factbook
Map of the country:
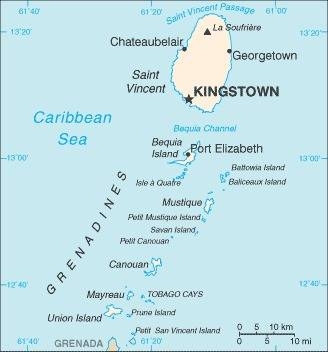
Source: CIA World Factbook

Area: 150 square miles
Inhabitants: 111.000 (2020), thereof 65% Blacks, 19% Mulattos, 5% Indians, 3% Europeans
Religions: 40% Anglican, 30% Protestant, 11% Roman Catholic
Density of Population: 739 inh./sq.mi.
Capital: Kingstown, 12.909 inh. (2012)
official Language: English
other Languages: Creole English
Currency: Eastern Caribbean Dollar (XCD, EC-$) = 100 Cents
Time Zone: GMT – 4 h
Source:
Wikipedia (D)

1498 · the Spanish seafarer Christoph Columbus discovers the island on the day of the Holy Vincent and names it "Isla de San Vincente", the island becomes a Spanish possession but was not colonized
1627 · England claimes the by Caribs inhabited island, but there follows none settlement or colonization
1672 · England claimes the by Caribs inhabited island again, but there follows once more none settlement or colonization
1673 · France claimes the by Caribs inhabited island, but there follows none settlement or colonization, the island was declared for a neutral zone
1719 · French settlers acquire land on the islands
1748 · Saint Vincent is ceded to the Caribs
1762 · United Kingdom occupys Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
1762 · Saint Vincent becomes a British colony
1776 · Saint Vincent becomes a British crown colony
1779–1783 · Saint Vincent is occupied by French troops
1793 · Captain William Bligh, who brings some Bread Fruit Trees from Tahiti to the island as food for the slaves
1795 · revolt of the Caribs
1838 · abolition of slavery
1838–1958 · part of the British Colony of the Windward Islands
1958–1962 · part of the British Colony of the "Federation of the West Indies"
27th of October 1969 · United Kingdom grants interior self administration (autonomy as with United Kingdom associated state)
27th of October 1979 · United Kingdom grants independence within the framework of the Commonwealth of Nations
Source:
Atlas zur Geschichte,
World Statesmen,
Wikipedia (EN)

The name "Saint Vincent" was awarded to this island by Columbus as he discovered it on the day of the Holy Vincent in the year 1498. Saint Vincent of Zaragoza lived in Zaragoza in the 3rd century and was the deacon of the church there. He died a martyr's death around the year 304 under Emperor Diocletian. Saint Vincent Island was named "Youloumain" by the mix of the former slaves with the vanished natives, in honor of Youlouca, the spirit of rainbows.
Source: Wikipedia (EN)


![]()






































![]()
